Definition of limit test:
Limit test is defined as a quantitative or semi-quantitative test designed to identify and control small quantities of impurities which are likely to be present in the substance.
Lead is one of the most undesirable impurities and enters through storage containers like bottle caps, as well as some apparatus.
It has two different variants of limit tests. The first one is more specific for lead.
TEST-1: Reaction with Dithizone: This test is official in IP and USP.
TEST-2: It is described under Limit Test for Heavy Metals after this limit test.
Apparatus: (Separating Funnel)

Reaction
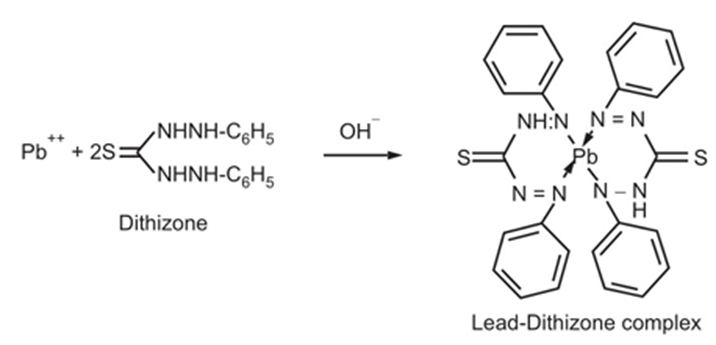
Principle
Its limit test is based upon the chemical reaction between lead and diphenylthio carbazone (dithizone) in alkaline solution to form lead dithizone, which is red in colour. (Dithizone itself is green in colour and the lead dithizone formed is violet in colour. Thus, the net resultant colour of the solution becomes red). The lead present in the impurity is first extracted using the dithizone extraction solution. To avoid interference by other metals and make the pH optimum, reagents like ammonium citrate, KCN and NH2OH.HCI are employed. Phenol red is used as an indicator to develop colour at the end of the process.
Procedure
Take two 50 ml Nessler cylinders. Label one as “Test” and the other as ‘Standard’.
| Standard | Test |
| 1. A standard lead solution (1 ppm Pb) is prepared equivalent to the amount of lead permitted in the sample under examination. | 1. A known quantity of the sample solution is transferred in a separating funnel. |
| 2. Add 6 ml of ammonium citrate. | 2. Add 6 ml of ammonium citrate. |
| 3. Add 2 ml of potassium cyanide and 2 ml of hydroxylamine hydrochloride. | 3. Add 2 ml of potassium cyanide and 2 ml of hydroxylamine hydrochloride. |
| 4. Make solution alkaline by adding ammonia solution. | 4. Make solution alkaline by adding ammonia solution. |
| 5. Extract with 5 ml of dithizone in chloroform solution, until it becomes green. | 5. Extract with 5 ml of dithizone in chloroform solution, until it becomes green. |
| 6. Dithizone extracts are shaken for 30 minutes with 30 ml of nitric acid and the chloroform layer is discarded. | 6. Dithizone extracts are shaken for 30 minutes with 30 ml of nitric acid and the chloroform layer is discarded. |
| 7. To the acid solution add 5 ml of standard dithizone solution. | 7. To the acid solution add 5 ml of standard dithizone solution. |
| 8. Add 4 ml of ammonium cyanide. | 8. Add 4 ml of ammonium cyanide. |
| 9. Shake for 30 minutes. | 9. Shake for 30 minutes. |
| 10. Observe the colour. | 10. Observe the colour. |
Observation
The intensity of the color of complex will depend on the amount of lead in the solution. The color produced in the sample solution should not be greater than standard solution. If color produces in sample solution is less than the standard solution, the sample will pass the limit test of lead and vice versa.