- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for control of Non-Conformance of Products and Procedure.
- SCOPE:
This SOP is applicable for control of Non-Conformance of Product and Procedure at {Company Name} {Company Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
QA Executive/Designee Preparation review and follow the SOP
Concerned Department (Production, Warehouse, QA, Engineering QC and HR) follow the SOP
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
Quality Assurance Head and Concerned Department Head.
- PROCEDURE:

- Any unauthorized deviation from SOP or any unauthorized process deviation from BMR leads to Non-Conformance.
- No deviation of practices from the SOP shall be allowed until and unless it is proposed with scientific rationale for a specific occasion by the Head of the Department and is authorized by Head-Quality Assurance.
- All non conformance products shall be quarantined and investigated. Product shall be properly labeled as rejected and shall be properly segregated and stored in separate area for proper evaluation and investigation.
- The control of Non–Conforming products procedure has been established to manage any material and product that does not conform to the specifications.
- The evaluation of material and product non conformance includes determination of the need for an investigation and notification of the persons or organization responsible for the Non–Conformance. Investigation includes verification of documents and discussion with the persons involved.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/control-of-non-conformance-of-products-and-procedure/
- All evaluation and investigations shall be properly investigated as per the respective SOP.
- Non-Conforming raw materials and unprinted packing materials shall be returned to vendor stating the reason for rejection for their corrective action as per respective SOP.
- Non-Conforming printed packing materials are destroyed as per SOP title destruction, disposal of rejected, non-moving and obsolete material as per the respective SOP in presence of QA at the site. Record of destruction to be maintained. If any Inprocess sample does not confirm to laid down specifications, then such materials are stored separately and labeled “HOLD” till investigation is completed and decision for the same is taken till investigation.
- If a Finish Product does not confirm to lay down specifications, then such materials are stored separately and labeled “HOLD” till investigation is completed and decision for the same is taken till investigation.
- After investigation, the proposed corrective action plan is to be implemented by the respective department heads under supervision of QA head.
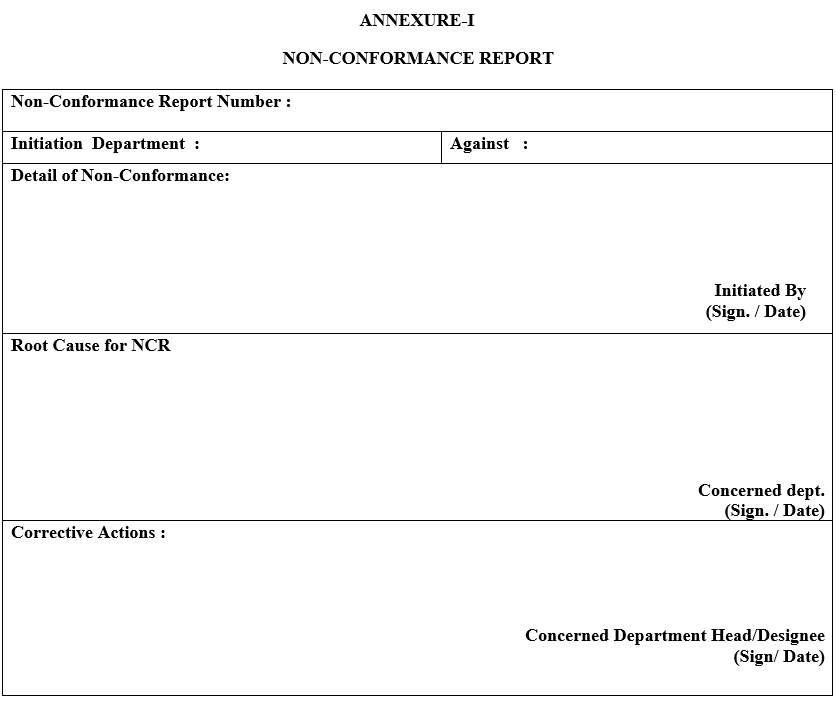
- Non-Conformance observed during routine shop floor Inspection shall be notified and recorded in Non-Conformance Report as per ANNEXURE-1.
- Original Copy will remain with Documentation Quality Assurance, Photocopy shall be retained with concerned department Head.
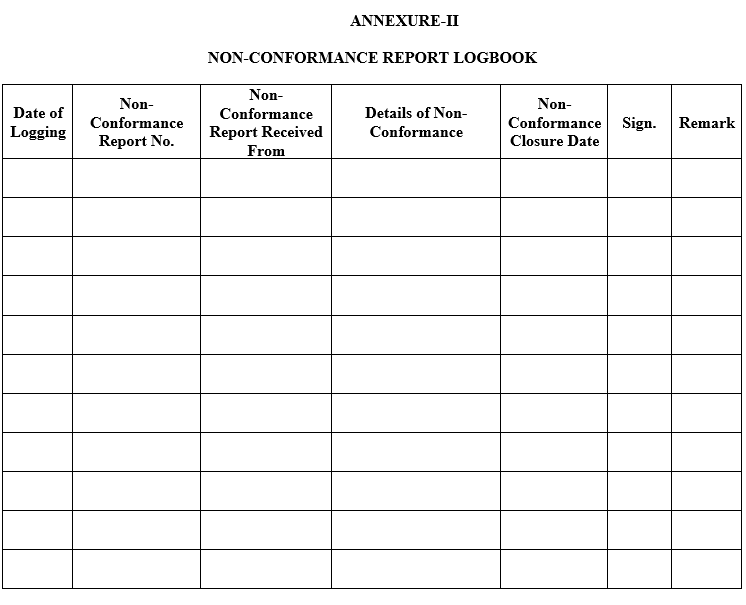
- Each Non-Conformance Report shall be numbered and its details shall be maintained in Non Conformance Report Log Book by Quality Assurance department as per ANNEXURE-II.
- Numbering of Non-Conformance Report:
- For each Non conformance Report a unique “Non conformance Report Number” shall be assigned by QA. Numbering system shall be mentioned as below
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/control-of-non-conformance-of-products-and-procedure/
NCR/YY/NNN
NCR: Stands for non-conformance report
YY: Stands for last two digit for the calendar year
NNN: Stands for serial No. start from 001, 002, 003………..
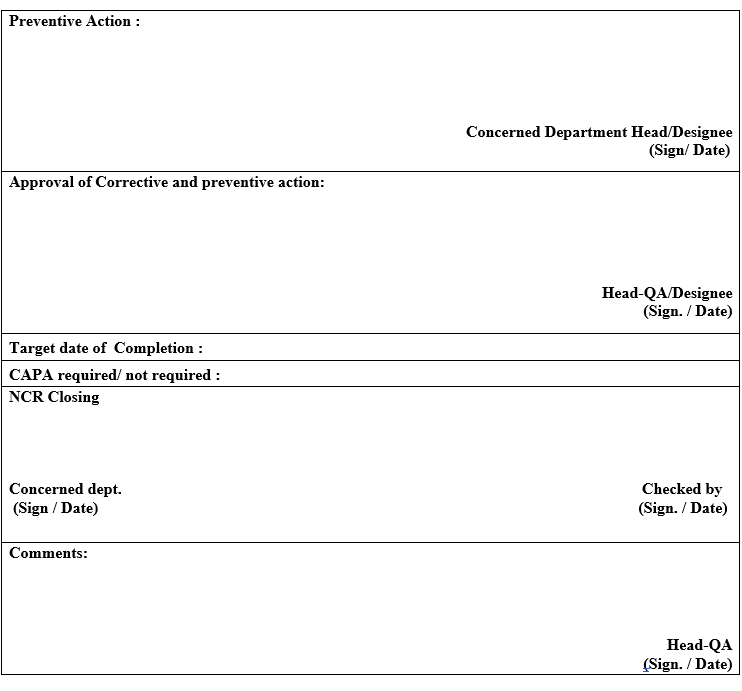
- The Initiating Department shall fill in the details of Non-Conformance along with immediate action and forward the Non-Conformance Report to concerned department.
- The concerned department shall investigate the root cause of non-conformance and the department head shall propose immediate corrective action taken and submit the Non-Conformance Report to Head-Quality Assurance.
- Suitable preventive action shall be proposed by concerned department head and it shall be authorized by Head-Quality Assurance to avoid reoccurrence in future and also define the responsibility and Target date of Completion date for corrective action.
- After getting preventive action from Quality Assurance, the concerned department shall incorporate the same before closing the Non-Conformance Report and then submit the Non-Conformance Report to Quality Assurance for closing.
- Documentation -Quality Assurance shall maintain all copies of the closed Non-Conformance Report.
- REFERENCES:
Not applicable
- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE |
| Annexure-I | Non-Conformance Report |
| Annexure-II | Non-Conformance Report Log Book |
- DISTRIBUTION:
| Control copy No. 1 | : | Head Quality Assurance |
| Control copy No. 2 | : | Head Production |
| Control copy No. 3 | : | Head Ware House |
| Control copy No. 3 | : | Head HR |
| Control copy No. 3 | : | Head Quality Control |
| Control copy No. 4 | : | Head Engineering |
- Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
- ABBREVIATIONS:
SOP
:
Standard Operating Procedure
QA
:
Quality Assurance
QC
:
Quality Control
HR
NCR
:
:
Human Resources
Non-Conformance Report
- REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be written manual |
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/control-of-non-conformance-of-products-and-procedure/
ANNEXURE-I
NON-CONFORMANCE REPORT
ANNEXURE-II
NON-CONFORMANCE REPORT LOGBOOK
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q1: What is a non-conformance in the context of pharmaceutical manufacturing? A1: In the pharmaceutical industry, a non-conformance refers to a deviation or failure to meet specified requirements, whether in terms of product quality, manufacturing processes, or procedural adherence. It is a departure from approved standards and may pose a risk to the safety, efficacy, or quality of a pharmaceutical product.
Q2: What is the role of Quality Assurance in controlling non-conformances in pharmaceutical manufacturing? A2: Quality Assurance (QA) plays a crucial role in controlling non-conformances by establishing and implementing systems for the identification, investigation, and resolution of deviations. QA ensures that appropriate corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are taken to address the root causes of non-conformances and prevent their recurrence.
Q3: How are non-conformances typically identified in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes? A3: Non-conformances can be identified through various means, including routine quality control testing, in-process monitoring, inspections, audits, and employee reports. It’s essential to have robust systems in place to promptly detect and document any deviation from established standards.
Q4: What is the process for investigating and documenting non-conformances in pharmaceutical manufacturing? A4: When a non-conformance is identified, a thorough investigation is conducted to determine its root cause. This involves collecting relevant data, analyzing the impact on product quality, and documenting the findings. The investigation process is often formalized and follows Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines.
Q5: How are corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) implemented to address non-conformances? A5: CAPA involves developing and implementing actions to correct the immediate issue (corrective action) and prevent its recurrence (preventive action). This may include process modifications, additional training, changes to procedures, or improvements to the quality management system. QA ensures the effectiveness of CAPA through monitoring and verification.
Q6: What measures are in place to ensure the timely resolution of non-conformances? A6: Timely resolution of non-conformances is critical to maintaining product quality. Pharmaceutical companies often have established procedures with defined timelines for the investigation, implementation of corrective actions, and completion of follow-up verifications. QA monitors adherence to these timelines to ensure prompt resolution.
Q7: How does the pharmaceutical industry prevent non-conformances through proactive measures? A7: Proactive measures to prevent non-conformances include robust quality management systems, ongoing training programs, thorough risk assessments, regular audits, and continuous improvement initiatives. By identifying potential risks and implementing preventive measures, the industry aims to reduce the occurrence of non-conformances.
Q8: What role do Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) play in controlling non-conformances? A8: SOPs provide detailed instructions for various processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They serve as a reference for employees to follow established standards and procedures. Ensuring that SOPs are well-written, up-to-date, and followed rigorously helps prevent deviations and non-conformances.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/control-of-non-conformance-of-products-and-procedure/