- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for Preparation, Review, Approval and Authorization of the Validation Master Plan.
- SCOPE:
This procedure is applicable for Validation Master Plans prepared for describing Validations/Qualifications of equipments, instruments, utilities and systems, processes, packaging, facility, analytical method, transportation and/or Computerized at {Company Name} {Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- Quality Assurance: Validations Executive and Validation Team shall prepare the Validation Master Plan. Review the Validation Master Plan for appropriateness with respect to the approaches and compliance to GMP and regulatory expectations. Impart training on the VMP. Monitor the implementation of the aspects of VMP in routine practices.
- Head-QA shall be responsible to Review and authorize the Validation master plan and Computerised Systems Validation Master Plan for the appropriateness with respect to the approaches and compliance to Aurobindo Quality policies/ procedures, GMP and regulatory expectations.
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
QA Head shall be Accountable for implementation of SOP.
- PROCEDURE:
- General:
- A Validation Master Plan (VMP) is a document that shall summarize the organization’s overall philosophy, intention and approaches to be followed for establishing performance adequacy of the equipment/utilities and systems/process/packaging/facilities/transportation/analytical methods and/or Computerized systems.
- The Validation Master Plan shall give an overview of the entire validation operations, its organizational structure, content and planning.
- Validation Master Plan shall be a summary document, which shall be brief, concise and clear.
- This shall outline briefly on layout of the operations, associated utilities and systems, the equipment, the processes/packaging/analytical methods and transportation to be validated along with the information as to extent of the qualification and validation, required documentation, SOPs, acceptance criteria and responsibilities.
- A Validation Master Plan shall be prepared for individual manufacturing facilities.
- Computerized systems Validation Master Plan shall be a common master plan and shall be applicable for {Company Name}.
- The Validation Master Plan shall be prepared based on the concepts/approaches mentioned in {Company Name} Policies.
- Preparation of Validation Master Plans:
- The Validation Master Plans shall be prepared in Microsoft word preferably with page setups of Margins: Top-1”, Bottom-0.5”, Left-0.5”, Right-0.3”, Paper-A4, Header-0.5”, Footer-0.5”, Fonts-Times New Roman with font size-12 and shall have complete pagination, with every page numbered sequentially from beginning to end at the header of the protocol. E.g. “Page 1 of 20” to “Page 20 of 20”.
- The VMPs shall contain the following sections in general;
- General:
Click the link to download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/procedure-for-preparation-of-validation-master-plan/
- Introduction: Brief description of the manufacturing site with different types of formulations manufactured.
- Objective and scope: To describe the purpose and the extent/limitation of the VMP.
- Roles and Responsibilities: To identify and describe the different groups/levels for different level of responsibilities in the qualification/validation life cycle.
- The typical different groups with their different level of responsibilities are as below;
- Validation Coordinator(s): QA and Central Qualifications and Validation Team responsible for spearheading all the qualification/validation activities in the unit like; Preparation and execution of qualification/validation plans/protocols and reports.
- Execution team: consisting of personnel from multidisciplinary team to plan, execute and review the tasks associated with validations/qualifications.
- Validation Task Force leader: In-charge of Central Qualifications and Validation Department or his designee to review validation protocols and reports during initial qualification and validation program and/or QA in-charge or his designee to Review of validation protocols, Monitor the progress to ensure completion of validations as per schedule etc.
- Validation Core Committee: comprising of departmental heads, Head of Central Qualifications and Validation Department and/or their designees for overall coordination of the validation program, review and approval of the qualification/validation protocols and reports.
- Validation policy: To describe the site overall approach and intention of all the validation activities to be performed.
- Approaches: Various approaches shall be adopted during validation/qualification of equipments, systems, processes and facilities.
- This section in VMP shall describe such approaches in detail: A V-Model approach shall be followed for qualification of equipment, systems and instruments.
- The element of the V-Model and approach for adoption of different levels of qualification shall be clarified in the VMP.
- A risk based approach shall be followed to demonstrate that the critical quality features are built into the facility, process equipment/systems, critical support systems and processes are fully functional for routine use to manufacture commercial products.
- A systematic risk management approach shall be followed at various stages of lifecycle related to design of facility, equipment, utility and system, manufacturing process, transportation and packaging to as a part of quality risk management system, decisions on the scope and extent of the qualification and validation shall be based on a justified and documented risk assessment of the facilities, equipment, utilities and processes.
- An impact assessment shall be performed by evaluating the impact of the system on the quality of the product. Evaluation shall also be extended to the system components level to determine if they are critical to establish the quality of products.
- The equipments/systems shall be classified to different levels like Direct impact/ In-direct impact/No impact systems based on their impact evaluation as per the Process equipment/ system qualification policy and the approach of qualification for these different levels shall be clarified in VMP.
- A list of the Equipment/system classification shall be annexed to the VMP. A bracketing approach shall be followed to validate the wide range of parameters reducing the activity. Bracketing approach can be adopted at the time of initial qualification / validation activities or while re-qualification activities, based on the risk associated with such proposition.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/procedure-for-preparation-of-validation-master-plan/
- Bracketing requires identification of the worst case (single ended bracket) to be challenged or the use of configurations that represent range of the items (double ended bracket) to be qualified.
- A life cycle approach for validations shall be adopted to ensure that quality is built into the systems/processes to perform their intended functions reliably, repeatedly, consistently and produce quality products from beginning to their retirement/end.
- Re-Qualification/Re-Validation approach shall be followed to ensure the validity of equipments, systems, process and facilities during any change and continued validated stage in the life cycle of them.
- The VMP shall describe the re-qualification/revalidation criteria and their frequency for equipment/systems and process.
- Computerized System Validation Master Plan may adopt only applicable approaches from the above mentioned.
- Validation programs: To describe the general approach, including typical procedures and attributes to be considered, during the qualification/validation, which includes facility, equipments/instruments, utilities and systems, process, packaging, cleaning, analytical methods, transportation and computer system validation etc. The Validation program also includes the Guidance on developing acceptance criteria.
- Validation management: Section describes various approaches such as change management, deviation management, calibrations, preventive maintenance etc. which, are routinely adopted for maintenance of qualified/validated status of the Equipment/Systems/utility/Processes/packaging and/or computerized Systems. Documentation during validation like protocols and reports, procedures, different formats for documenting with their reference shall be discussed in the VMP.
- A Validation Plan (VP) shall be prepared as applicable, whenever there is a major modification, expansion or addition in the existing facility or whenever there is a new equipment, process, utility and system is being validated or qualified.
- A Validation schedule/calendar shall be prepared for all the equipments, systems, utilities in the facility which shall be validated/qualified initially and/or periodically re-validated.
- A list of executed validations shall be prepared on a periodic frequency and shall be attached to VMP’s. Such list may include Equipments Qualification, Instrument Qualification, Systems validation, Process validation, Aseptic simulation study etc.
- Some of the qualification/validation activities may require the use of documents/services provided by supplier and/or external agencies (consultants). Procedure for management of these external agencies shall be clarified in the VMP.
- Abbreviations and glossary: To list the abbreviations used with their full forms and the definitions of the terminology used.
- References: shall have list of reference documents.
- Annexure: shall have listed the attachments. The following approved:
- Schedule for Validation/Qualification Activities
- Annual Schedule for Re-Qualifications/Re-Validations
- List of executed validation list
- Validation plan etc.
- Change history: To tabulate the changes in VMP throughout the documents life cycle.
- Review and approval of VMP:
- The prepared Softcopies (Microsoft word documents) VMP shall be saved in an appropriately identified folder in drive through a local PC.
- Print copy of the VMP and shall be review, approval and authorized.
- After authorization of the VMP, the authorized VMP shall be effective by QA and retains in the document section of the QA for routine use.
- Numbering System:
Validation Master Plan shall contain eleven Alphanumeric Characters (Six Alphabets, Three Numeric and Two Separators). Validation Master Plan shall be assigned with a Unique Number, once number is allotted to Validation Master Plan, the same number shall not be assigned.
For Example: First Validation Master Plan shall be numbered as PGH/VMP/001
Where,
| PGH | : | Pharma Guide Hub |
| ‘/’ | : | Is Separator |
| VMP | : | Indicate the code of Validation Master Plan |
| ‘/’ | : | Is Separator |
| 001 | : | Indicate the Serial Number of Validation Master Plan |
- Review and Revision:The Validation Master Plan shall be reviewed every two years.
- The Annexure attached to the Validation Master Plan shall be updated/revised as required on periodic basis without revising the Validation master plan.
- Validation Master Plan shall be revised due to any change which is required to be incorporated or due to any typographical error in the approved document, appropriate change management procedure shall be followed for revising the VMP.
- All changes made shall be entered in brief in the ‘Change History’ and attached at the end of the VMP. Change history shall indicate all the changes associated with each of the versions.
- If there are no changes during the review, change history shall be revised mentioning ‘Review done – No changes required’ under the column changes made and approved in a same way as VMP.
- DEFINITIONS:
- Validation: Documented evidence that the process, equipment, facilities or systems operating within established parameters, can perform effectively and reproducibly giving results meeting predetermined specifications.
- Qualification: Qualification is a process of assurance that the specific system, premises or equipment are able to achieve the predetermined acceptance criteria to confirm the attributes what it purports to do.
- Validation Master Plan: The documented plan for qualification of a facility or part of a facility that identifies the layout of the operation, the associated utilities and systems, the equipment, and the processes to be validated. Validation Master Plan also provides information as to extent of the qualification and validation (IQ, OQ& PQ) required documentation, SOPs, acceptance criteria and responsibilities.
- Validation Plan: The documented plan for a system/facility with brief overview of considerations on the aspects of qualification/validations.
- Validation Protocol: The written and approved document of an experimental sequence of tests that, when executed as prescribed, are intended to produce documented evidence that the equipment or system does what it is designed or claims to do reproducibly.
- Validation Report: A document summarizing the results derived from the execution of a protocol. The final report shall include a conclusion, which indicates validation success or failure and designates proven acceptable ranges for all critical process parameters as determined by the execution of the validation protocol.
- Quality Risk Management: A proactive means to identify and control potential quality issues during research, development, manufacturing and distribution of a product or services. A systematic application of management polices procedure and practices to the tasks of analyzing, evaluating and controlling risk. Specifically, a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the drug product across the product life cycle.
- Calibration: The performance of tests and retests to ensure that measuring equipment (e.g. for temperature, weight, pH) used in a manufacturing process or analytical procedure (in production or quality control) gives measurements that are correct within established limits.
- Revalidation: Validation of a previously validated system that has been changed or modified. Revalidation can be performed as the result of the change to the system, or a time based assessment.
- Risk Based Approach: A risk based validation program is designed to demonstrate that the critical quality features which are built into the facility, critical support systems and processes are fully functional for routine use to manufacture commercial products. The risk based approach is also applicable to define qualification criteria, including re-qualification criteria/frequency, for equipment and utilities.
- Bracketing approach: A validation method that tests the extremes of a process or product. The method assumes the extremes will be representative of all the samples between the extremes
Click the link to download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/procedure-for-preparation-of-validation-master-plan/
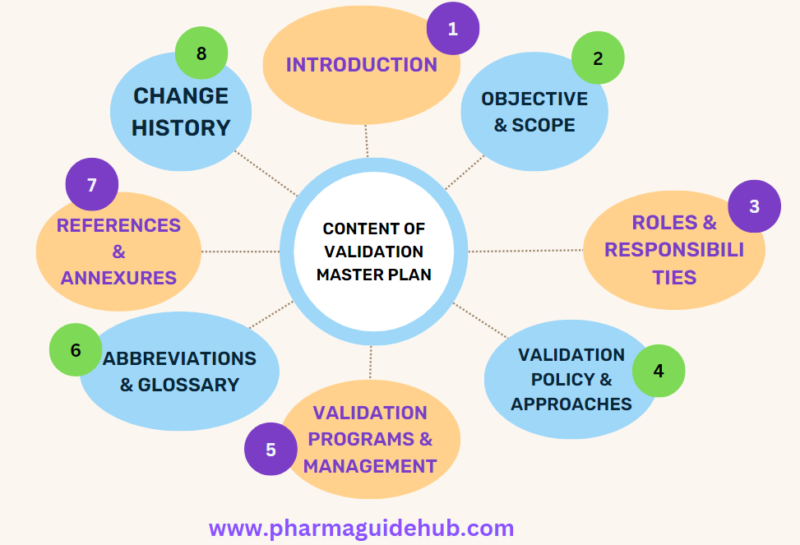
- CONTENTS OF VMP:
- INTRODUCTION
- OBJECTIVE AND SCOPE
- ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
- VALIDATION POLICY
- VALIDATION APPROACHES
- VALIDATION PROGRAMS
- VALIDATION MANAGEMENT
- ABBREVIATIONS AND GLOSSARY
- REFERENCES
- ANNEXURES
- CHANGE HISTORY
- REFERENCES:
- USFDA 21 CFR part 211
- EU Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice– Qualification and Validation (Vol-4, Annex-15)
- Good manufacturing practices (GMP)-Validation (WHO)
- ANNEXURES:
Not Applicable
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
- DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No. 01 : Head Quality Assurance
- Controlled Copy No. 02 : Head Quality Control
- Controlled Copy No. 03 : Head Engineering
- Controlled Copy No. 04 : Head Production
- Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
- ABBREVIATIONS:
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| No. | : | Number |
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| GMP | : | Good Manufacturing Practices |
| VMP | : | Validation Master Plan |
| PGH | : | Pharma Guide Hub |
- REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To Be Written Manual |
Click the link to download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/procedure-for-preparation-of-validation-master-plan/
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q: What is a Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: A Validation Master Plan (VMP) is a document that summarizes an organization’s overall philosophy, intentions, and approaches for ensuring the performance adequacy of equipment, utilities, systems, processes, packaging, facilities, transportation, analytical methods, and/or computerized systems. It provides an overview of the entire validation operations, organizational structure, content, and planning.
Q: What should be included in the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: The Validation Master Plan should outline the layout of operations, associated utilities and systems, equipment, processes, packaging, analytical methods, and transportation to be validated. It includes information about the extent of qualification and validation, required documentation, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), acceptance criteria, and responsibilities. Additionally, it is prepared for individual manufacturing facilities, and for computerized systems, a common master plan is applicable for the specific company.
Q: What is the preferred format for preparing Validation Master Plans (VMPs)?
A: Validation Master Plans are preferably prepared in Microsoft Word with specific page setups, including margins (Top-1″, Bottom-0.5″, Left-0.5″, Right-0.3″), paper size (A4), header (0.5″), footer (0.5″), and Times New Roman font with size 12. Each page should be sequentially numbered from beginning to end at the header of the protocol.
Q: What are the different sections that Validation Master Plans (VMPs) generally contain?
A: Validation Master Plans typically contain sections such as Introduction, Objective and Scope, Roles and Responsibilities, Validation Policy, Approaches, Validation Programs, Validation Management, Abbreviations and Glossary, References, Annexures, and Change History.
Q: What are the different groups and their responsibilities mentioned in the Validation Master Plan (VMP) preparation process?
A: The different groups and their responsibilities include:
- Validation Coordinator(s): Responsible for spearheading qualification/validation activities.
- Execution Team: Consisting of personnel from a multidisciplinary team for planning, executing, and reviewing validation tasks.
- Validation Task Force Leader: In charge of reviewing validation protocols and reports during the initial qualification and validation program.
- Validation Core Committee: Comprising departmental heads and heads of the Central Qualifications and Validation Department for overall coordination of the validation program.
- Validation Policy: Describing the overall approach and intention of all validation activities.
Q: What are the different approaches mentioned for validation/qualification in the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: The approaches mentioned in the VMP include:
- V-Model Approach: Followed for the qualification of equipment, systems, and instruments.
- Risk-Based Approach: Adopted to demonstrate that critical quality features are built into the facility, processes, equipment, and systems.
- Bracketing Approach: Followed to validate a wide range of parameters, reducing activity.
- Life Cycle Approach: Adopted to ensure that quality is built into systems/processes throughout their life cycle.
- Re-Qualification/Re-Validation Approach: Followed to ensure the validity of equipment, systems, processes, and facilities during any change.
Q: What does the Validation Program include according to the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: The Validation Program describes the general approach, including typical procedures and attributes considered during the qualification/validation process. It covers facility, equipment/instruments, utilities and systems, processes, packaging, cleaning, analytical methods, transportation, and computer system validation. The program also includes guidance on developing acceptance criteria.
Q: How is the numbering system for Validation Master Plans (VMPs) structured?
A: The Validation Master Plan is assigned a unique number with eleven alphanumeric characters (Six Alphabets, Three Numeric, and Two Separators). For example, the first Validation Master Plan might be numbered as PGH/VMP/001, where PGH stands for Pharma Guide Hub, ‘VMP’ indicates the code for Validation Master Plan, and ‘001’ indicates the Serial Number.
Q: What is the frequency of reviewing and revising the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: The Validation Master Plan should be reviewed every two years. Additionally, the annexures attached to the VMP should be updated/revised as required on a periodic basis without revising the main VMP. Revision of the VMP is required in case of any changes or typographical errors, following appropriate change management procedures. All changes are recorded in the ‘Change History’ section.
Q: Can you provide definitions for key terms related to validation mentioned in the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: Certainly. Here are definitions for key terms:
- Validation: Documented evidence that a process, equipment, facilities, or systems can perform effectively and reproducibly within established parameters.
- Qualification: Assurance that a specific system, premises, or equipment can achieve predetermined acceptance criteria to confirm its intended attributes.
- Validation Master Plan: A documented plan for the qualification of a facility or part of a facility, identifying the layout, utilities, systems, equipment, and processes to be validated.
- Validation Plan: A documented plan for a system/facility with a brief overview of considerations on the aspects of qualification/validations.
- Validation Protocol: A written and approved document of an experimental sequence of tests intended to produce documented evidence that the equipment or system performs as designed.
- Validation Report: A document summarizing the results derived from the execution of a protocol, including validation success or failure and acceptable ranges for critical process parameters.
- Quality Risk Management: A proactive means to identify and control potential quality issues during the product life cycle, involving a systematic process for risk assessment, control, communication, and review.
- Calibration: The performance of tests to ensure that measuring equipment used in a manufacturing process or analytical procedure gives correct measurements within established limits.
- Revalidation: Validation of a previously validated system that has been changed or modified, either due to system changes or a time-based assessment.
- Risk-Based Approach: A validation program designed to demonstrate that critical quality features are built into the facility, support systems, and processes for routine use.
- Bracketing Approach: A validation method that tests the extremes of a process or product, assuming the extremes are representative of all samples between them.
Q: What are the contents of the Validation Master Plan (VMP)?
A: The contents of the VMP include Introduction, Objective and Scope, Roles and Responsibilities, Validation Policy, Validation Approaches, Validation Programs, Validation Management, Abbreviations and Glossary, References, Annexures, and Change History.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/procedure-for-preparation-of-validation-master-plan/