OBJECTIVE
To lay down the procedure for cleaning of sampling aids such as unit dose sampler, sampling dies, bulk sampler and sampling trays.
SCOPE
This SOP is applicable for operation and cleaning of Thief Sampler at {Company Name} {Company Location}.
RESPONSIBILITY
Production– Operator / Officer shall be responsible to clean the unit dose sampler, sampling dies and sampling trays after completion of sampling activity.
Quality Assurance – QA officer / Executive shall be responsible to ensure the cleanliness of the unit dose sampler, sampling dies and sampling trays as per SOP.
PROCEDURE
Cleaning Procedure for Unit dose Sampler and Dies:
After completion of sampling at different stages of manufacturing of drug product, affix “TO BE CLEANED” label as per SOP to the unit dose sampler and transfer to respective wash area.
Disengage the sampler and remove dies carefully from the unit dose sampler.
Nylon brush shall be used to remove the material adhering to the inner shaft and outer tube.
Sampler and Dies are cleaned with potable water followed by purified water till no trace of material is observed.
Finally wipe the unit dose sampler and dies with 70% IPA.
Ensure unit dose sampler and dies are dried.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/operation-and-cleaning-of-sampling-rod/
Attach the conical end piece to the outer tube of the sampler then insert the inner shaft and wrap the sampler with polythene film and affix “CLEANED” label as per SOP.
Cleaned dies shall be kept in separate cleaned container.
If the unit dose sampler is idle for more than 6 days, affix the label, “EQUIPMENT NOT IN USE CLEAN BEFORE USE” as per SOP and clean the unit dosage sampler before usage.
Cleaning Procedure for Unit dose Sampler and Dies( Bottom Triplicate Pellet Sampler and Dies):
After completion of sampling at different stages of manufacturing of drug product, affix “TO BE CLEANED” label as per SOP “Cleaning of Equipments and Area” to the unit dose sampler and transfer to respective wash area.
Remove the dies and disengage the sampler with the help of Allen key carefully from the unit dose sampler.
Nylon brush shall be used to remove the material adhering to the inner shaft, outer tube and dies.
Sampler and Dies are cleaned with potable water followed by purified water till no trace of material is observed.
Finally wipe the unit dose sampler and dies with 70% IPA.
Ensure unit dose sampler and dies are dried.
Attach the conical end piece to the outer tube of the sampler and insert the inner shaft then fix the dismantled part with the help of Allen key and wrap the sampler with polythene film and affix “CLEANED” label as per SOP .
Cleaned dies shall be kept in separate cleaned container.
If the unit dose sampler is idle for more than 6 days, affix the label, “EQUIPMENT NOT IN USE CLEAN BEFORE USE” as per SOP and clean the unit dosage sampler before usage.
Cleaning Procedure for Unit dose Sampler and Dies (Liquid sampler and Dies)
After completion of sampling at different stages of manufacturing of drug product, affix “TO BE CLEANED” label as per SOP to the unit dose sampler and transfer to respective wash area.
Remove the dies and disengage the sampler with the help of Allen key carefully from the unit dose sampler.
Nylon brush shall be used to remove the material adhering to the inner shaft, outer tube and dies.
Sampler and Dies are cleaned with hot water followed by purified water till no trace of material is observed.
Finally wipe the unit dose sampler and dies with 70% IPA.
Ensure unit dose sampler and dies are dried.
Attach the conical end piece to the outer tube of the sampler and insert the inner shaft then fix the dismantled part with the help of Allen key and wrap the sampler with polythene film and affix “CLEANED” label as per SOP.
Cleaned dies shall be kept in separate cleaned container.
If the unit dose sampler is idle for more than 6 days, affix the label, “EQUIPMENT NOT IN USE CLEAN BEFORE USE” as per SOP and clean the unit dosage sampler before usage.
Cleaning Procedure for Bulk Sampler:
After completion of sampling at different stages of manufacturing of drug product, affix “TO BE CLEANED” label as per SOP to the bulk sampler and transfer to respective wash area.
Disengage the sampler carefully.
Nylon brush shall be used to remove the material adhering to the inner shaft and outer tube.
Sampler is cleaned with potable water followed by purified water till no trace of material is observed.
Finally wipe the bulk sampler with 70% IPA.
Ensure bulk sampler is dried.
Attach the conical end piece to the outer tube of the sampler then insert the inner shaft and wrap the sampler with polythene film and affix “CLEANED” label as per SOP .
If the bulk sampler is idle for more than 6 days, affix the label, “EQUIPMENT NOT IN USE CLEAN BEFORE USE” as per SOP and clean the bulk sampler before usage.
Cleaning procedure for sampling trays:
After completion of sampling at different stages of manufacturing of drug product, affix “TO BE CLEANED” label as per SOP to the sampling trays and transfer to respective wash area.
With the help of lint free cloth sampling tray shall be cleaned with potable water followed by purified water till no traces of material is observed.
Finally wipe the sampling trays with 70% IPA, and affix “CLEANED” label as per SOP.
REFERENCE:
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/operation-and-cleaning-of-sampling-rod/
Not Applicable
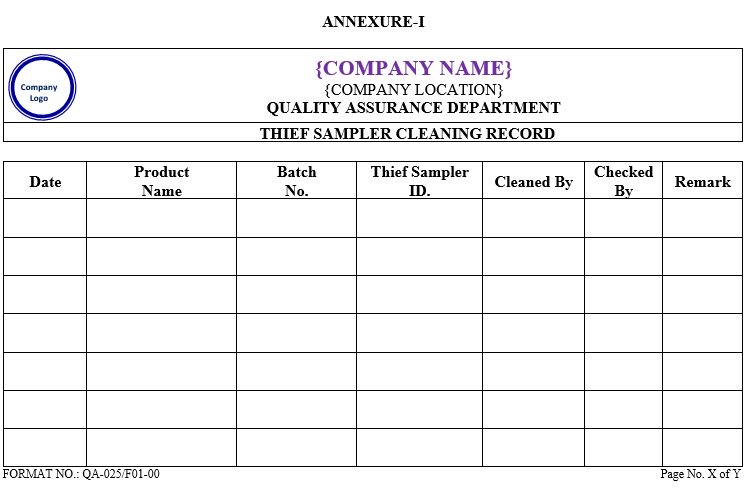
- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE | FORMAT No. |
| Annexure-I | Thief Sampler Cleaning Record | QA-025/F01-00 |
Not Applicable
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No. 01 : Head Quality Assurance
- Controlled Copy No. 02 : Head Production
- Controlled Copy No. 03 : Head Quality Control
- Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
- ABBREVIATIONS:
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| QC | : | Quality Control |
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be recorded manual. |
ANNEXURE-I
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/operation-and-cleaning-of-sampling-rod/
Frequently Asked Questions?
1. Why is the cleaning of sampling aids crucial in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: The cleaning of sampling aids is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry to prevent cross-contamination, ensure the accuracy of analytical results, and maintain the integrity of pharmaceutical products.
2. What are the primary sampling aids used in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: Common sampling aids in the pharmaceutical industry include scoops, spatulas, containers, pipettes and sampling rods used to collect representative samples during various stages of production.
3. What is the purpose of cleaning sampling aids before and after each use?
Answer: Cleaning sampling aids before and after each use is essential to eliminate any potential residues, contaminants, or traces of previous samples, ensuring the reliability and validity of subsequent analyses.
4. What cleaning methods are commonly employed for pharmaceutical sampling aids?
Answer: Common cleaning methods include thorough rinsing with appropriate solvents, autoclaving, washing with detergents, and, in some cases, validated cleaning validation processes to meet regulatory standards.
5. How often should sampling aids be cleaned in a pharmaceutical manufacturing environment?
Answer: The frequency of cleaning depends on the nature of the samples and the specific processes. Generally, sampling aids should be cleaned before and after each use, and more frequently if the risk of contamination is high.
6. What validation processes are involved in ensuring the effective cleaning of sampling aids?
Answer: Validation processes may include swab testing, visual inspection, and analytical testing to verify the complete removal of residues and contaminants, meeting regulatory requirements and industry standards.
7. How can the risk of cross-contamination be minimized during the cleaning of sampling aids?
Answer: Dedicated equipment, segregation of sampling aids based on their use, and the use of validated cleaning procedures are essential in minimizing the risk of cross-contamination during cleaning.
8. What documentation is necessary to demonstrate the effectiveness of cleaning processes for sampling aids?
Answer: Documentation should include standard operating procedures (SOPs), cleaning protocols, validation reports, and records of cleaning activities to provide evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements.
9. Are there any specific regulatory guidelines governing the cleaning of sampling aids in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Yes, regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA provide guidelines on cleaning validation, which pharmaceutical companies must adhere to in order to meet quality standards and ensure patient safety.
10. How can the pharmaceutical industry ensure continuous improvement in the cleaning of sampling aids?
Answer: Regular training of personnel, periodic reviews of cleaning procedures, incorporation of technological advancements, and a proactive approach to addressing emerging challenges are essential for ensuring continuous improvement in the cleaning of sampling aids in the pharmaceutical industry.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/operation-and-cleaning-of-sampling-rod/