OBJECTIVE:
To lay down the procedure that describes cleaning validation approach and requirement for preparation, review, approval and execution of Cleaning Validation Protocol and Report.
SCOPE:
This procedure is applicable to the Cleaning Validation program for {Company Name} {Location}
RESPONSIBILITY:
Quality Assurance: Executive/Designee shall be responsible to prepare the Cleaning Validation Protocol and Impact Assessment Report. To execute the protocol for cleaning validation/periodic verification and compile the report. To review the Cleaning Validation Protocol, Report and Impact Assessment Report and Conduct the training on the Cleaning Validation Protocol.
QC: Executive/Designee validation sampling as per protocol. To perform testing and report the results. To perform cleanability study and Visual residue limit determination study. To perform analytical method validation. Head QC to review the Cleaning Validation Protocol, Report and Impact assessment Report.
ACCOUNTABILITY:
QA Head shall be Accountable for implementation of SOP.
PROCEDURE:
General:
Cleaning Validation Studies shall be conducted to ensure that the cleaning procedures for Type C cleaning are effective, adequate, and shall consistently remove the residues (Active Pharma Ingredients, microbial, endotoxins and cleaning agents wherever applicable) to acceptable levels. The following cleaning procedures of shared facilities shall be validated:
Product contact surfaces such as equipment parts, tools etc.
Non-product contact surfaces such as external surfaces of the equipment, filter grills etc.
Cleaning procedures of dedicated manufacturing facilities/ equipment/ tools / Non product contact surfaces such as external surfaces of the equipment, filter grills etc. shall be verified for their effectiveness.
Impact assessment for cleaning validation shall be done during introduction of new product in the facility to determine the requirement of formal cleanability study. This impact assessment shall be done based on solubility (in cleaning agent), cleanability, ADE\PDE \Potency of the new product.
Cleaning validations shall be performed for difficult to clean product (Worst case product) from all the products available in a manufacturing suit/ line.
A Maximum Allowable Carryover (MACO) or Maximum Allowable Residue (MAR) limits for the identified worst case product shall be determined by using:
- Health-based limits (ADE/PDE).
- Fourman Mullen approach (based on minimum value from 10 ppm criterion and dose criterion) for the dedicated facilities such as multiple Penicillin, Cephalosporin and Penam products.\
The minimum MAR value obtained in the product group shall be considered for acceptance limit of MAR in cleaning validation.
The analytical methods adopted for sampling and analysis of the samples shall be validated prior to use and shall be at least as sensitive as required by the MAR.
The analytical method validation studies shall consider recovery studies verification from various types of product contact surfaces such as Stainless Steel, other materials of construction and for those materials of construction greater than 5% of the total product contact surface area.
For cleaning validations, minimum of three consecutive runs shall be considered. In case wherever three consecutive runs are not available such as initial process optimization/exhibit batches (Pivotal batch/test batch) the cleaning evaluation shall be carried out based on available data and the cleaning validation shall be concluded only after completion of three runs.
In instances where cleaning validation is not complete, cleaning verification by chemical analysis shall be performed after each campaign.
The Clean Equipment Hold Time studies and Dirty Equipment Hold Time shall also be established through a validation program.
Cleaning procedure validation status shall be maintained by periodic verification program.
Routine monitoring consists of visually clean verification and if the MAR limits are below the visual detection range a chemical analysis shall also be performed and documented.
Results from cleaning validation / verification shall be maintained in a database to allow statistical evaluation.
Personnel involved in cleaning shall be adequately trained in the cleaning procedures.
Personnel involved in cleaning validation sampling shall be adequately trained in the sampling techniques.
Personnel involved in visual cleanliness verification shall be subjected for eye examination on periodic frequencies, not less than once per year.
For campaigns and product dedicated modules campaign lengths shall be determined by evaluating the residue for microbial load, related substance, and hard to clean after campaign etc.,
Type A/Type B cleaning process is used within the campaign length and the acceptable residue level is visually clean. After the campaign, Type C cleaning shall be used and the acceptable level is visually clean/MAR limit.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
Validation / Re-validation and Verification:
An Impact Assessment for evaluating the requirement of validations/re-validation of cleaning procedures shall be done whenever following changes are necessitated:
- Addition of new product
- Change in product contact surface area/equipment chain
- Change in batch sizes
- Change (decreased) MAR values
- Change in process formula etc.
Cleaning procedures shall be revalidated due to the following
To Establish the Cleaning Validation at your site please write us at pharmaguidehub@yahoo.com
- Change in cleaning agent or its concentration wherever applicable.
- Change in cleaning procedure (SOP).
Maximum Acceptable Residue (MAR) calculation:
The MAR acceptance limit calculation for chemical residue shall be based on Health-based (ADE/PDE) criteria. The minimum MAR value (separately for swab and rinse) obtained, shall be selected as acceptance criteria for MAR.
For the dedicated facilities such as Penicillin, Cephalosporin and Penam products the MAR acceptance limit calculation for chemical residue shall be based on Dose Criteria and 10 ppm criteria. The minimum MAR value obtained from both Dose Criteria and 10 ppm criteria (separately for swab and rinse), shall be selected as acceptance criteria for cleaning validation.
The calculation is as given below:

Maximum allowable carryover limit of Product A into total Batch of the Product B (L2) is as given below:
L2 = L1 ´ Minimum Batch size of product B
Maximum allowable carryover limit of Product A per Sq. cm of surface area (L3) is as given below:

Maximum allowable carryover limit of Product A per swab area (L4a) is as given below: L4 a= L3 ´ Swab area (Sq. cm).
Concentration of residue in the extracted swab sample(L4b) is given as below:
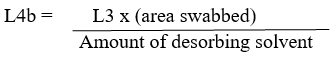
Rinse concentration (L4c) of the active in any rinse solution is as given below:
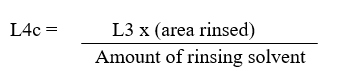
Where,
A is the Product for which cleaning is to be performed
B is the next proposed product to be processed.
Preferably, the safety factor of 1/1000th (0.001) of the minimum therapeutic dose shall be considered for the oral formulations whereas for the injectable and ophthalmic formulations, a safety factor of 1/10000th (0.0001) of the minimum dose shall be considered for Dose criteria.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
Note: While calculating the equipment surface area, +5% of the obtained values may be taken to prevent error due to manual measurements.
Whenever the cleaning limits are not achievable any one or a group of below given options may be used with proper justification documented in the cleaning validation protocols:
- Improve the cleaning method
- Increase in swab surface area
Lower LOQ/LOD of the analytical method by and of the following and revalidate analytical method:
- Increasing the injection volume
- Increasing the flow rate
- Changing the detection wavelength
- Decrease shared equipment area by dedicating pieces of equipment or parts
- Increase batch size of the following product
- Administratively control which products can be manufactured in series.
If there is not enough data to determine an ADE/PDE the following Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) will be used as placeholders until sufficient data is available for a toxicological evaluation to determine an ADE/PDE. Once the ADE/PDE value available recalculate the MAR Limit.
- An ADE of 1 mcg/day will be assigned if the compound is genotoxic.
- An ADE of 10 mcg/day will be assigned if the compound is carcinogenic
- An ADE of 100 mcg/day will be used if the compound is neither genotoxic or carcinogenic
A cleaning validation Maximum Acceptable Residue (MAR) shall be maintained area/ equipment/ product wise.
Worst Case Product selection:
As a part of Impact Assessment perform the cleaning assessment to determine which is the best cleaning procedure (process, detergent, time, etc.).
Cleaning Assessment (Cleanability study)Based on impact assessment of cleaning validation if the product identified as difficult to clean, performs the initial cleaning development work.
This can be conducted at laboratory scale.
The cleanability studies are performed to provide a more focused look at critical cleaning process parameters such as time, temperature, concentration of detergent and cleaning agent and to demonstrate the effectiveness of the cleaning parameters.
The worst-case product is applied to different material of construction coupons; air dried for 24 hours and cleaned using the previously identified cleaning parameters.
A coupon is considered to be clean if it is visually clean and water break-free.
Cleanability shall be graded as Easily cleaned, cleaned with extra effort, very difficult to clean.If the New MAR value is observed to be less than the results of worst-case product, cleaning processes shall be appropriately revised and revalidated.
After preparation of Impact assessment report evaluate the impact on the worst case product and MAR value.
If its impacting worst case molecule, initiate process of cleaning validation by performing analytical method validation and Visual Residue Determination study as per the common procedure.
The worst-case product shall be selected based on a solubility, hardest-to-clean (low cleanability) and ADE/PDE/potency within the same cleaning procedure.
- The least soluble product manufactured in respective manufacturing module/area shall be considered as the worst case product. If there is more than one product having least water-soluble active ingredient then hardest-to-clean (low cleanability) product shall be considered, if the product having same solubility and cleanability then drug product with lowest ADE shall be considered the worst case.
- If a drug product contains multi active ingredients, the least soluble active ingredient shall be considered.
For the facilities such as Penicillin, Cephalosporin and Penam, worst case product shall be selected based on the parameters such as solubility, hardest-to-clean (low cleanability) and potency within the same cleaning procedure.
- The least soluble product manufactured in the respective manufacturing module/area shall be considered as the worst case product. If there are more than one product having least water-soluble active ingredient then low cleanability product shall be selected as worst case product in the product group, if the product having same solubility and cleanability then drug product with high potency shall be considered the worst case.
- If a drug product contains multi active ingredients, the least soluble active ingredient (if competent candidate there, high potent) shall be considered.
All cleaning procedures of equipment in manufacturing area/suite/modules shall be validated with the worst-case product, if the equipment is not utilized by the worst case product, the next worst case product using this equipment shall be considered for cleaning validation.
For Packaging equipments, if the worst-case product is a coated tablet and/or capsule, worst case product among the uncoated tablets shall also be considered.
Visual Inspection and Visual Limits:
After the cleaning of equipment, visual inspection will be performed prior to other sampling. Equipment surfaces shall be visually clean. Visual inspection is part of the cleaning validation acceptance criteria for all equipment. The clean equipment must contain no visible residue.
The Visual Residue Limit (VRL) will be determined on stainless steel. Stainless steel is by far the most prevalent material for construction of manufacturing equipment. VRLs on other materials of construction will be determined on an ‘as needed’ basis for those materials of construction greater than 5% of the total product contact surface area.
The VRL protocol shall be prepared as per the SOP. The study can be executed in parallel with the swab and rinse recovery studies or qualification of personnel performing visual inspections.
Clean and Dirty Hold times:
Clean and dirty hold time studies shall be validated to determine the maximum time dirty equipment can be held prior to cleaning and the maximum time clean equipment can be held before requiring a re-clean.
Clean and dirty hold times to be verified by the study based on the needs and practices of the -operations.Each study will be carried out 3 times on each piece of equipment.
This may be three iterations on the same piece of equipment or, where more than one of the same pieces of equipment exists, achieved using two or three units. (Clean equipment and dirty equipment hold time study plans shall have rationale for selection of the equipment, material and timelines).
The studies will be carried out based on a pre-approved protocol.
The clean and dirty hold time studies can be carried out during the cleaning validation.
Microbial samples of predefined locations shall be taken from the equipment as part of the clean hold time study and analysed as part of the acceptance criteria
Recovery studies:
Swab and rinse recovery studies will determine how much of the residue is recovered during sampling. Swab and rinse recovery studies will be conducted to bracket the cleaning acceptance limit or below where data is typically reported.
The results will be used to support the cleaning validation and ongoing monitoring.
The swab and rinse recoveries will be determined on stainless steel. Stainless steel is by far the most prevalent material for construction of manufacturing equipment.
Recoveries from other materials of construction will be determined on an ‘as needed’ basis for those materials of construction greater than 5% of the total product contact surface area.
The Recovery study shall always be targeted to achieve not less than 75%, consider the correction factor while calculating the results.
Updation of master list shall be done, master list for ADE value along with product list to be updated for addition of new product and new ADE value for that product.
While updating the Equipment list follow the Grouping/Bracketing approach. Also update the cleaning procedures for addition of new equipment or change in cleaning procedure.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
Equipment Grouping/ Bracketing:
Equipment will be grouped based on physical characteristics: size, geometry, complexity, degree of disassembly and cleaning procedure (e.g. similar tablet presses, filling machines, vessels, storage containers).
Within a group, representative equipment will be identified and validated to represent the entire group. If the entire equipment group is cleaned using the same cleaning procedure, then the entire group can be validated using one study.
Any equipment or equipment groupings not represented in the worst case or representative grouping will also be validated with an additional study.
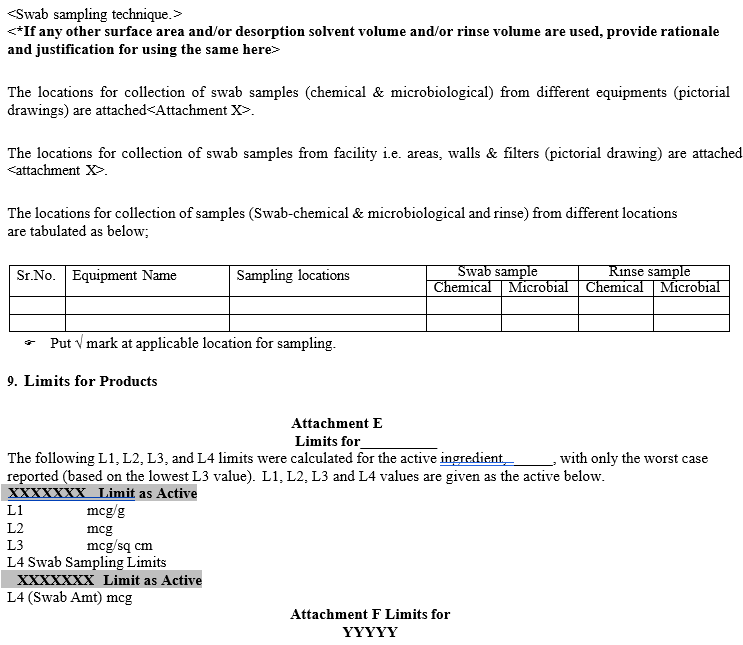
Selection of Sampling Method:
Either of two sampling methods; direct surface sampling (swab method) or indirect sampling (use of rinse solutions) shall be used.
Swab sampling technique shall be selected primarily for sampling.
Rinse sample technique shall be used wherever inaccessible areas of equipment that cannot be routinely disassembled.
A combination of the swab and rinse sampling shall also be considered wherever applicable. E.g. Product transfer hoses, transfer lines etc.
Location for swab sampling shall be selected as hardest to clean areas, which are reasonably accessible for swabbing.
Additional study shall be performed to encompass determination of the appropriate swab locations for each equipment type for cleaning validation/ evaluation and cleaning verification.
- An initial evaluation of each piece of equipment will be performed and documented to identify the hardest to clean locations and the rationale for their selection. Swab locations shall be selected so as to represent the whole product contact surface (in divided sections) of the equipment and also hard to clean locations shall be considered based on difficulty to clean possibility to retain residue, surface smoothness, crevices and material of construction based on equipment design configuration and operational experience.
- A protocol-based study shall be conducted for each type of process equipment with worst case product to evaluate the appropriateness of the locations selected for swab sampling. A pre-defined statistical evaluation will be applied to the data obtained from three consecutive cleaning runs/ procedures.
- If the results of all sampling locations are below the quantification limit, i.e., all sample locations were equally and thoroughly cleaned, then the sampling locations shall be selected based on the hardest to clean locations identified in the initial evaluation of each piece of equipment (difficult to clean, possibility to retain residue, surface smoothness, crevices, and material of construction based on equipment design configuration and operational experience).
- Based on the outcome, a master document with pictorial representations of swab sampling locations for each type of equipment in the facility shall be made and followed as reference for further cleaning validation/periodic verification.
- A master document for equipment product contact surface area calculation.
- A master document with pictorial drawings of product contact surfaces of equipment with locations identified for swabbing.
Sampling Procedure:
For every cleaning process, visual inspection of equipment/surface shall be done prior to sampling.
After completion of the cleaning process, visual inspection of equipment/ surfaces shall be performed and after satisfactory visual inspection, samples shall be collected by swabbing and/or rinse sample method.
Swabbing method for chemical residue can be performed by using non-fiber shredding non-contaminant sampling aids (ready to use swabs).
The technique adopted shall be studied during the cleaning analytical method validations.
For non-fiber shredding swab (ready to use swabs)Use the non-fiber shredding, non-contaminant sampling aids such as taxwise swabs.
Dip the sampling aid in diluents in respective test tube as identified for the equipment part and squeeze it against the wall of the test tube using forceps.
Swab the surface of equipment as per the following swabbing pattern. Subsequently it shall be swabbed at 90° angle to the previous strokes as shown below. A template (made of SS/ Teflon/ PVC) of required size can be used to mark the sampling area.
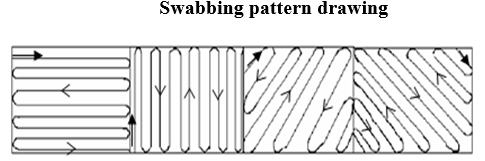
The swab shall be removed and placed in a labelled test tube containing the diluent.
Transfer the sample to QC laboratory, analyze for residue content by suitable method of analysis. Typically, 4 x 4 (16 cm2) surface area shall be swabbed of each equipment. Wherever the surface area of 4 x 4 Sq.cm is not available, swab the entire available surface. And record the surface area swabbed.
For Microbial Load, the sample collection shall be performed by swab as stated below:
Swab a (5×5), 25 Sq.cm surface area of the equipment as per the Swabbing pattern drawing as stated above.
Use sterile swabs with suitable desorption medium for swabbing.
Transfer the swab sample aseptically to the Microbiology Laboratory and perform the analysis as per the specifications by suitable validated method. Microbial swab and chemical swab sampling shall be done on two separate areas
Rinse Sampling procedure:
The equipment product contact part shall be finally rinsed with a known quantity of rinse solvent (preferably 5-10% of the equipment volume).
Collect minimum of 100 ml of sample from final rinse for chemical residue and 100 ml in sterilized bottles for microbial analysis and send samples for analysis.
For chemical residue analysis take required amount of sample solution and analyses for residue content by suitable analytical method (HPLC or any suitable analytical method).
For microbial load, perform the analysis by suitable validated method.
Sample hold time studies by simulating the storage conditions of samples in routine cleaning validation shall be evaluated.
Acceptance Limit:
- The equipment/surfaces shall be Visually Clean after the cleaning process.
- For the product contact surfaces, the least MAR in the product grouping obtained shall be considered as acceptance chemical residue limit.
- For the product non-contact surfaces such as external surface of equipment, filter grills etc., an acceptance chemical residue limit of 100 PPM per swab shall be considered.
- For walls and floors an acceptance criterion is visually clean.
- For detergents (wherever applicable) the limits shall be based on the health-based and if the data is not available, preferred limits would be NMT 5 PPM.
- If results are not detected the result shall be recorded as “< the actual LOD value”.
To Establish the Cleaning Validation at your site please write us at pharmaguidehub@yahoo.com
The acceptance limit for microbial load is as follows for total bacterial count:
- For oral dosage formulations.
- Total bacterial count shall be NMT 50 CFU/swab surface.
- Total bacterial count shall be NMT 50 CFU/ml (rinse)
- Yeast and molds shall be absent.
- Pathogens shall be absent.
For sterile dosage formulations, the rinse solution:
- Shall meet applicable bio load limits of WFI.
- Shall meet Endotoxin level of WFI as per USP requirement.
Maintenance of Validation Status:
The periodic verification shall be done once in a year (± 1 month) with product, precisely the worst-case product to cover all the equipments, for those equipment on which worst case product is not taken, consider the worst case product from the group of products sharing that equipment.
Compare the periodic verification data to the initial validation data to demonstrate continued control of the cleaning process.
Periodic verification may consider the next worst case product, in case the actual worst case has not been planned during the review period.
For sterile formulations, during routine cleaning procedure evaluations the final rinse may be subjected to residue analysis and/or compliance to WFI specification (as instructed in site SOPs/protocols).
A periodic verification schedule shall be prepared for all the product contact equipments.
If a cleaning validation study for a specific line is repeated within the scheduled annual monitoring period for a specific line/ block, such annual monitoring program for the line shall be discounted.
The annual monitoring program in such cases shall be resettled and annual monitoring shall be planned after 1 year from the new dates.
Documentation – Cleaning Validation Protocol and Report:
Cleaning Validation Protocol
- Shall be prepared in MS-Word and Calculation report for worst case shall be generated using SOP.
- Cleaning Validation protocols generated shall be reviewed and shall be ensured to have the sections defined in section.
- The following details shall be added/modified in the protocol in-addition to details generated by the System:
Cover sheet
Table of Contents.
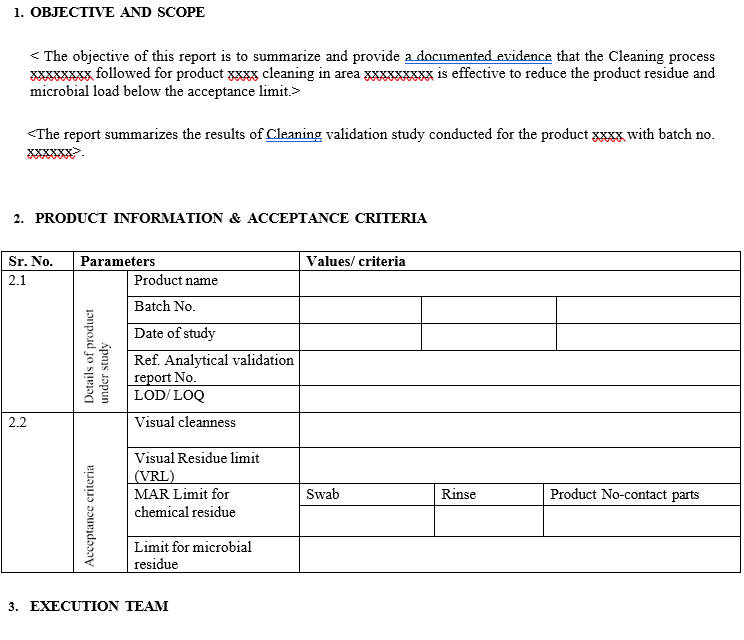
Objective and Scope.
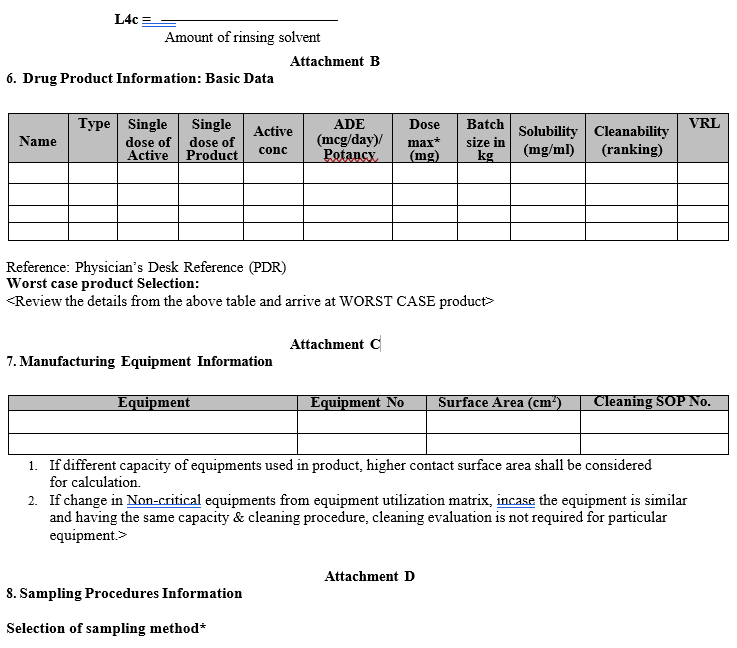
Drug product information table with solubility details of the API, ADE/PDE, Maximum daily dose, Batch size in Kg. / Nos and worst-case product selected from the list of products based on solubility, hardest to clean, and ADE/PDE.
Sampling Procedure information with Sampling method selection and Sampling locations.
Acceptance criteria for visual inspection, chemical (Maximum Acceptable Residue) and microbial load.
Attachment of Residue report
Impact assessment shall be conducted and if this impact assessment includes performing cleaning re-validation, protocol preparation shall be done.
If the impact assessment does not mandate to perform cleaning re-validation, in such cases the cleaning validation protocol need not be generated.
The final cleaning validation protocol and/ or impact assessment report shall be saved in appropriately identified folder.
These documents shall be reviewed and approval.
Cleaning Validation Report:
shall be generated after execution of the validation protocol. It shall typically consist of following:
- Cover sheet
- Table of contents
- Objective and scope
- Product information and acceptance criteria
- Execution team members
- Visual inspection results
- Product/chemical residue results
- Microbial load results
- Statistical evaluation
- Deviation/ NCR if any
- Final report (Summary and conclusion)
- Attachments
The Cleaning Verification Report shall be prepared for the cleaning verification study performed annually to verify the continued validation status of the cleaning process.
Numbering System: Cleaning Validation Protocols and Reports shall be numbered as per SOP.
Statistical evaluation:
Use excels spread sheet to perform the statistical evaluation of cleaning validation analytical results.
At least 6 independent data points are required to initiate and to calculate limits (Alert and Action).
Preferably, at least 40 independent data points are required to derive the permanent limit.
Data of analytical results of cleaning validation shall be included upon the availability of data.
For each year, a trend report shall be obtained from the excel file and shall be compiled for each product.
For each periodic verification / re-validation, trend report shall be obtained from the excel file and shall be compiled with report.
If there is any out of trend observed in the quarterly trend, the same shall be investigated and appropriate corrective and preventive action shall be taken.
Calculation: Complete the following steps to establish control limits:
Enter the individual results in excel spread sheet.
When at least 6 results are available, calculate Alert and Action (2-sigma and 4- sigma limits).
The formula for calculating the Alert Limit and Action Limit is given below;

Interpretation of Results:
Cleaning validation results shall indicate that all the samples collected post cleaning shall comply with stated acceptance criteria.
If acceptance criteria are not met, initiate process non-conformance and investigation shall be conducted. If a laboratory error does not exist, investigation shall be extended to execution of cleaning procedure of the particular process equipment. If investigation concludes that cleaning procedure execution is incorrect, the equipment is cleaned again as per the procedure.
If investigation concludes no discrepancies during execution of cleaning procedure, revise the cleaning procedure to ensure proper cleaning of location/parts of the equipment and revalidate.
Definitions:
Cleaning Validation: A documented evidence that, the cleaning procedure shall consistently remove the residue of the products below acceptable levels. Cleaning validation is performed with three consecutive batch change over when ever there is a new cleaning process.
Cleaning Verification: A documented evidence that ensures the effectiveness/ continued validated state of the existing cleaning procedure to remove residue of the products below acceptable levels. Cleaning verification is performed with single batch change at defined intervals for reassessment or incase of any single batch verification study.
Cleaning Re-validation: A documented evidence that, the cleaning procedure shall consistently remove the residue of the products below acceptable levels after the change to equipment, product or process. Cleaning validation is performed with three consecutive batch change over whenever there is a change in the validated cleaning process, equipments or product in cleaning aspect.
Campaign Length: The predetermined maximum number of consecutive batches allowed in manufacturing or packaging within a single campaign and the maximum allowable time the equipment is used during manufacturing or packaging in a single campaign.
Clean Hold Time: The time from the end of the cleaning process until it is used again.
Cleaning Type A: Cleaning procedures that are followed between batches of the same product.
Cleaning Type B: Cleaning procedures that are followed between batches of the same product for the equipments in which wet processing is carried out.
Cleaning Type C: Cleaning procedures that are followed when changing over to a different product or after the campaign length.
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
Dirty Hold Time: The time from the end of product manufacturing until it is cleaned.
Health-Based Limit: A limit based on the health risks to patients as determined by a toxicological and pharmacological assessment. Also known as limited determined from the acceptable daily exposure (ADE) or permitted daily exposure (PDE).
Water break-free (WBF): is a qualitative test that indicates the cleanliness of a metal surface. On a clean surface free from organic residue, water sheets evenly without breaking in the water film as it runs from the surface of the metal panel.
Dose Criteria: Not more than 0.1% of minimum therapeutic dose of any product should appear in the maximum daily dose of the subsequent product.
10 PPM criteria: Not more than 10mg of drug should appear in 1 Kg of subsequent product.
Flow Chart
Template (1) for Equipment product contact surface area calculation
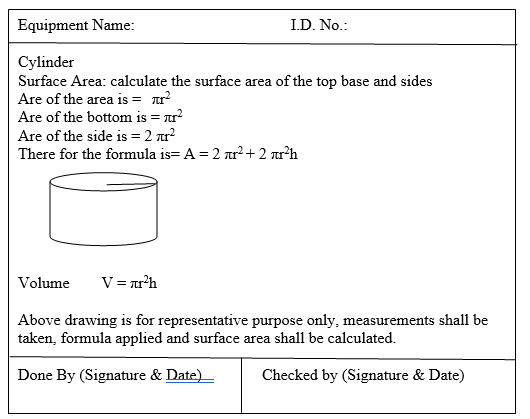
Template (2) for Sampling locations of Equipment
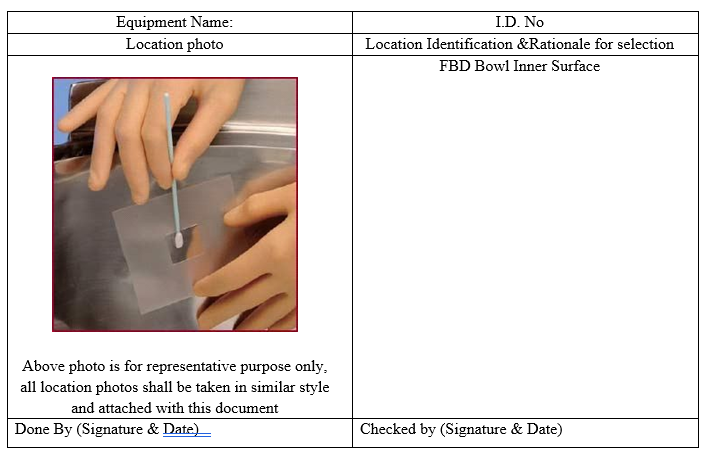
Template (3) for Visual inspection for Cleaning Validation/ Verification
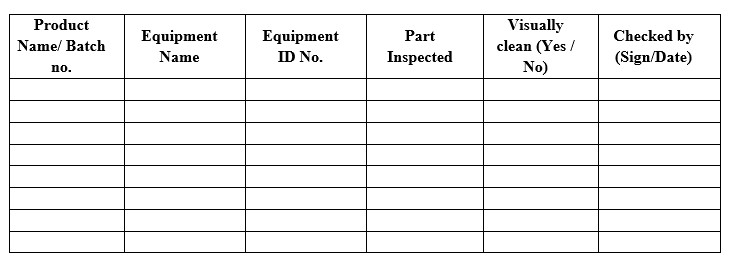
Template (4)
IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR CLEANING VALIDATION
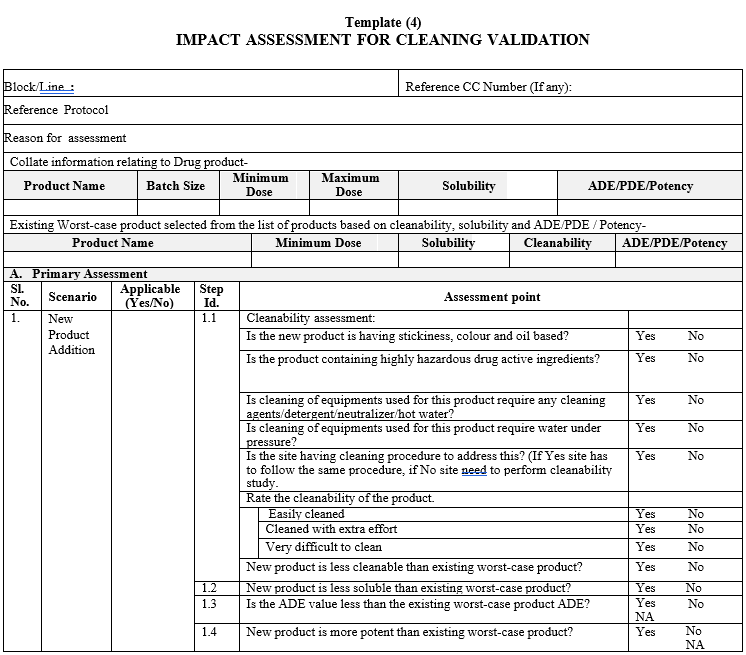
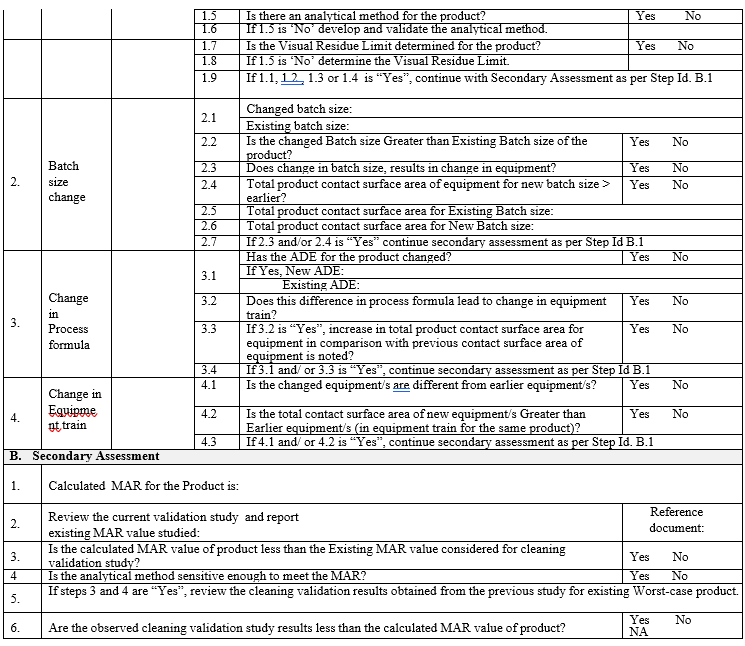

Template (5) for Cleaning Validation Protocol





Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
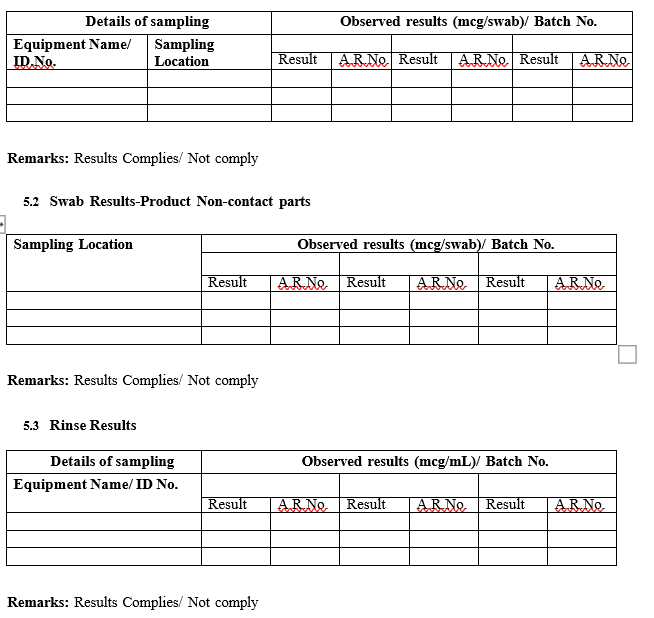
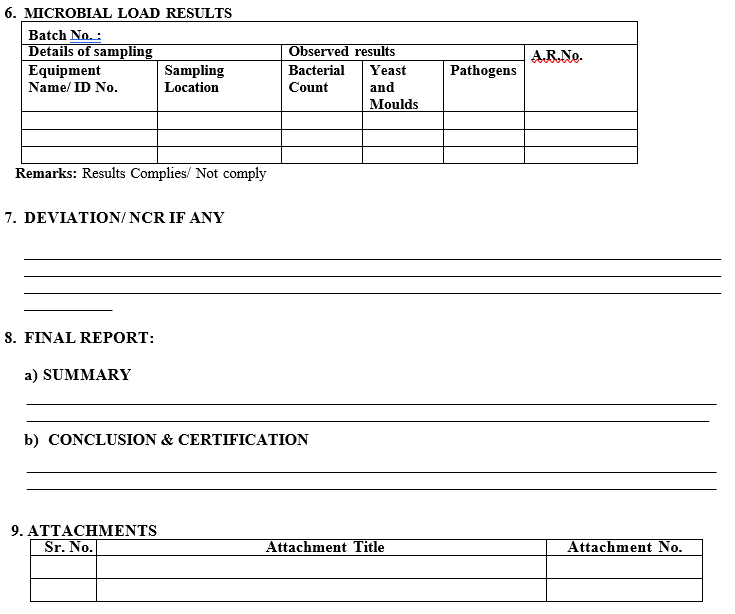
Template (6) for Cleaning Validation Report

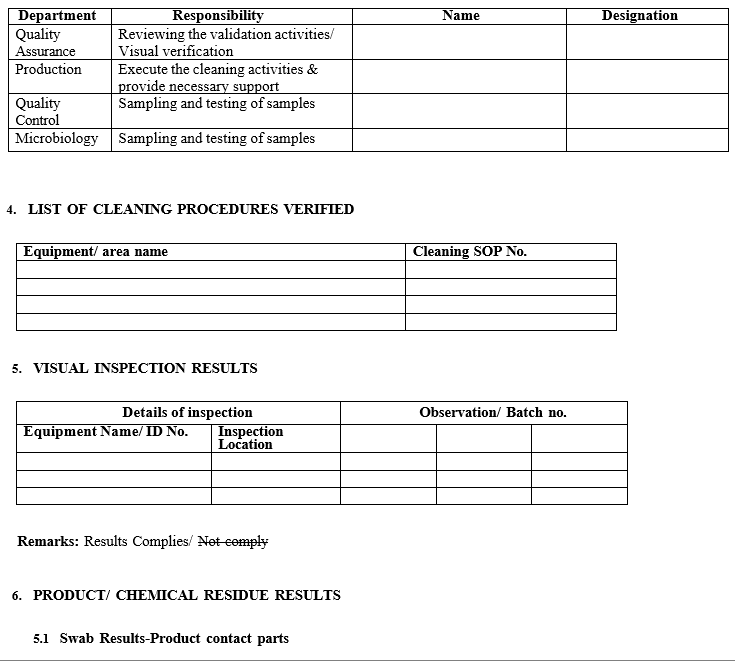
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/
Template (7) For Routine cleaning verification schedule for all the product contact equipments
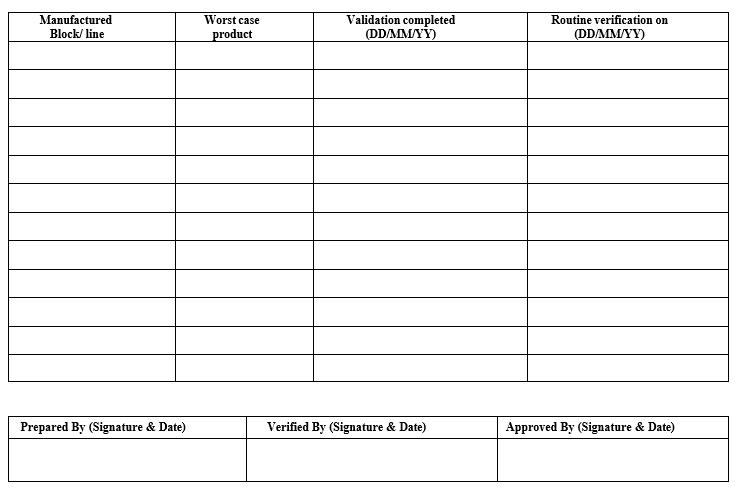
REFERENCES:
Not Applicable
ANNEXURES:
Not Applicable
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No. 01 : Head Quality Assurance
- Controlled Copy No. 02 : Head Production
- Controlled Copy No. 03 : Head Quality Control
- Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
ABBREVIATIONS:
| ADE | : | Acceptable Daily Exposure |
| No. | : | Number |
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| API | : | Active pharmaceutical ingredient |
| HPLC | : | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| LOQ | : | Limit of Quantification |
| NMT | : | Not more than |
| NMT | : | Not more than |
| LOD | : | Limit of Detection |
REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To Be Written Manual |
Click the link to download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/cleaning-validation-programme/



