OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for collection, storage, analysis, review & evaluation of Stability study samples of drug products and evaluate the shelf life and storage condition of drug product.
- SCOPE:
This SOP is applicable to procedure for the To lay down a procedure for collection, storage, analysis, review & evaluation of Stability study samples of drug products and evaluate the shelf life and storage condition of drug product at {Company Name} {Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- QA Officer/Executive – To follow the SOP.
- QA Manager/Designee/QC Manager/Designee, Review, technical correction, training and monitoring of SOP.
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
QA Head shall be accountable for implementation of SOP.
- PROCEDURE:
- SELECTION OF BATCHES.
- First three commercial batches shall be taken under consideration for stability study in following condition:
- New product
- The stability sample shall be collected based on the composition instead of brand name.
- One batch shall be kept for stability study in case of major changes like:
- Change in equipment having same operating principle but differ in design characteristics.
- Minor Change in manufacturing process having no potential impact on finished product quality.
MINOR CHANGES:
- Without changing the Excipient composition to a significant level Ex. change in diluents, color percentage to meet the physical parameters.
Two batches shall be kept for stability study in case of major changes like:
- Change in equipment having different class (i.e. differ in operating principle as well as design characteristics).
- Change in manufacturing process/formula having potential effect on finished product quality.
MAJOR CHANGES:
Changing the Excipient composition to a significant level to have a potential effect on product.
- Change in the basic principle.
- Change in manufacturing location having equivalence in equipment and environmental condition.
- Change in manufacturing location having no equivalence in equipment and environmental condition.
- Change in vendor
- Change in primary packaging materials.
Any other reason as specified by Head Quality Assurance.
Every year one batch of each product shall be kept on long term stability study.
Stability studies should be performed on different strength and container size of the Drug product with application of bracketing or Matrixing.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
BRACKETING:
Bracketing is the design of a stability schedule such that only the extremes of certain design factors are tested at all time points.
- Different strengths.
- Different pack size and/or fill.
Stability of intermediate levels represented by stability or tested extremes.
Bracketing design not appropriate, if tested samples are not the extremes.
Bracketing can be applied to studies with multiple strengths of identical or closely related formulations as given below, but are not limited to:
- Gummy solutions of different strengths with formulations that differ only in minor Excipient (diluents, color and sweetening agents).
- If the weight of actual active is less than 5.0% of the total weight.
Bracketing can be applied to studies with multiple strengths, different container size and/or fill where the relative amounts of Drug substance and Excipient change in a formulation, if justified with the stability profile of different strength of development or clinical batches.
In cases where different Excipient are used among different strengths, bracketing should not be applied.
Applicable without justification for same container closure system where either size of fill varies.
If both container size and fill vary, largest or smallest containers may not represent the extremes of all packaging configurations.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
Extremes should be selected comparing various characteristics:
- Container wall thickness.
- Closure geometry.
- Surface area to volume ratio.
- Heads space to volume ratio.
With justification, bracketing applicable with same container when the closure varies, if investigations for physico-chemical stability for solid dosage forms have shown not sensitive to moisture.
If during testing one of extremes no longer expected to be marketed, study maintained to support bracketing intermediates.
If stability of extremes differs, shelf life of intermediates should not exceed least stable extreme.
For example: If three different strength like 500, 1000 and 1500 with container size 100, 200 and 300 g product shall be kept for stability after applying bracketing will be as follows:
| Strength (µg.) | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | |||||||
| Batch No. | B1 | B2 | B3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | |
| Container Size (g) | 100 | |||||||||
| 200 | ||||||||||
| 300 | ||||||||||
To reduce the risk applying bracketing the number of strengths or container sizes should be balanced with the total number of strengths or container sizes as follows:
| Number of strength | Strength to be tested |
| 1-2 | All |
| 2-4 | Lowest and highest |
| ≥5+ | Lowest, middle and highest |
| Number of Pack sizes | Pack Sizes to be tested |
| 1-2 | Smallest |
| 2-4 | Smallest and biggest |
| ≥5 | Smallest, middle and biggest |
MATRIXING:
Matrixing is the design of a stability schedule such:
- That a selected subset of the total number of possible samples for all factor combinations would be tested at a specified time point.
- At a subsequent time point, another subset of samples for all factor combinations would be tested.
Matrix design assumes that the stability of each subset of samples tested represents the stability of all samples at a given time point.
The differences in the samples for the same Drug product should be identified as:
- Covering different batches.
- Different strengths.
- Different sizes of the same container closure system.
- Possibly in some cases, different container closure systems.
Matrixing design shall be applied on following:
- Batches made using the same process and equipment.
- Container size and fill in the same closure system.
Matrixing design applicable with justification (different container closure systems are similar in moisture, or the product is not effected by moisture) if:
- The relative amounts of the Drug substance and Excipient change.
- Different Excipient are used.
- Different container closure system.
A matrix design should be balanced such that each combination of factors is tested to the same extent over the duration of the study.
Initial and end point values should be included for all samples.
At least three time points, including initial, should be available for each selected combination, through the first 12 months.
For accelerated or intermediate storage condition, a minimum of three time points are necessary.
Any matrix design should retain an adequately ability to detect stability differences within factors or among factors.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
If one strength or container size/ or fill is no longer intended for marketing, testing should be continued.
STORAGE CONDITIONS:
The storage condition for Accelerated stability study shall be at temperature 40° C ± 2°C and humidity75 % ± 5 %.
The storage condition for long term stability study shall be at temperature 30° C ± 2°C and humidity 75 % ± 5 %.
If product failing in both accelerated and long term stability study, stability shall be performed at the storage conditions i.e. 25° C ± 2° C and humidity 60 % ± 5 % or storage conditions on the label given accordingly.
SAMPLE QUANTITY:
Quantity of each sample kept shall be at least 50 % extra than required for complete analysis of the product at each station of every condition.
SAMPLING AND PACKING:
Sufficient quantity of the sample shall be drawn for stability study at different interval during packing, so that it will represent whole batch.
Sample shall be packaged in the simulated container closure system as packaging proposed for storage and distribution.
TESTING FREQUENCY:
For Accelerated stability study; in this case sample shall be analyzed at an interval of 0, 3 and 6 months.
For Long Term stability study: in this case sample shall be analyzed at interval of initial, every third month for first year, every six month for second year and thereafter yearly up to proposed shelf life i.e. 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36…
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
An additional testing shall be performed after proposed shelf life up to one year after the expiry of the product for long term stability study depend on the result obtained.
CHARGING OF SAMPLES IN STABILITY CHAMBER:
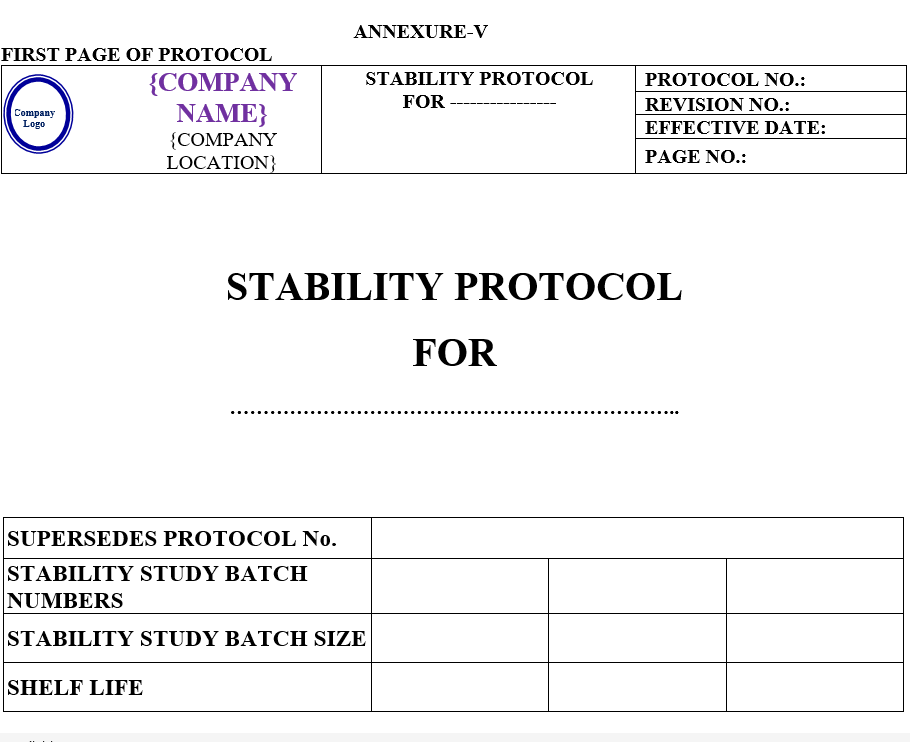
QC-Executive shall raise ‘Stability Request Form’ (SRF) attached as per Annexure-VI.
A unique number shall be provided by QA-Executive to each SRF and record shall be maintained as per format Annexure-V.
SRF number shall consist of 10 alphanumeric characters as SRF-XXX/XX.
Where:
- First three characters ‘SRF’ represent ‘STABILITY REQUEST FORM’.
- Fourth character ‘-’ is a separator.
- 5th, 6th and 7th character will be sequential number viz. 001,002, 003, ……….and 999.
- 8th character ‘/‘is a separator
- 9th and 10th character shall be last two digit of current year i.e. for year 2024 it will be 24.
QA Executive/Designee shall submit stability samples along with SRF to Quality Control department. Record shall be maintained as per Annexure-VI.
Before charging QC Executive /Designee shall prepare stability protocol as per Annexure-V.
Quality Assurance Head shall approve the stability study sheet with his/her recommendations.
Executive-QC/Designee shall receive the sample and perform labeling as per following information:
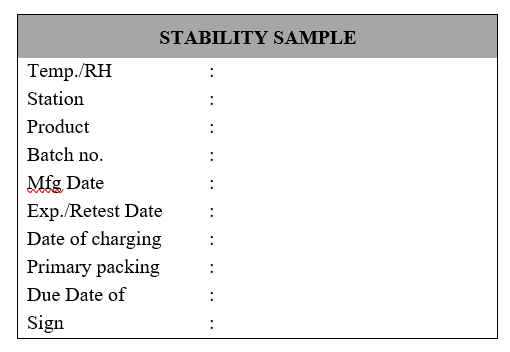
QC Executive/Designee shall distribute samples in different aliquots, for different testing intervals.
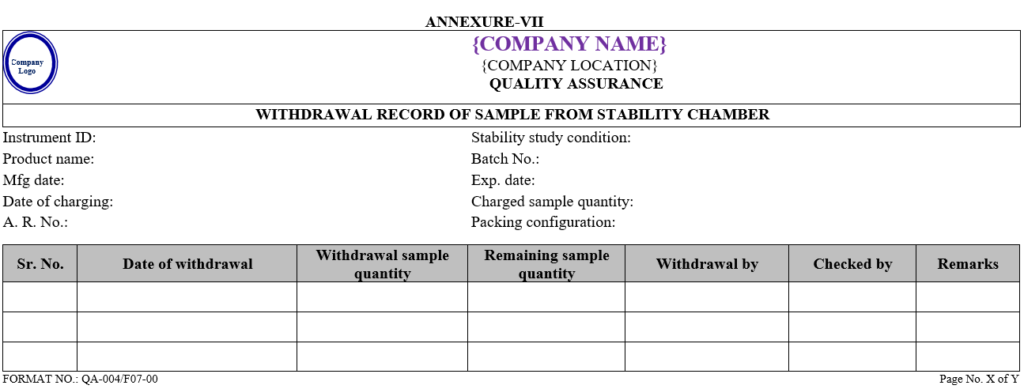
Executive-QC/Designee shall charge sample in stability and record of the same shall be maintained as per Annexure-VIII.
MONITORING OF STORAGE CONDITION:
Temperature and relative humidity record of stability chambers shall be maintained automatically through temperature/ RH monitoring device at an interval of 30 min.
If any excursion in temperature or humidity then investigation shall be performed as per SOP.
In case of any deviation in the recommended temperature or relative humidity conditions, QC Executive/Designee shall take immediate action to rectify the equipment malfunctioning.
During the period of rectification of stability chamber, samples shall be store below 25° C for long term and Accelerated stability samples.
If any breakdown is observed in stability chamber then inform to engineer person through breakdown intimation slip and as soon as possible stored samples shall be transferred to spare chamber within same condition as per previous storage condition.
TESTING:
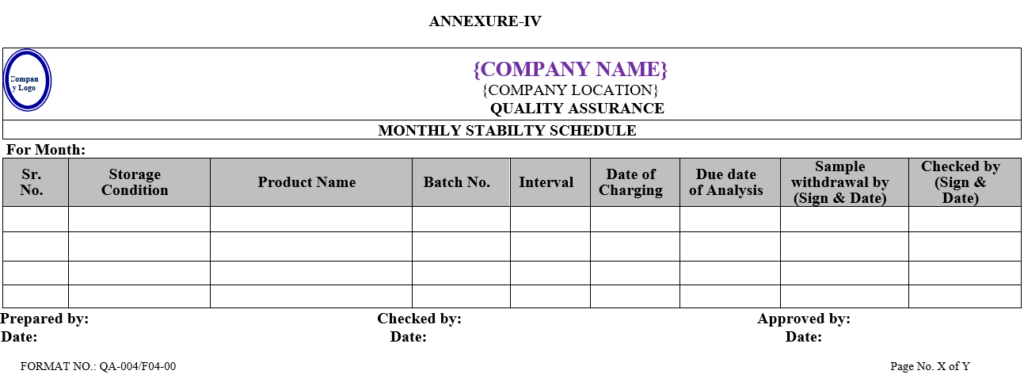
- Executive-QC/Designee shall prepare monthly analysis schedule/Calendar of analysis for stability sample as per Annexure-IV.
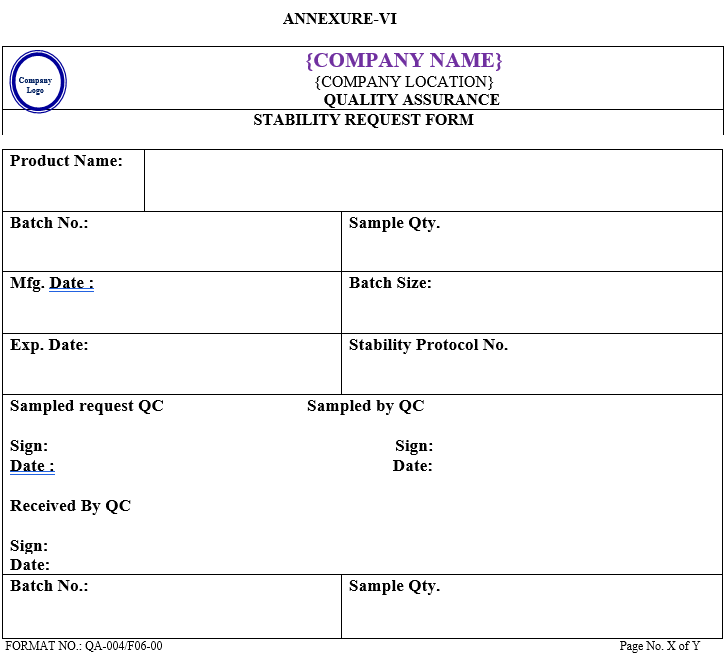
- The QC Executive shall withdraw the sample on the due date of analysis and allot the sample to the analyst for analysis record of sample withdrawal shall be maintained as per Annexure-VII.
- The samples which are taken out for analysis must be entered in Inward Log book for withdrawal samples shall be maintained as per Annexure-VII. Separate log book for long term /Accelerated should be maintained as per Annexure-I & II, respectively.
- The results of the tested samples must be entered in raw data sheet for Gummy must be entered into the log book as per Annexure-VII.
- Test shall be performed as per approved stability study protocol.
- Testing shall be performed as standard testing procedure and raw data shall be maintained by QC department.
- Stability sample shall be analyzed at specified interval. In both case +7 days deviation is allowed.
- The sample shall be kept at room temperature (NMT 25℃) if the analysis is not done within 7 days up to 30 days at room temperature.
- If there is any change in the STP, the next stations samples shall be analyzed by both the old and new methods and then the results of both the analysis shall be compared.
- If there is major difference in the impurity and dissolution profile then both methods shall be used till last station.
- The samples of the remaining stations shall be analyzed only by the new methods.
- If sample which are not analyzed within stipulated time then investigation shall be performed as per SOP.As per investigation further analysis shall be carried out.
EVALUATION OF STABILITY:
- After analysis QC Executive/QC Manager shall review and evaluate the results and raw data submit to QA.
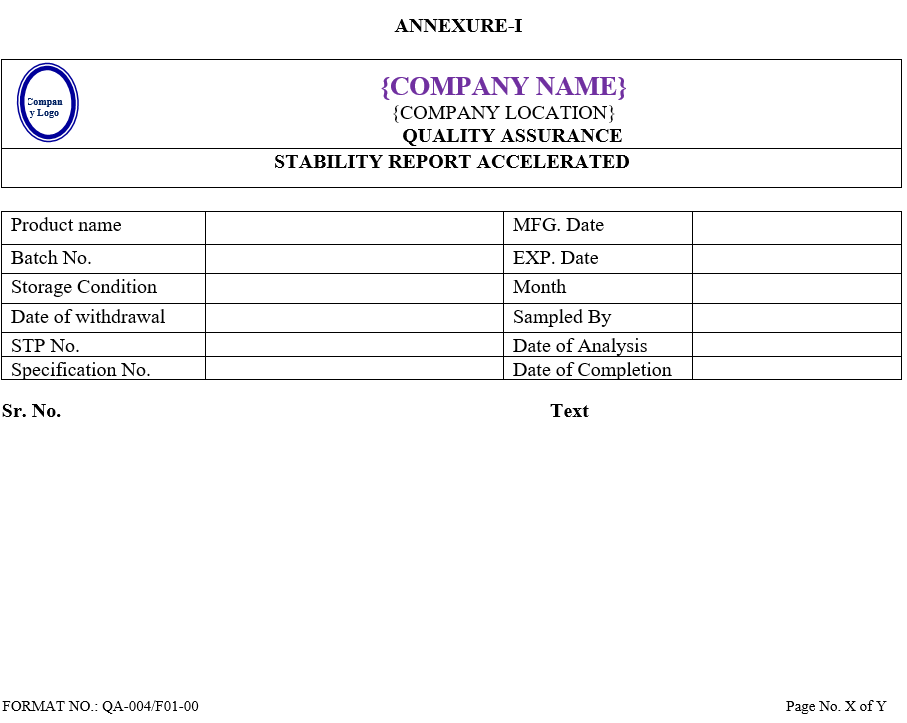
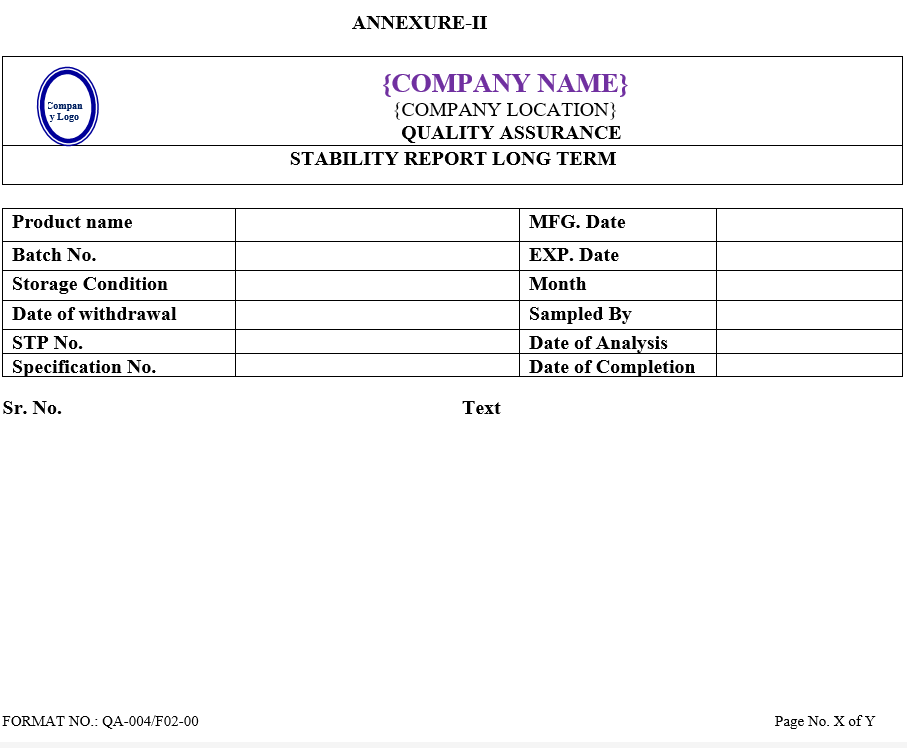
- After analysis QC Executive shall prepare summary sheet of observation found for Accelerated and long term stability studies as per Annexure-I & II, respectively and Annexure-IX in case product is failing in both studies.
- Any significant change or failure observed with respect to specification shall be communicated to Quality Assurance Head as per Annexure-IX.
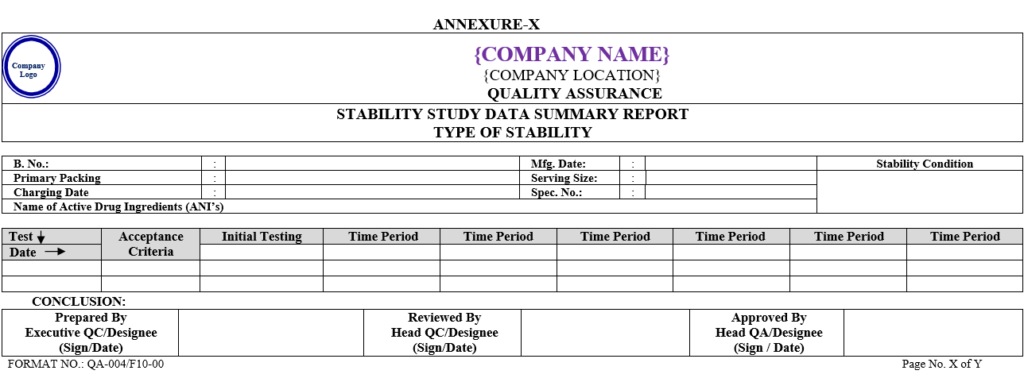
- After completion of stability study summary report shall be prepared as per Annexure-X By QC executive.
STABILITY FAILURE:
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
- Stability studies shall be discontinued if product fails in limits at any time station of long term stability study. If a product fails in accelerated stability study, then only long term stability shall be continued. This decision shall be taken by Head Quality Assurance as per current version of format number.
- If stability failure is reported for a batch under study, a batch trail shall be initiated for assessing the disposition of the affected batch
- QC-Executive/Designee shall perform investigation for the OOS against Pharmacopeia Specification. This investigation shall be as per the SOP on OOS.
- If product failing on accelerated as well as long term, stability study shall be performed at temperature 25°C ± 2°C and RH 60%± 5%.
- The product shall be recalled for disposal in case of stability failure within the labeled shelf life of the product as per respective SOP.
- SHELF LIFE / RETEST PERIOD ASSIGNMENT:
- Shelf life / Retest period shall be proposed on the following factor:
- Two year shelf life based on satisfactory performance of accelerated stability testing for 6 months.
- Long term stability data shall be used to confirm the shelf life assigned as above; or extended beyond 2 year based on actual data.
- Stability sample shall be disposed off after completion of Stability testing as per respective SOP.
- Before application all samples should be retested at 12 months or at the last time point before submission to regulatory authority.
- Matrixing and bracketing can be applied as per suitability of product, but not simultaneously.
- PRECAUTIONS DURING STABILITY STUDY:
- Ensure that the defined withdrawal schedule for individual product should not cross the lead-time of testing.
- Always confirm temperature and humidity conditions of respective stability (Accelerated & long term stability study) chamber.
- Ensure that the daily observations record of Temperature & Humidity is maintained.
- Ensure the calibrated stability chambers are used for charging of products.
- Ensure the usage of qualified working standard during stability testing.
STABILITY STUDY PROTOCOL
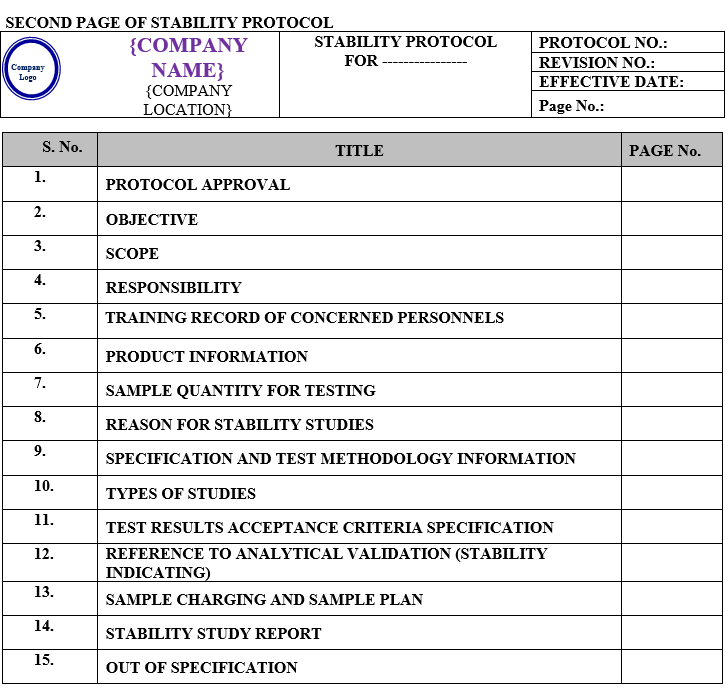
The stability study protocol shall contain following contents:
| Protocol approval |
| Objective |
| Scope |
| Responsibility |
| Training record of concerned personnel |
| Product information |
| Sample quantity for testing |
| Reason for stability study |
| Specification and test methodology information |
| Types of studies |
| Test results acceptance criteria specification |
| Reference to analytical validation (stability indicating) |
| Sample charging and sample plan |
| Stability study report |
| Out of specification |
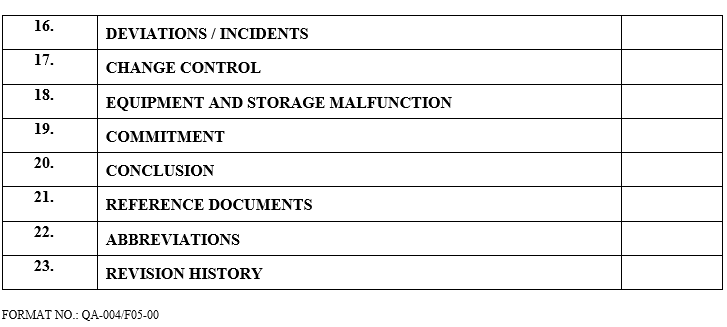
| Deviations / incidents |
| Change control |
| Equipment and storage malfunction |
| Commitment |
| Conclusion |
| Reference documents |
| Abbreviations |
| Revision History |
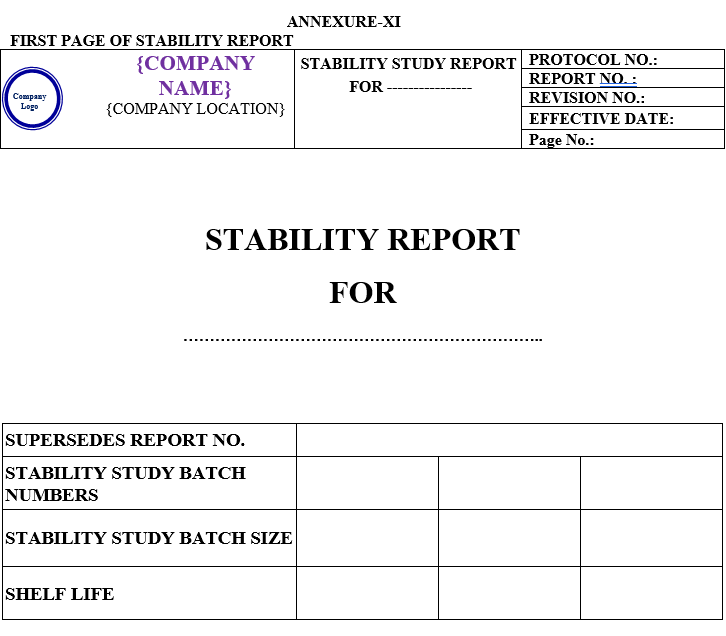
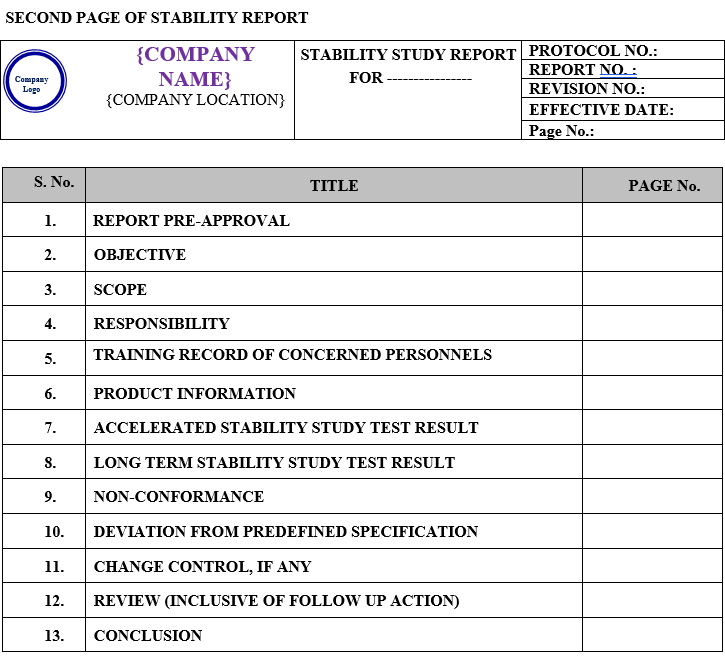
STABILITY STUDY REPORT:
Stability Study Report shall contain the following Contents:
| Report pre-approval |
| Objective |
| Scope |
| Responsibility |
| Training record of concerned personnel |
| Product information |
| Accelerated stability study test result |
| Long term stability study test result |
| Non conformance |
| Deviation from predefined specification |
| Change control, if any |
| Review (inclusive of follow up action) |
| Conclusion |
| Recommendation |
| Abbreviations |
| Report post approval |
| Revision History |
CLIMATIC ZONES FOR STABILITY STUDIES:
The climate is different in all the countries in the world. Stability study of the pharmaceutical drug should be done according to the climatic conditions of the country. According to the ICH Guidelines for stability studies, the climate of the world is divided into five different zones.
| Zone | Type of Climate |
| Zone I | Temperature Zone |
| Zone II | Mediterranean/Subtropical Zone |
| Zone III | Hot Dry Zone |
| Zone IVa | Hot Humid/Tropical Zone |
| Zone IVb | Hot Higher Humidity |
LONG TERM STABILITY TESTING CONDITIONS
| Zone I | 21℃±2℃ | 45% RH ± 5 % RH | 24 Months |
| Zone II | 25℃±2℃ | 60% RH ± 5 % RH | 24 Months |
| Zone III | 30℃±2℃ | 35% RH ± 5 % RH | 24 Months |
| Zone IVa | 30℃±2℃ | 65% RH ± 5 % RH | 24 Months |
| Zone IVb | 30℃±2℃ | 75% RH ± 5 % RH | 24 Months |
| Refrigerated | 5℃±3℃ | No Humidity | 24 Months |
| Frozen | -15℃±5℃ | No Humidity | 24 Months |
ACCELERATED AND INTERMEDIATE STABILITY TESTING CONDITIONS
| Accelerated Ambient | 40℃±2℃ | 75% RH ± 5 % RH | 6 Months |
| Accelerated Refrigerated | 25℃±2℃ | 60% RH ± 5 % RH | 6 Months |
| Accelerated Frozen | 5℃±2℃ | No Humidity | 6 Months |
| Intermediate | 30℃±2℃ | 65% RH ± 5 % RH | 6 Months |
REFERENCE:
ICH Guidelines Q1A (R2) & Q1B.
ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE | FORMAT No. |
| Annexure -I | Stability report accelerated | QA-004/F01-00 |
| Annexure- II | Stability report long term | QA-004/F02-00 |
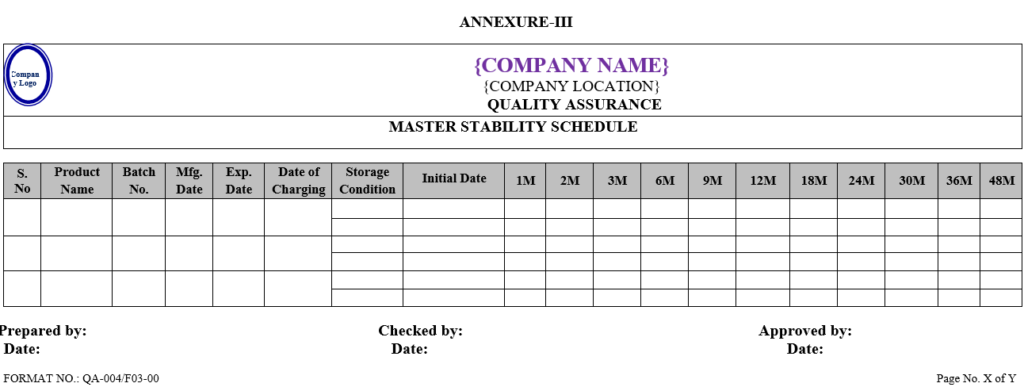
| Annexure -III | Master stability schedule | QA-004/F03-00 |
| Annexure -IV | Monthly stability schedule | QA-004/F04-00 |
| Annexure -V | Stability study protocol | QA-004/F05-00 |
| Annexure- VI | Stability request form | QA-004/F06-00 |
| Annexure -VII | Withdrawal record of sample from stability chamber | QA-004/F07-00 |
| Annexure -VIII | Stability sample record | QA-004/F08-00 |
| Annexure -IX | Stability report long term (if product is failing in both studies) | QA-004/F09-00 |
| Annexure-X | Stability Study Data Summary Report | QA-004/F10-00 |
| Annexure-XI | Stability study report | QA-004/F10-00 |
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No.01 : Head Quality Assurance
- Controlled Copy No.02 : Head Quality Control
- Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
ABBREVIATIONS:
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| QC | : | Quality Control |
| No. | : | Number |
| RH | : | Relative Humidity |
| OOS | : | Out of Specification |
REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be added manual |
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/
ANNEXURE-I
ANNEXURE-II
ANNEXURE-III
ANNEXURE-IV
ANNEXURE-V
ANNEXURE – VI
ANNEXURE – VII
ANNEXURE-VIII
ANNEXURE-IX
ANNEXURE-X
ANNEXURE-XI

Frequently Asked Questions ?
Q1: What is a stability study in the context of pharmaceuticals? A:
A stability study is a systematic process of assessing how the quality of a pharmaceutical product changes over time under the influence of various environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light. It helps determine the shelf life and storage conditions of a drug product.
Q2: Why are stability studies important in the pharmaceutical industry?
A: Stability studies are crucial to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. They help establish appropriate storage conditions, shelf life, and expiry dates. Regulatory authorities require stability data as part of the drug approval process.
Q3: What are the key environmental factors considered in stability studies?
A: The primary environmental factors are temperature, humidity, and light. These factors can impact the chemical and physical stability of pharmaceutical products. Other factors such as oxygen exposure and pH may also be considered based on the nature of the drug.
Q4: How is the shelf life of a pharmaceutical product determined?
A: Shelf life is determined by conducting accelerated and long-term stability studies. Accelerated studies use elevated temperatures to simulate the impact of time in a shorter period. Long-term studies are conducted under recommended storage conditions. The data from both studies are used to estimate the product’s shelf life.
Q5: What are the regulatory requirements for stability studies?
A: Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, provide guidelines on stability testing for pharmaceutical products. These guidelines detail the requirements for conducting stability studies, including study design, storage conditions, sampling, and testing frequency.
Q6: How often should stability samples be tested during a study?
A: The testing frequency varies based on the duration of the study. Typically, samples are tested at various time points, including 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months for long-term studies. Accelerated studies may involve more frequent testing, such as monthly intervals.
Q7: Can stability studies be outsourced to a contract laboratory?
A: Yes, pharmaceutical companies often outsource stability studies to contract testing laboratories. These laboratories specialize in conducting various tests, including stability testing, and may offer cost-effective and efficient services.
Q8: What is the role of packaging in stability studies?
A: Packaging plays a crucial role in protecting pharmaceutical products from environmental factors. Stability studies often include an assessment of the impact of different packaging materials on product stability.
Q9: How are stability-indicating methods used in stability studies?
A: Stability-indicating methods are analytical techniques that can detect changes in the drug substance or product over time. These methods are used to assess the stability of a pharmaceutical product and identify degradation products.
Q10: What actions should be taken if stability results indicate a problem?
A: If stability results indicate a problem, further investigations are conducted to identify the cause. Depending on the severity, corrective actions may include reformulation, adjusting storage conditions, or revising packaging. Regulatory agencies should be informed if significant issues arise.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document:
https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/conducting-of-stability-study/




