- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for corrective and preventive action.
- SCOPE:
This SOP is applicable to the identification and implementation of CAPA for deviations, incidents, OOS, and breakdowns at {Company Name}{Company Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- All department personnel should follow the instructions as per procedure.
- QA Sr. Executive-Review and technical correction of SOP
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
The QA Head shall be accountable for the implementation of SOP.
- PROCEDURE:
- The corrective action(s) and preventive action(s) shall be identified only through root cause analysis of:
- Deviations/Incidents
- OOS test results.
- Breakdowns.
- Market complaints and adverse findings and reactions
- Other non-conformances, if any
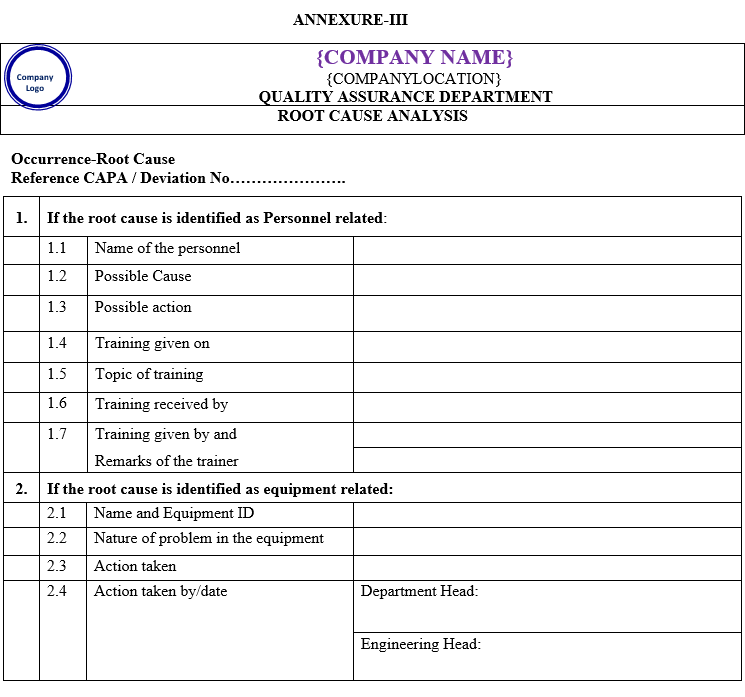
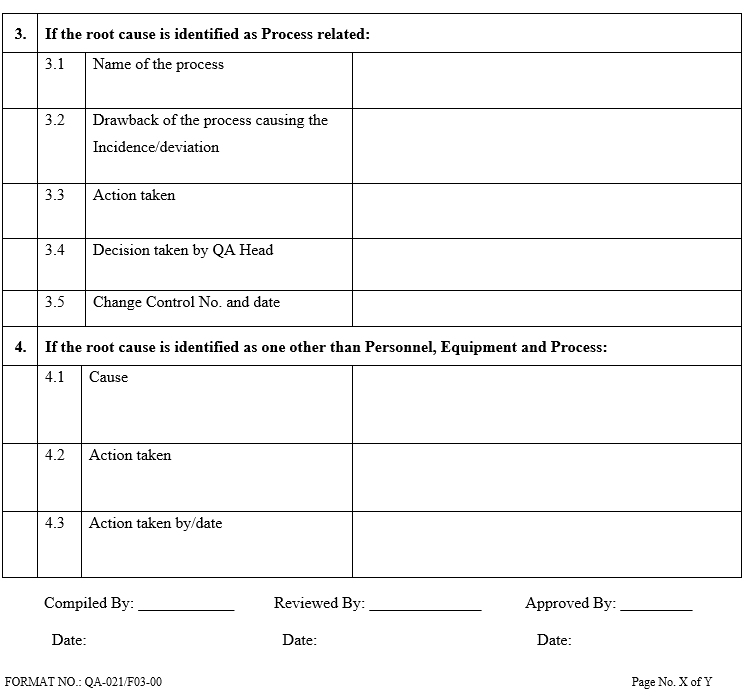
- The root-cause analysis for any of the above shall be performed by the investigation team of experts. For example, in the event of a laboratory-related deviation, the team shall consist of the QC manager, QC analyst or officer, and QA.
- The root cause analysis shall be performed using statistical quality control (SQC) tools, such as failure mode of effect analysis (FMEA).
- The root cause analysis shall require knowledge and expertise on the products, processes, equipment, SOPs, utilities, laboratory controls of testing, GMPs, regulatory and other systems.
Once the root cause(s) or most probable causes are identified, a record of root cause analysis and the SQC tool employed will be prepared. This shall have clear-cut conclusions with the signatures of the team members.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/
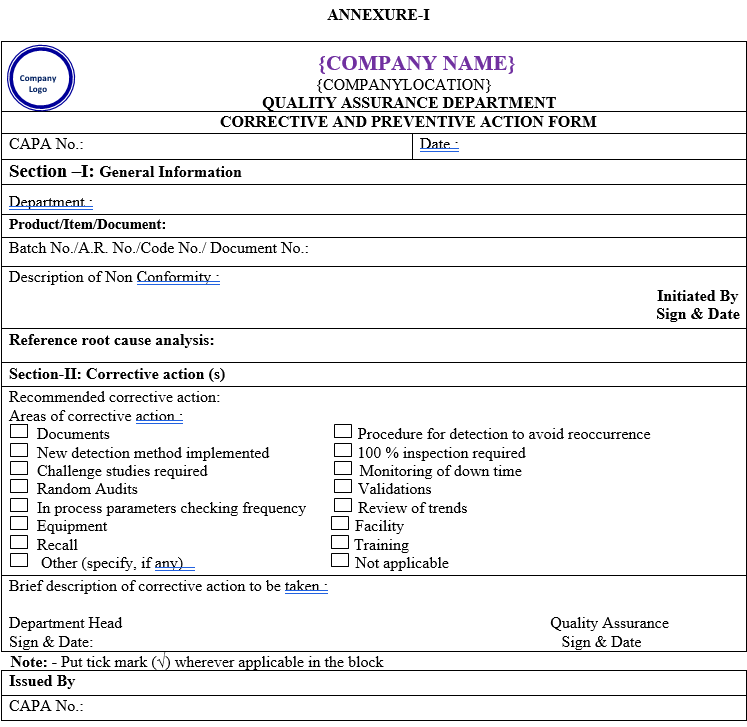
The corrective action and preventive action forms shall be filled out and initiated by the QA department as per Annexure-I.
The root cause analysis reference and the actual cause(s) shall be entered in the CAPA form.
The investigation team members shall then identify the corrective action (s) and preventive action (s) and record them in the CAPA form.
DEFINITION OF CORRECTIVE ACTION & PREVENTIVE ACTION:
- Corrective action: These are the steps that are taken to remove the cause of exhausting nonconformity or undesirable situation.
- Preventive action: These are the steps that are taken to eliminate the root cause of potential nonconformity or other undesirable situation.
IMPLEMENTATION OF CAPA:
The affected department shall be responsible to undertake the prescribed corrective action (s) and preventive action (s) in consultation with QA and other department experts.
The CAPA actions shall be completed within the target date agreed and recorded in the CAPA form.
The impact/risk of the corrective action (s) proposed shall be studied and recorded in the CAPA form.
Similarly, the impact/risk of the preventive action (s) proposed shall be studied and recorded in the CAPA form.
The implementation of CAPA shall be recorded by the department head and QA in section- IV of CAPA form by the department head.
The evaluation of CAPA implementation to adequacy shall be done by Quality Assurance and recorded in section-V of the CAPA form.
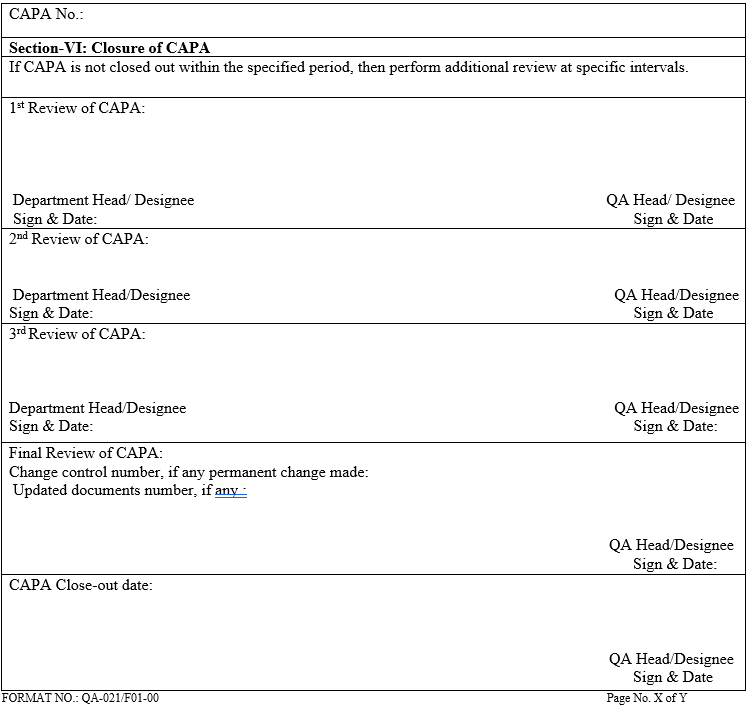
The final review of CAPA closure shall be done by QA and closed in section-VI and signed with date.
In case the closure is not done within the target date, then a second review or third review shall be done by QA.
The corrective actions generally shall include:
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/
- Immediate correction to the operation, activity, machine, so that the activity is completed.
- Removal of rejects/defectives if any generated due to the deviation/failure/breakdown/ OOS/complaint.
- Salvage of the situation and recovery process.
The preventive actions generally shall include:
- Training to the concerned personnel as well others who were not involved in the particular activity, batch, operation, process or time. This will help others to have awareness of the problem, its consequences on GMPs, product quality and productivity.
- Root cause analysis to determine actual causes/ factors and eliminate the causes/factors to prevent recurrence in future.
- Actual implementation, evaluation and confirmation of suitability of preventive action, so that other hidden problems do not arise.
If permanent change require then permanent change can be implemented as per the SOP for change control (SOP No. QA/017) and change control number to be written on the CAPA form.
A CAPA number shall be issued by QA department, the number of CAPA form shall be assigned as: ZZZ/CAPA/XX/YYY.
Where,
ZZZ – Indicates to the initial of company name
CAPA- Indicates to corrective action and preventive action
XX – Indicates to year i.e. 22, 23………
YYY- Indicates to serial No. starting from 001,002…….
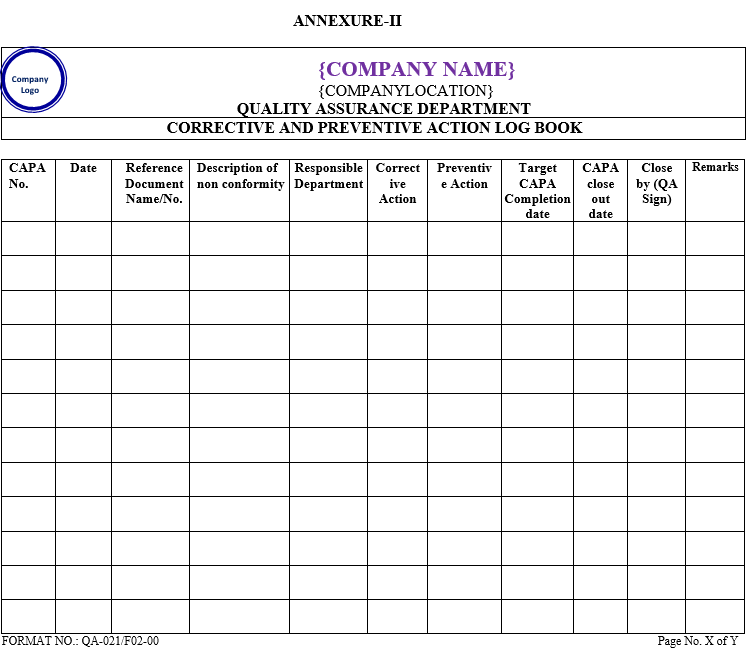
Log book of CAPA shall be maintained by QA officer/executive as per Annexure-II.
CLOSURE OF CAPA:
- After the post implementation evaluation of change implemented, QA Executive / designee shall do the closure of the CAPA.
- Ensuring results and supporting data.
- Completion of the required activities /documents identified during the evaluation and approval.
- Periodic quarterly review shall be performed by QA during March, June, September and December of each year to check for the closure of the CAPA Form, which is waiting for closure.
- All activities pertaining to the implementation of CAPA shall be completed with 180 working days from the date of approval of CAPA. If activity is not completed, then extension can be granted for maximum 90 days. Maximum 2 extensions can be taken. If after 2 extensions task is not closed, then based on justification of head QA CAPA can be reject or if further any extension is required then it can be approved for further extension.
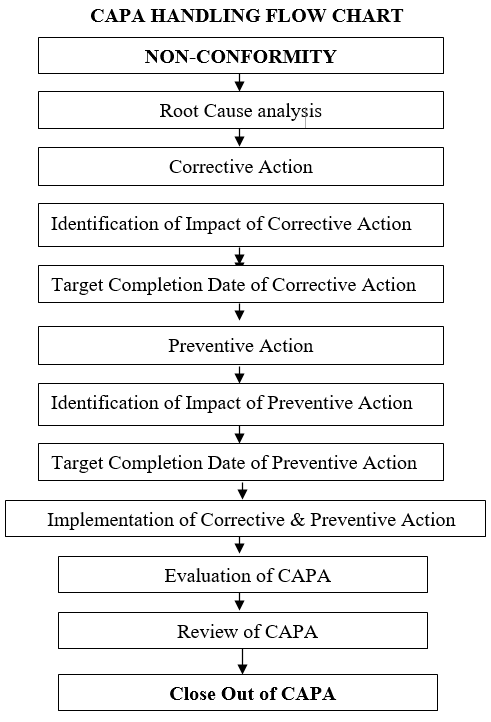
- Handling of CAPA shall be as per the following flow chart.
REFERENCE:
ICH Q10.
ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE | FORMAT No. |
| Annexure-I | Corrective & Preventive Action Form | QA-021/F01-00 |
| Annexure-II | Corrective & Preventive Action logbook | QA-021/F02-00 |
| Annexure-III | Root cause analysis | QA-021/F03-00 |
| Annexure-IV | Justification for delay | QA-021/F04-00 |
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No.01 : Head Quality Assurance
- Controlled Copy No.02 : Head Quality Control
- Controlled Copy No.03 : Head Production
- Controlled Copy No.04 : Head Engineering
- Controlled Copy No.05 : Head Warehouse
Master Copy : Quality Assurance Department
ABBREVIATIONS:
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| CAPA | : | Corrective & Preventive Action |
| cGMP | : | Current Good Manufacturing Practices |
| Ltd. | : | Limited |
| OOS | : | Out of specification |
| CEA | : | Cause of effect analysis |
| FMEA | : | Failure mode of effect analysis |
| ICH | : | International conference on harmonization |
| SQC | : | Statistical quality control |
REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be write manual |
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/
ANNEXURE-I


Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/
ANNEXURE-II
ANNEXURE-III
ANNEXURE – IV
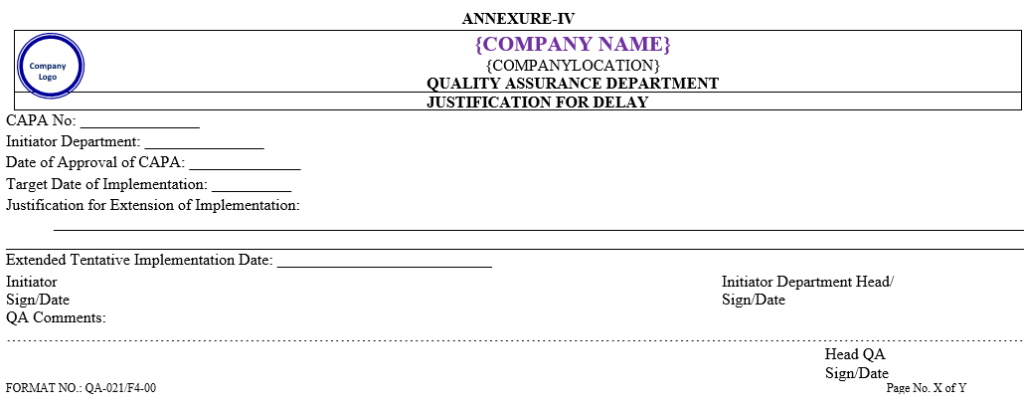
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/
Frequently Asked Question:
Question: What is CAPA?
Answer: CAPA stands for Corrective Action and Preventive Action, a system for analyzing, correcting, and preventing issues. It outlines procedures to solve the issue, it also analyzes the cause of the problem to prevent its recurrence.
Question: What Should Trigger CAPA?
Answer: Not every deviation or nonconformance requires a CAPA. An unnecessary CAPA can result in additional costs, processes slowdowns, and inefficient usage of the organization’s resources. It also becomes difficult for the team to follow up, resulting in an uncompleted pile of CAPA’s. Conversely, uncompleted CAPA’s can be a serious compliance problem. There are certain situations, that when they occur, can trigger a CAPA.
Question: Differences between Corrective and Preventive Actions?
Answer: The process used for corrective actions and preventive actions is very similar and the steps outlined in this document can be used for either. However, it is important to understand the differences and also be aware of the implications involved in performing and documenting each.
- Corrective Action:
- A corrective action is a reaction to a problem that has already occurred. It assumes that a nonconformance or problem exists and has been reported by either internal or external sources. The actions initiated are intended to: a) fix the problem and b) modify the quality system so that the process that caused it is monitored to prevent a reoccurrence. The documentation for a corrective action provides evidence that the problem was recognized, corrected, and proper controls installed to make sure that it does not happen again.
- To address the Corrective Action clause you should be identifying the root cause of non-conformances that have already taken place and implementing immediate corrective actions to contain the situation and long term corrective actions to prevent their re-occurrence.
2. Preventive Action:
A preventive action is initiated to stop a potential problem from occurring. It assumes that adequate monitoring and controls are in place in the quality system to assure that potential problems are identified and eliminated before they happen. If something in the quality system indicates that a possible problem is or may develop, a preventive action must be implemented to avert and then eliminate the potential situation. The documentation for a preventive action provides evidence that an effective quality system has been implemented that is able to anticipate, identify and eliminate potential problems.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/corrective-and-preventive-action-capa/