- PROCEDURE:
- Instrument Set Up:
- Setup the chromatographic System (GC) as per the respective operation SOP’s.
- Connect the respective column to chromatographic system.
- Ensure it is fixed properly.Depending up on the methodology, ensure fix HS-Syringe or Liquid injector Syringe.
- Ensure proper movement of pistons of syringe.Verify the condition of the septa at inlet of the system.
- If required replace the septa.Ensure respective gasses are connected with appropriate pressure as per SOP.
- Open the gas regulator of the required gases mentioned in respective STP/Approved procedure.
- Pre Conditioning:
- Pre condition the column at a temperature less than 50°C from the recommended maximum temperature by the column manufacturer (as mentioned on the original pack /certificate) for not less than 1hour.
- Setting of the Method:
- Analyst shall verify the availability of respective method set in the respective project of chromatographic data system and set the instrument.
- If method set is not available,
- Method set shall be prepared as per respective Standard Testing Procedure (STP) / Approved Method (as applicable).
- Method set (as applicable) shall be reviewed as per respective Standard Testing Procedure (STP) / Approved Method and it shall be Locked (wherever applicable).
- Preparation of Sample set (Sample Sequence):
- Sample set shall be prepared as per respective STP / SOP.
- Typically, the following sequence shall be followed while preparing the sample set;
a) Conditioning
b) Blank or Diluent
c) System Suitability / Standard solution
d) Sample solutions
e) Bracketing Standard / System suitability (as applicable).
- If any change to the above sequence shall be justified by the Analyst. The same shall be recorded in the work sheet.
- In sample set, enter Sample Name, Batch Number, Stability Condition / station, vial number, injection Vol (µL), # of Injections, Function, Run Time(Minutes), A.R. Number, Column ID, Level / amounts (as applicable), Next Inject Delay (minutes), any other details as per respective Operating SOP /STP and select corresponding Method Set.
- Print the Instrument method, method set and sample set. Sign with date, attach to first sample worksheet and submit to Reviewer I for review.
- Reviewer I shall review the Instrument method, method set and sample set as per respective standard test procedure / approved procedure, work sheets and sign with date.
- Any errors identified in the sample set during review shall be corrected with suitable comments (Sample set modified based on reviewer observations) in the Chromatographic Data system and same shall be saved.
- Conditioning:
- Run the sample set
- Condition the system with recommended gasses as mentioned below and monitor on the computer screen.
- In case of ‘Isothermal methods’, Conditioning shall be given for about 30 minutes or as per respective STP recommendations.
- In case of ‘Temperature Program methods’, Conditioning shall be given at least one run time.If the baseline is not satisfactory after conditioning as per the above alter sample set to include additional conditioning until satisfactory base line is achieved (i.e., free from unwanted noise and un-acceptable peaks / drift).
- Blank and / or Diluent injection:
- Inject blank and / or diluent as mentioned in the STP (if not inject one diluent).
- Blank and / or diluent chromatogram shall have stable base line.
- Blank or diluent chromatogram shall not be considerable if unacceptable drift / extraneous peaks were foundIf stable baseline is not achieved, alter the sample set, include additional blank or diluent injection, save the sample set with comments (Additional blank or diluent included to ensure elution pattern) and run the sample set.
- If unacceptable drift / extraneous peaks were found in blank and / or diluent injection even after giving additional Blank and / or diluent injection the section In-charge shall take appropriate action (such as verification of glass wool and liner condition) to achieve stable baseline.
- The details of the same shall be mentioned in the comments in Chromatographic Data System.
- Preparation of Analytical Solutions:
- Parallel prepare System Suitability and / or Standard / Sample Solutions as per respective standard test procedure / approved procedure and transfer into appropriate GC vials (Head space vials or Vials for liquid sample) and close / crimp the vials appropriately to ensure volatile solvents / gas does not escape from vials.
- All vials shall be identified with solution details (Numerical part of system number / Vial No. for example 001/1), and care shall be taken to ensure vials are positioned in correct place as per the sample sequence in system auto sampler.
- System Suitability and Sample analysis:
- Process the system suitability chromatogram with corresponding processing method.
- If the integration of the peaks is not satisfactory the analyst shall amend the processing method and saved with suitable comments.
- Verify the system suitability parameters as per respective STP.Continue the analysis if the system suitability solution meets the Acceptance criteria.
- Handling of System Suitability Failures:
- If system suitability parameters are not meeting the acceptance criteria; then the sample sequence shall be aborted with comments (System suitability not achieved) in CDS and initiate Process Non conformance as per the SOP.
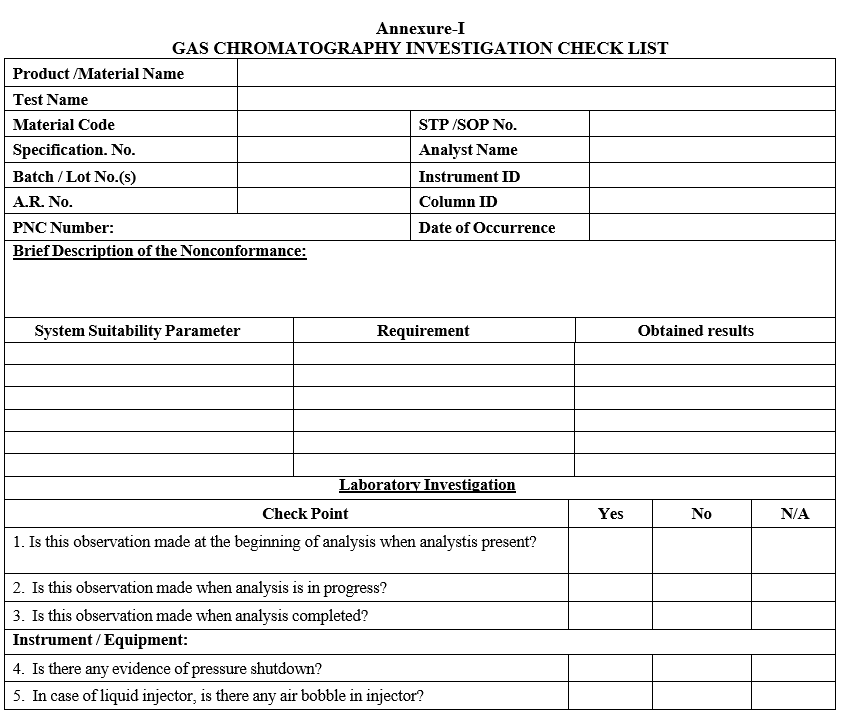
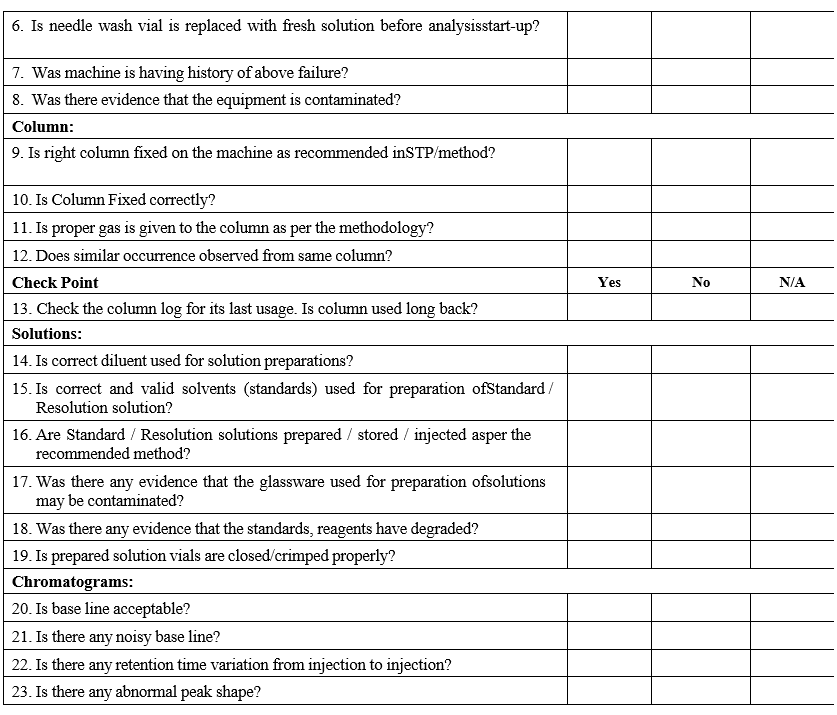
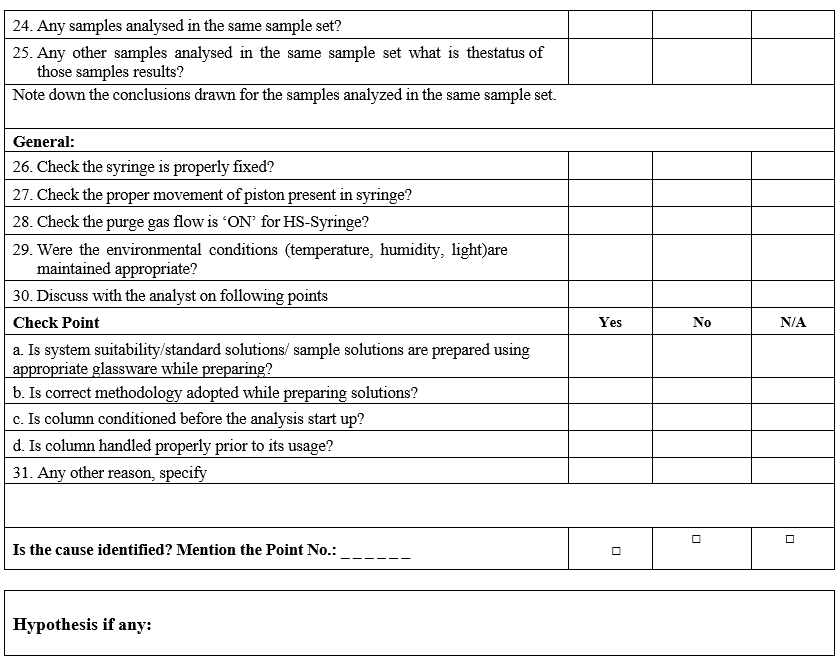
- Conduct the investigation as per GC Investigation check list.
- Follow the decision tree as defined in the GC Analysis Flow chart for further steps;
- If obvious error is identified, correct the error and continue the analysis with next version of sample set after establishing the system suitability.
- If obvious error is not identified, include additional conditioning and repeat the system suitability.
- If analyst is not available, analysis shall be continued by the second analyst.
- If solutions are having stability, use same solutions or else prepare fresh solutions and record all the details of fresh preparations in next copy of the same A.R. No. Worksheet.
- If system suitability parameters are not met even after additional conditioning; follow the guidance given below:
- Clean the jet / replace the glaswool / replace the septa / replace the syringe / change the diluent / condition the column as per the manufacturer’s recommendation followed by repeat analysis.
- If system suitability is not complying disregard the chromatographic data with comments.
- Based on the decision by the in charge QC /Designee, analysis shall be continued by using different GC or the different column (above all the steps shall be followed) while the investigation is continued.
- The QC in charge/Designee can follow appropriate actions based on the failure/incident.
- Wherever System suitability failures are observed after acquisition of samples, chromatograms shall be processed, printed and investigated as per Format-I.
- Handling of unexpected failures due to System:
- In case if sequence is interrupted after initiating the analysis due to any system failures, a Process Non Conformance shall be initiated.
- The following but not limited shall be considered for correcting the failures.
- System failure due to low Gas pressure or flame out:
- Ensure the required gas pressure is achieved; give condition to the column / system, followed by system suitability.
- Communication failures between system and CDS: Establish the communication between system and CDS, followed by system suitability and analysis.
- Handling of unexpected variations in Chromatographic run:
- In case if unexpected variations are occurred after initiating the analysis, a Process Non Conformance shall be initiated.
- The following are some of the unexpected variations and action to be considered.
- Retention Time variation / Shift.
- Unstable Base line / humps or drift or noise / Electronic spikes.
- Partially acquired Chromatograms.
- For all such above variations, the chromatograms shall be processed and the data shall be reported in work sheet.
- In case of liquid analysis:
- If solution stability exists, the same standard / sample solution from same GC vial shall be re-injected after establishing system suitability.
- In case of Headspace Liquid analysis:
- If solution stability exists, the retained standard / sample solution shall be filled in to GC Headspace vials and analysis shall be repeated after establishing system suitability.
- In case of Headspace analysis (Analysis of sample as such):
- Prepare samples from retained sample and repeat the analysis after establishing system suitability.
- The re-injected / repeated analysis results shall be compared with initial results. If results are comparable, initial chromatographic results shall be ‘DISREGARDED’ and re-injected / repeated analysis results shall be considered for reporting of results.
- If re-injected / repeated analysis results are not comparable with initial results, an investigation for the variation in the results shall be conducted and shall be concluded accordingly.
- During the analysis, if required to change the priority of analysis or to include any other sample, analyst shall ‘Alter the sample set’, save the sample set with appropriate comments. Printout of the altered sample set shall be reviewed by reviewer and run the sample set. Altered sample set shall be attached to the respective work sheet.
- In case if analysis is continued in the next shift, second analyst shall prepare new sample set starting with the next vial number of initial sample set. Sample set printout shall be reviewed by reviewer.
- Attach the printout of sample set to the respective work sheet.Whenever sample sequence is completed, to analyze any additional samples; If GC setup and column conditioning is not disturbed, analyst shall prepare new sample sequence starting with one bracketing standard followed by samples, Bracketing Standard / system suitability as applicable.
- In all such cases, the time gap between last bracketing standard of initial sample sequence and beginning bracketing standard of proceeding sequence shall not be more than 4 hours. Make sure the last bracketing standard injection is completed within the solution stability as recommended in STP.
- Processing and Reporting of Chromatograms:
- Verify the suitability of processing parameters used for processing of standard chromatograms.
- If system suitability parameters are not meeting the acceptance criteria; then the sample sequence shall be aborted with comments (System suitability not achieved) in CDS and initiate Process Non conformance as per the SOP.
- Conduct the investigation as per GC Investigation check list.
- Follow the decision tree as defined in the GC Analysis Flow chart for further steps:
- If obvious error is identified, correct the error and continue the analysis with next version of sample set after establishing the system suitability.
- If obvious error is not identified, include additional conditioning and repeat the system suitability.
- If analyst is not available, analysis shall be continued by the second analyst.
- If solutions are having stability, use same solutions or else prepare fresh solutions and record all the details of fresh preparations in next copy of the same A.R. No. Worksheet.
- If system suitability parameters are not met even after additional conditioning; follow the guidance given below.
- Clean the jet / replace the glaswool / replace the septa / replace the syringe / change the diluent / condition the column as per the manufacturer’s recommendation followed by repeat analysis.
- If system suitability is not complying disregard the chromatographic data with comments.
- Based on the decision by the in charge QC/Designee, analysis shall be continued by using different GC or the different column (above all the steps shall be followed) while the investigation is continued.
- The QC in charge/Designee can follow appropriate actions based on the failure/incident.
- All affected chromatograms shall be disregarded by stamping as “DISREGARD” with signature and indicating the reason for disregarding. Such chromatograms shall be attached along with report and same shall be verified by the reviewer.
- Report the data in work sheet
- In the absence of the acquired analyst, second analyst shall process the chromatograms and report the data in worksheet after transferring test from 1 st analyst to second analyst.
- Chromatographic data shall be reviewed as per respective SOP.
- Chromatographic data resulted into Out of Specification (OOS) shall be reviewed as soon as OOS results are observed by the analyst.
- Chromatographic data shall be reviewed within 2 working days from the date of reporting the data in the worksheet.
- Respective Logbook entries shall be made while performing the respective activity.
- After completion of analysis, column shall be conditioned as per procedure given above.
- Store the column as per the recommendations in the original pack.Complete the investigation (If any) with final conclusions and corrective actions in Format-I.
- QC In-charge / Manager shall review the investigation report, corrective actions taken, proposed preventive actions and submit the PNC to QA.
- Head-QA / Designee shall evaluate the final conclusions and approve the PNC.
- All chromatographic PNC’s shall be trend quarterly by QA to identify the recurring PNC’s.
- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE NO. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE |
| Annexure-I | Gas Chromatography Investigation Check List |
Annexure-I
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY INVESTIGATION CHECK LIST