- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down the procedure for the qualification of visual Inspection procedure.
- SCOPE:
This SOP is applicable for the qualification of visual Inspection at {Company Name} {Company Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- Technical Assistant – Performs visual inspection according to this SOP and documents findings.
- Executive – Ensures inspectors are trained and qualified for visual inspection.
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
Production Head
Head Quality Assurance
- PROCEDURE:
Visual inspection is a probabilistic process and the specific detection probability observed for a given product for visible particles that will vary with differences in Product formulation, Particle characteristics and Package design.
- INSPECTION PROCESS FLOW:
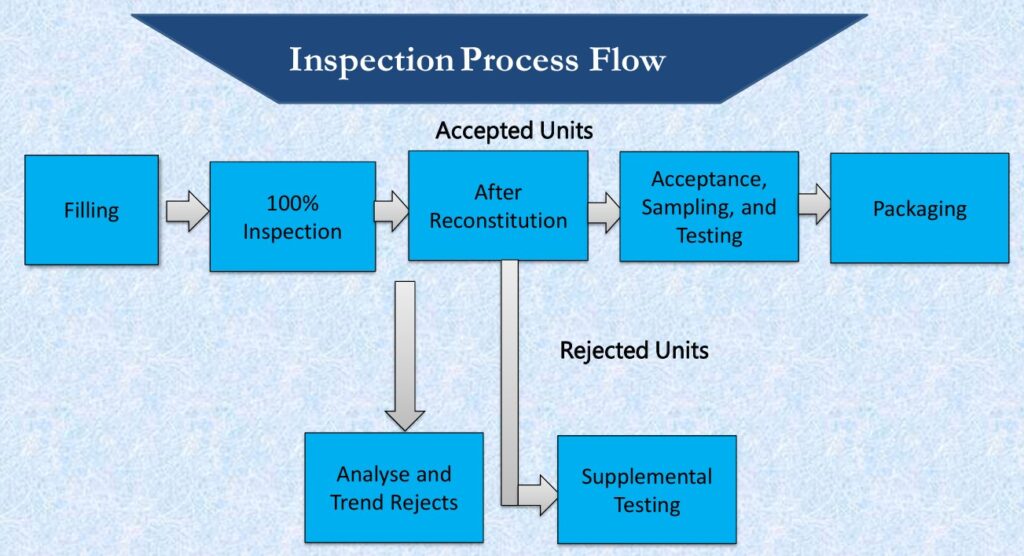
- TYPES OF DEFECTS:
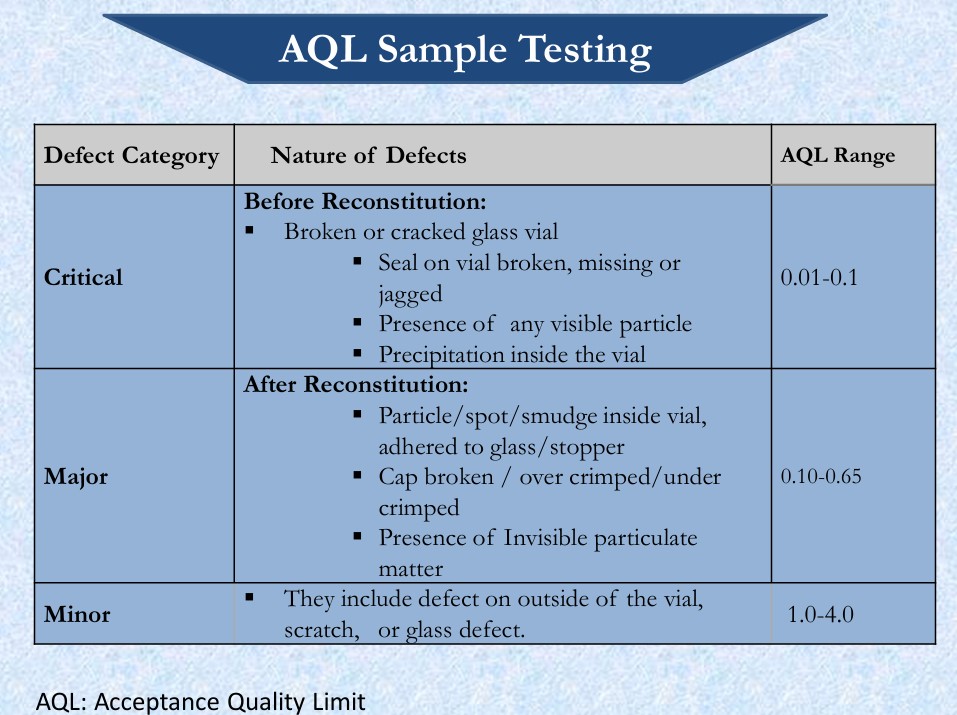
- Critical Defects: That cause serious adverse reaction or death of patients & any non conformity that compromise the integrity of container and thereby risks microbiological contamination of the sterile product.
- Major Defects: That carries the risk of a temporary impairment or medically reversible reaction, or involves a remote probability of a serious adverse reaction.
- Minor Defects: These defects do not impact product performance or compliance; they are often cosmetic in nature, affecting only product appearance or pharmaceutical elegance.
- CLASSIFICATION OF REJECTIONS
- As per USP40–NF35 Supplement I: Chapter1790 each unit (container, closure and its content) of Injectables product should be inspected as part of the routine manufacturing process.
- This inspection should take place at a point when and where defects are most easily detected (e.g. before printing).
- This inspection may be performed at-line or in-line with filling or packaging or in a separate, off-line inspection department.
- Defects are:
- Neck Problem
- Black/Surface/Solution Particle
- Twist Problem
- Less Volume, High Volume
- Extra Plastic
- Cavity No. and its Clarity
- Dirty Ampoule, Rough Surface
- Empty Ampoule, Deep Line
- AQL SAMPLE TESTING FOR PARENTERAL PRODUCT:
- For Small Volume Parenteral:
- Parenteral products should be essentially free from any visible particles” USP <1>, <790> <790>& <1790>.
- As per USP40–NF35 Supplement I: Chapter1790 each unit (container, closure and its content) of Injectables product should be inspected as part of the routine manufacturing process.
- This inspection should take place at a point when and where defects are most easily detected (e.g. before printing).
- This inspection may be performed at-line or in-line with filling or packaging or in a separate, off-line inspection department.
- Defects are:
- Neck Problem
- Black/Surface/Solution Particle
- Twist Problem
- Less Volume, High Volume
- Extra Plastic
- Cavity No. and its Clarity
- Dirty Ampoule, Rough Surface
- Empty Ampoule, Deep Line
- AQL SAMPLE TESTING FOR PARENTERAL PRODUCT:
- CRITICAL PROCESS PARAMETERS
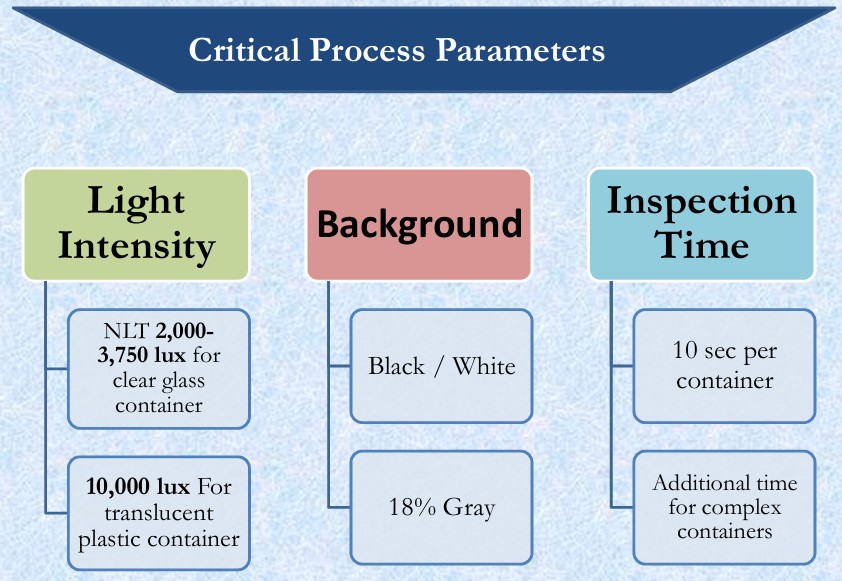
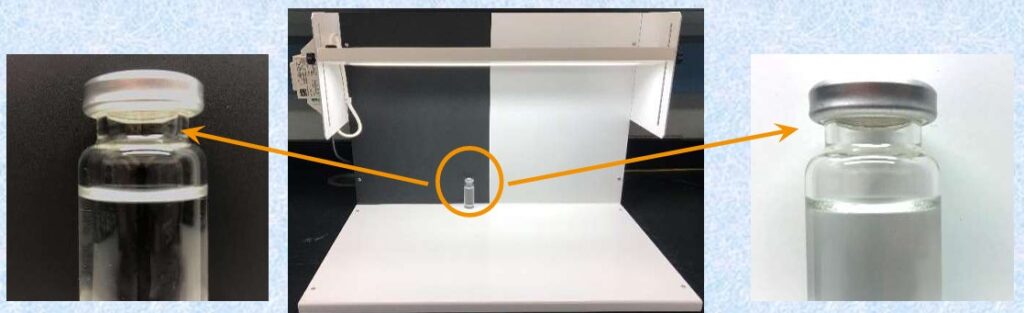
VISUAL INSPECTION APPARATUS FOR PARENTERAL PRODUCT:
- Vertical matte black panel.
- Vertical non-glare white panel next to black panel.
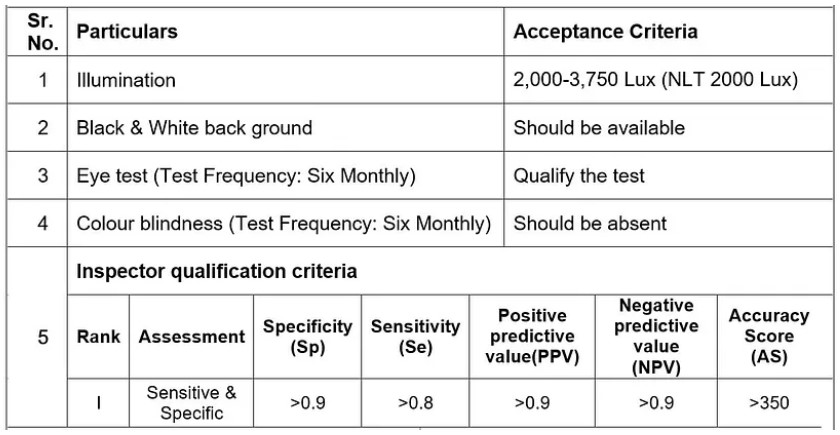
- Adjustable lamp holder with shaded, white light source and a diffuser (two 13W fluorescent tubes, each 525 mm (20.7 in) in length is suitable), illumination at the viewing point is between 2,000 and 3,750 lux for clear glass ampoules.
- Higher values are preferable for coloured glass and plastic containers.
- Sampling Plan of Vials For Reconstitution / Optical:
- Sample size code letters (Table 1 ISO2859-1)
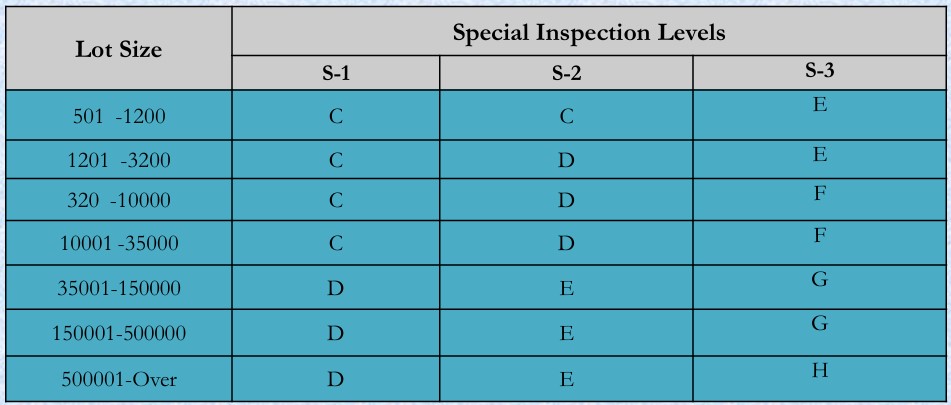
Note: In case of critical defects only S1 sampling plan is use; which means person should be able to inspect 100% defects. However, for major & minor defects we can shift towards S2&S3 inspection levels.
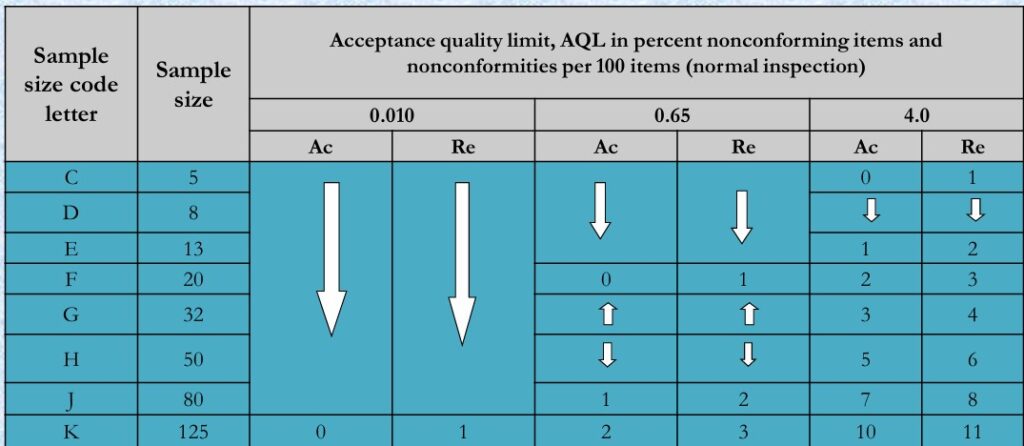
- Single Sampling Plans For Normal Inspection:
- Table 2A ISO-2859-1
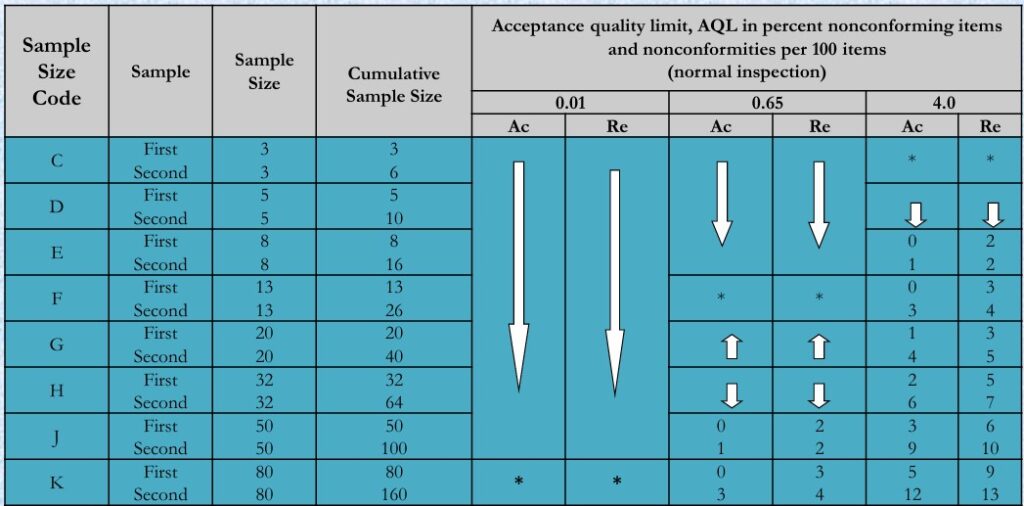
- Double Sampling Plans for Normal Inspection:
- Table 3A ISO2859-1
- Visual Inspection Trials
- Data For 10 Out Of 100 Vials
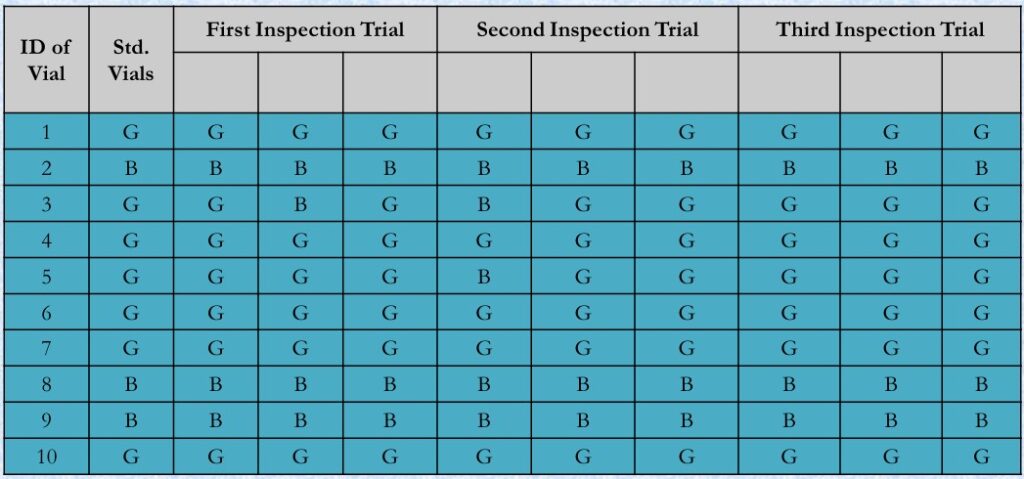
- AQL for general Product (Tablet & Liquid):
- Under normal inspection, AQL levels range from 0.065 to 6.5. The larger the AQL level, the more lenient the inspection.
- For general consumer products inspection, AQL level is usually set at 2.5, which implies a zero tolerance for critical defect, 2.5 for major defects, and 4 for minor defects.
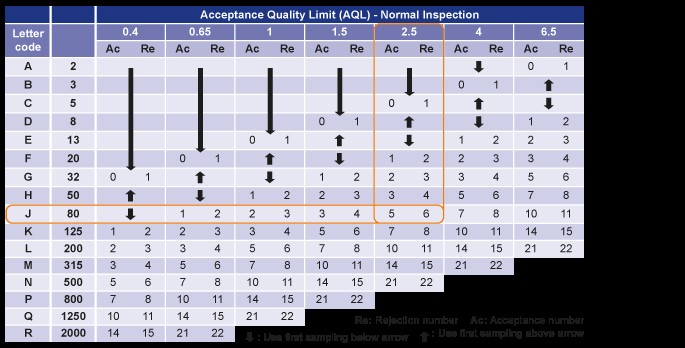
- With the inspection level and AQL level fixed, we can start using AQL for inspection. In the first AQL table, assuming the lot size is 1000 and the inspection level is GII, the letter code J is obtained.

- Moving to the second AQL table and using the letter code J, you will know that the sampling size of this batch of goods is 80 units. Assuming the AQL level is 2.5, the acceptance number is 5 and the rejection number is 6. In other words, the AQL suggests that you accept this batch of products if five or fewer defects are identified in the inspection, but to reject the batch if six or more defects are found.
- Determination of sampling plan:
- Critical Defects: 0,
- Major Defects: AQL2.5
- Minor Defects: AQL4.0
- For Oral Liquid section
- Foreign /Black particles, Fiber material in bottle.
- Sealing of caps.
- Cut or center out of Caps.
- Volume Variation.
- Deform shape etc.
- For Oral Solid Dosage Form section.
- Foreign product, foreign material.
- Tablet not in uniform size.
- Missing debossing.
- Abnormal discoloration of products.
- Large dark staining on product.
- Blooming, Bridging.
- Color Variation.
- Orange Peel/Roughness.
- Twinning
- Blushing
- Cracking/Splitting.
- Peel Off.
- Shade variation, Infilling.
- REQUALIFICATION CRITERIA
- Requalification of visual inspectors shall be done in case of following reasons:
- Any major type of rejection/abnormalities found incidentally.
- Any major change in visual inspection booth.
- Change in qualification procedure.
Frequency: Six Month ± one month (For Parenteral section).
Frequency: Yearly ± one month (For Oral Liquid and tablet section)
- DOCUMENTATION
Results and reports shall be compiled in a binder. Binder shall contain the following sequentially.
- Summary Report
- Requalification Protocol
- Test Reports and Certificates
Summary report shall be in narrative form, which describes the work as well as conclusion / certification regarding acceptability. Summary Report shall contain the following:
- Approval
- Objective
- Acceptance criteria
- Brief validation methodology
- Evaluation of results
- Final result summary
- Deviation, failure investigation reports and corrective actions (if any)
- Conclusion
- SUMARRY & CONCLUSION
- Based on the review of results a conclusion shall be drawn and documented in the summary report. Conclusion shall be a clear statement of compliance or non-compliance of the Visual Inspector Qualification with the acceptance criteria of the performance qualification protocol.
- Datasheet #1 Medical Checkup of Eye Record
Selection Criteria:
Character:
- The inspector should realize the importance of his task.
- The inspector should be able to perform respective work.
- Ability to learn and adapt new ideas.
- The inspector should have good observation skills and should also be patient
Prerequisites
- Pre-employment Health check.
- Pre-employment eye test– requirement > 90 % corrected
- All operators should have a near vision visual acuity/ colour blindness test prior to inspector training. The achievement of 14/14 acuity is required

- Training of Visual Inspectors:
- Training of relevant SOPs and Work-Instructions.
- Introduction to defects using training kits.
- Learning individual defects using training kits and defect libraries
- Requalification once a year
- Datasheet #2 Qualification Kit for Visual Inspection
- Quantity of Ampoules for Qualification: 100
- True Positive Ampoules: 20 Ampoules, True Negative Ampoules: 80 Ampoules
- Prepared By (Date/sign) Approved By (Date/sign)
- Datasheet #3 Visual inspection record document for SVP section VISUAL CONDITIONS:
- 2,000–3,750 Lux (NLT 2000 Lux) for coloured ampoules or plastic container.
- Black and white backgrounds.
- At least 10 seconds viewing against each background.
- TYPE OF REJECTIONS:
- Neck Problem
- Black/Solution/Surface Particle
- Twist Problem
- Rough Surface
- Less Volume
- Extra Plastic
- High Volume
- Cavity No. and its Clarity
- Dirty Ampoule
- Empty Ampoule
- Deep Line
- SELECTION OF VISUAL INSPECTOR:
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the eye medical checkup in order to assess visual acuity.
- Color blindness of each personnel shall be verified.
- Each trainee shall be followed by training programmed for visual inspections.
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the visual inspection kit in order to assess visual acuity.
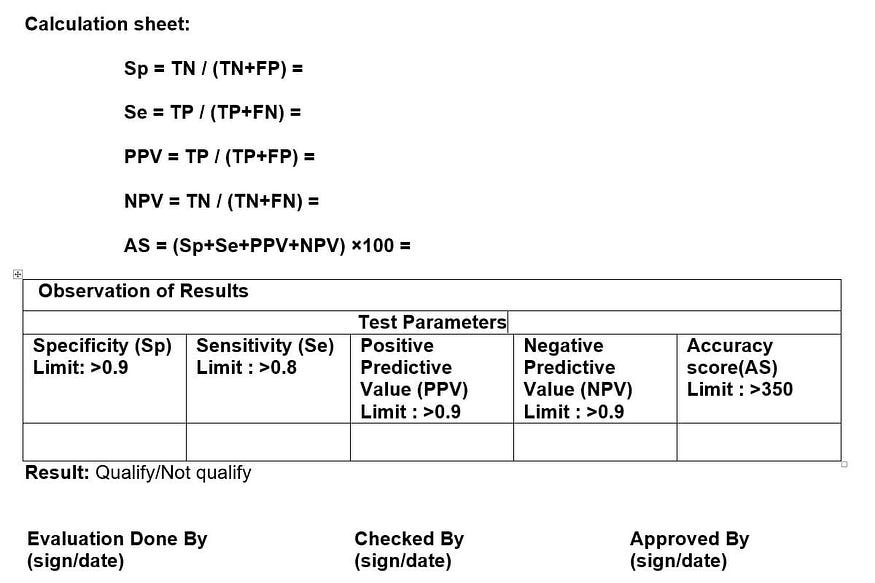
- CALCULATION OF RELIABILITY:
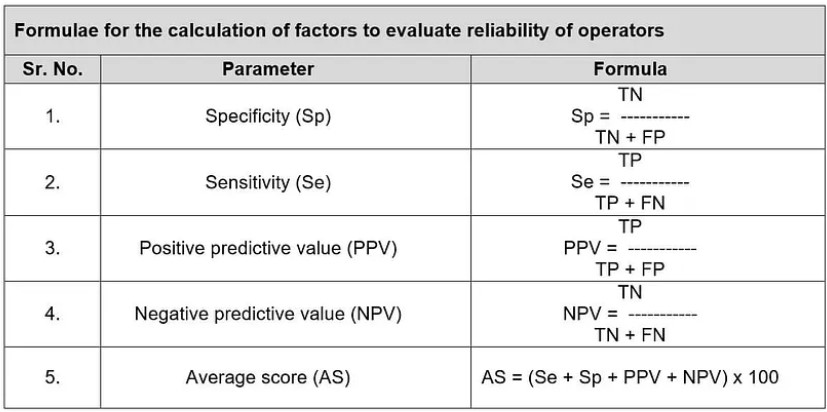
- Sensitivity (Se): representing the detection of non-conformity.
- Specificity (Sp): representing only the detection of conforming vials.
- Positive predictive value (PPV): being the probability that a detected non-
conformity is true. - Negative predictive value (NPV): being the probability that a conformity result is true.
- True Positive (TP): 20 Positive (Defective Ampoule) ampoule of the validation
- True Negative (TN): 80 Negative (good Ampoule) ampoule of the validation kit.
- False Positive (FP): Good Ampoule counted as defective by the visual.
- False Negative (FN): Defective Ampoule counted as good by the visual
- On the basis of these four factors (Sp, Se, PPV and NPV) evaluate the accuracy score of inspector.
- Inspectors who get the scores mentioned in above table will qualify the test and are able to do the visual inspection.
- In-process Quality Assurance person shall observe and verify the whole Qualification activity.
- ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA:
- PROCEDURE FOR VISUAL INSPECTION:
- Visual inspection of ampoules is carried out by trained employee/person under visual inspection booth. Ampoules are visually inspected for various kinds of possible abnormalities as define above. All visual inspector shall be qualified before induction in visual inspection as per following procedure:
- Preparation of ampoules for qualification:
- Select 20 positive and 80 negative ampoules. Negative and positive units were chosen from either from same batch or from different batches which covers all the types of rejection define above.
- Different qualification ampoules shall be prepared.
- A defects album shall be prepared and Training shall be performed to all selected Inspectors. All selected inspectors should be passed in eye test and colour blindness by using the above test samples and defects album.
- Qualification shall be performed by using the above test samples. Keep the entire (positive and negative) ampoules in box / crates for individual inspector.
- Gently swirl or invert each individual container, making sure that no air bubbles are introduced.
- Observe for 5 seconds in front of the white panel. Repeat in front of the black panel.
- Keep the rejected ampoules in different crates after visual Inspection.
- After completion of visual inspection of ampoules, stop the activity and inspect rejected ampoules and find out whether all the known rejection recovered during checking or not.
- If all the known rejected ampoules/vials, ampoules recovered/qualify the acceptance criteria during visual inspection that means that the visual inspector is fit for visual inspection process.
- Note: Put (√) if ampoules are good. Mention the code shown below for different type of defect.
- Evaluation Table
- Datasheet #4 Visual inspection record document for oral liquid dosage VISUAL CONDITIONS:
- NLT 1000 Lux.
- Black and white backgrounds.
- At least 5 seconds viewing against each background.
- TYPE OF REJECTIONS:
- Dent Problem
- Black/ White Particle
- Rough Surface
- Less Volume
- Extra Plastic
- High Volume
- Dirty Bottle
- Empty Bottle
- Deep Line/ Deep Scratch Over Bottle And Screw Cap.
- SELECTION OF VISUAL INSPECTOR-
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the eye medical checkup in order to assess visual acuity.
- Color blindness of each personnel shall be verified.
- Each trainee shall be followed by training programmed for visual inspections.
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the visual inspection kit in order to assess visual acuity.
- True Positive (TP): 20 Positive (Defective Bottle) ampoule of the validation
- True Negative (TN): 80 Negative (Good Bottle) ampoule of the validation kit.
- False Positive (FP): Good Bottle counted as defective by the visual
- False Negative (FN): Defective Bottle counted as good by the visual
- On the basis of these two factors (FP, FN) evaluate the accuracy score of inspector.
- Inspectors who get the scores mentioned in above table will qualify the test and are able to do the visual inspection.
- In-process Quality Assurance person shall observe and verify the whole Qualification activity.
- ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA PROCEDURE:
- Visual inspection of bottles is carried out by trained employee/person under visual inspection booth. Bottles are visually inspected for various kinds of possible abnormalities as define above. All visual inspector shall be qualified before induction in visual inspection as per following procedure:
- Preparation of bottles for qualification:
- Select 20 positive and 80 negative bottles. Negative and positive units were chosen from either from same batch or from different batches which covers all the types of rejection define above. Different qualification bottles shall be prepared.
- A defects album shall be prepared and Training shall be performed to all selected Inspectors. All selected inspectors should be passed in eye test and colour blindness by using the above test samples and defects album.
- Qualification shall be performed by using the above test samples. Keep the entire (positive and negative) bottles in box / crates for individual inspector.
- Gently swirl or invert each individual container, making sure that no air bubbles are introduced.
- Observe for 5 seconds in front of the white panel. Repeat in front of the black panel.
- Keep the rejected bottles in different crates after visual Inspection.
- After completion of visual inspection of bottles, stop the activity and inspect rejected bottles and find out whether all the known rejection recovered during checking or not.
- If all the known rejected bottles, ampoules recovered/qualify the acceptance criteria during visual inspection that means that the visual inspector is fit for visual inspection process.
- VISUAL INSPECTION RECORD Visual Inspector name
- Result: Qualified / Not qualified.
- Datasheet #5 Visual inspector’s record VISUAL CONDITIONS:
- CLASSIFICATION OF REJECTIONS:
- Critical
- Foreign product, foreign material.
- Tablet not in uniform size.
- Missing debossing.
- Abnormal discoloration of products.
- Large dark staining on product.
- Foreign product, foreign material.
- Wrong appearance.
- Tablet not in uniform size / Wrong punch shape.
- Abnormal / discoloration of products.
- Major
- Blooming, Bridging.
- Chipping.
- Color Variation/ Mottling.
- Cratering.
- Flaking.
- Orange Peel/Roughness.
- Splitting.
- Sticking.
- Twinning.
- Chipping or Minor breaking.
- Illegible de-bossing.
- Illegible embossing.
- Layer separation.
- Lamination.
- Cracking / Broken tablet.
- Double impression.
- Soft tablets.
- Picking.
- Sticking.
- Dark spot / Black spot / Color particles.
- Capping.
- Binding.
- Minor
- Blushing
- Cracking/Splitting.
- Peel Off.
- Pitting.
- Shade variation, Infilling.
- Mottling.
- Rough surface.
- Shade Variation.
- Shade variation.
- Dust on Tablet.
- De-bossing or score is not well defined.
- SELECTION OF VISUAL INSPECTOR-
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the eye medical checkup in order to assess visual acuity.
- Color blindness of each personnel shall be verified.
- Each trainee shall be followed by training programmed for visual inspections.
- All visual inspectors had to gone through the visual inspection kit in order to assess visual acuity.
- ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA: PROCEDURE:
- Visual inspection of tablets is carried out by trained employee/person on visual inspection table. Tablets are visually inspected for various kinds of possible abnormalities as define above. All visual inspector shall be qualified before induction in visual inspection as per following procedure:
- Preparation of tablets for qualification:
- Select 20 positive and 80 negative tablets.. Negative and positive units were chosen from either from same batch or from different batches which covers all the types of rejection define above. Different qualification tablets shall be prepared.
- A defects album shall be prepared and Training shall be performed to all selected Inspectors. All selected inspectors should be passed in eye test and colour blindness by using the above test samples and defects album.
- Qualification shall be performed by using the above test samples. Keep the entire (positive and negative) tablets in box / crates for individual inspector.
- Keep the rejected tablets in rejection box after visual Inspection.
- After completion of visual inspection of tablets, stop the activity and inspect rejected tablets and find out whether all the known rejection recovered during checking or not.
- If all the known rejected tablets, tablets recovered/qualify the acceptance criteria during visual inspection that means that the visual inspector is fit for visual inspection process.