- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for standard operating procedure for investigation.
- SCOPE:
This procedure shall be applicable for performing the investigation and root cause analysis for non conformances observed at {Company Name}{Company Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- Personnel of concerned department, who is encountered with incident / deviation / complaint that are related to the quality, efficacy and safety of product, shall be responsible to report the same and take part in the investigation.
- Initiator Department Head & designated person in QA shall nominate the investigation team for carrying out the investigation to detect the root cause / probable root cause of the non conformance and preparation of investigation report.
- Initiator Department Head shall be responsible for the review of investigation of the root cause analysis for non conformances, review of reports and CAPA.
- QA Head shall be responsible for review and approval of investigation report and approving the CAPA thereafter.
- Plant Head/ GM Technical shall be responsible to provide the resources and review of investigation.
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
QA Head shall be accountable for implementation of SOP.
- PROCEDURE:
- DEFINITIONS :
- Non conformances: The non fulfillment of a specified requirement. Examples of non conformances are incidents, deviation, Product complaints, audit observations (Internal & External), Product Recall.
- Cause Analysis: This action requires the question “Why did it go wrong?” to be asked instead of just “What has gone wrong?”
- Risk Assessment: A systematic process of organizing information to support a risk decision to be made within a risk management process. It consists of the identification of hazards, analysis and evaluation of risks associated with exposure to those hazards.
- Root Cause: This section shall be used to find out the assignable cause for the situation arised.
- Impact Analysis: This section shall be used to list the impact of the preventive actions proposed.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
- Investigation shall be performed for non conformances like deviation, incident, complaints, product recall, and audit observations etc:
- OOS/OOT investigation shall be performed as per SOP and in certain specified/identified cases corresponding SOP shall be applicable following recommendation by the QA Head or his designee.
- Initiator Department Head & designated person in QA shall nominate the investigation team for carrying the investigation to detect the root cause of the non conformance. Investigation team shall be cross functional on basis of nature of problem identified.
- For an effective investigation of non conformances following steps shall be followed:
- The problem shall be defined for which the investigation is required.
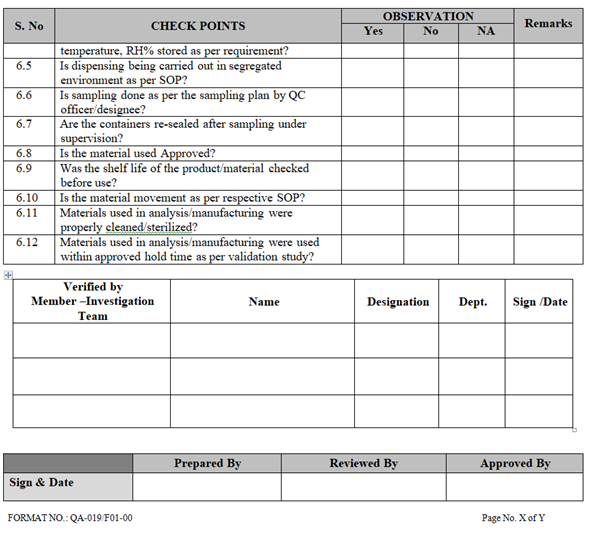
- Collect all the information / evidence related to the problem. Wherever applicable use the check list for investigation as per Annexure-I.
- The investigation process shall follow a clearly defined procedure to identify the true cause associated with the problem.
- If we are to evaluate the many so-called root cause analysis method.
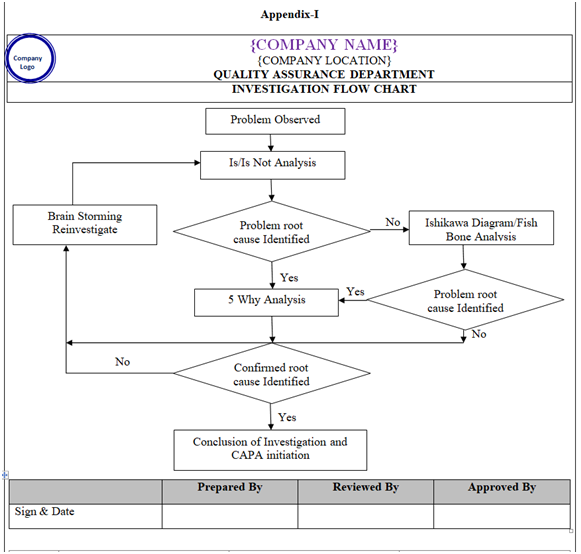
- Appropriate tool like is- Is Not Diagram, Why –Why Analysis, Fish–Bone analysis (Ishikawa Diagram), Brain Storming to be used for investigation as applicable (Refer Appendix-I).
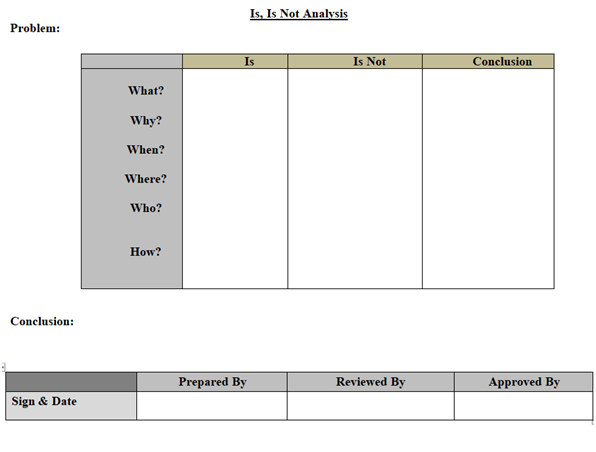
- Is /Is Not Diagram: Is – Is not diagram includes any tool that shows the four steps of the comparative analysis process. An example of an Is-Is Not Diagram is the spec and work sheet. This tool takes the four steps and structures them into the workable format for capturing data and information for a problem/Event. (Refer appendix-1).
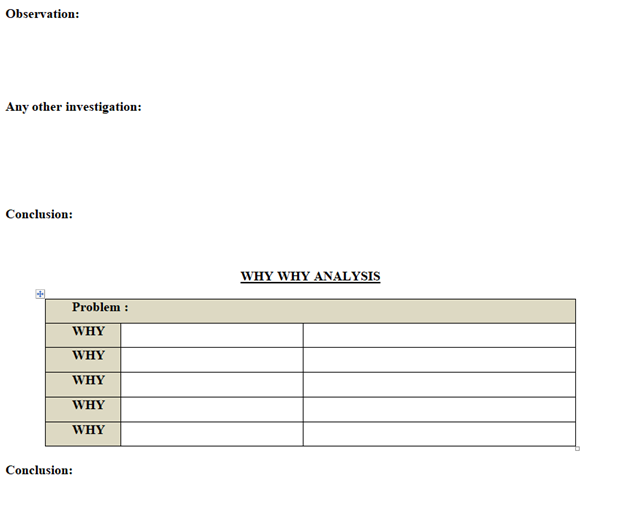
- Why- Why Analysis – One of many brainstorming method also known as the “five Whys” method. This is the most simplest root cause analysis process and involves repeatedly asking “why” at least five times or until you can no longer answer the question .Five is an arbitrary figure .The theory is that after asking “Why” five times we shall probably arrive at root cause .The root cause shall identified when asking “why” does not provide any more useful information .This method produces a linear set of casual relationships and uses the experience of the problem owner to determine the root cause and corresponding solution. (Refer appendix-1).
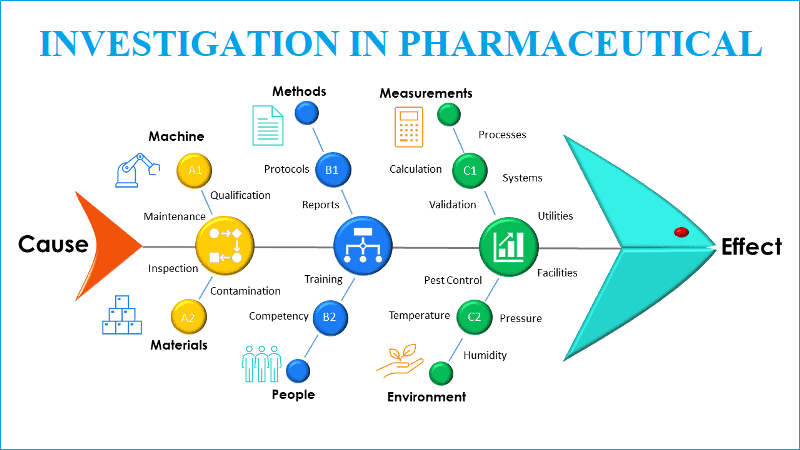
- Fish Bone Diagram (Cause and Effect Diagram): (Refer appendix-1)
- Man: This category takes in to consideration the human element that may affect the problem. It considers the people that touch the process.
- If the person s involved in activity is not trained.
- If new person involved in activity.
- If person is competent for the activity.
- Relevant experience of the concern personnel.
- Material: This category takes into the consideration the substances out of which the product can be made. It considers all material that touches the process.
- If material is not appropriate.
- Any change in vendor
- Vendor is not qualified
- Change in specification / grade or material
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
- Machine: This category takes in to the consideration the equipment used that may affect the problem. It considers the equipment that touches the product, process and system.
- If periodic Preventive maintenance of machine not done.
- If any breakdown has occurred during process.
- If machine Qualification/ Requalification done.
- If instrument /Equipment showing actual reading.
- If machine setting done between the activity.
- Method: This category takes in to the consideration the method/ process that may affect the problem
- If batch processed as per written instructions mentioned in Batch Manufacturing record.
- If any change in machine process and product parameter.
- Measurement: This category takes in to the consideration measurement that may affect the problem. Measurement considers the measurements used for the product, process system.
- Calibration of equipment/Instruments.
- Mother Nature / Environment: This category takes in to the consideration the Environmental factors that may affect the problem. It considers the environmental factor that touches the process.
- Fish Bone Diagram (Cause and Effect Diagram):
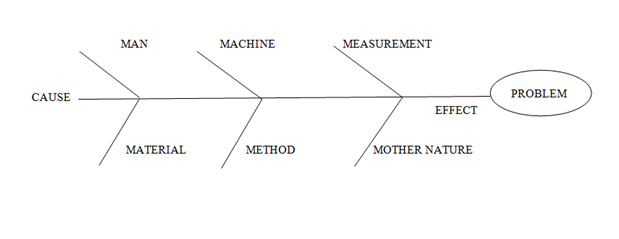
Investigate with sufficient depth so as to identify the root cause / probable root cause. The examples of possible causes are given below:
- Personnel not adequately trained
- Procedures inadequate
- Personnel trained but did not follow standard operating procedure (trained but forgot, working too fast, took shortcuts and used wrong procedures)
- Equipment used not qualified
- Area cleaning / equipments cleaning not adequate
- Error in environmental monitoring
- Error in Preventive Maintenance
- Error in calibration
Investigation shall be done by review of concerned documents i.e. BMR, BPR, logbooks, relevant SOP’s, analytical data, raw data, stability data, preventive and breakdown maintenance data, calibration records, validation reports and any other relevant documents shall be reviewed to collect maximum possible and relevant data.
If required necessary interrogation shall be done up to doer/performer level to find out the route cause.
After going through all relevant documents and data collected through the discussions with relevant personnel, Investigation team will suggest the next step such as resampling, retesting, extra testing and any other measure required (wherever applicable) to complete the investigation. However, any Resampling, retesting or extra testing required shall be approved by Head QA.
Based upon investigation outcome, team shall identify the root cause of the non conformance.
After identification of root cause of the problem Impact/Risk assessment shall be performed, wherever applicable.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
Designated person from QA shall confirm the authenticity and completeness of the data and analyze the data to identify potential product and quality problems for which corrective action and preventive actions are required.
CAPA shall be decided based on scientific and logical justifications to prevent future reoccurrence of the similar problem.
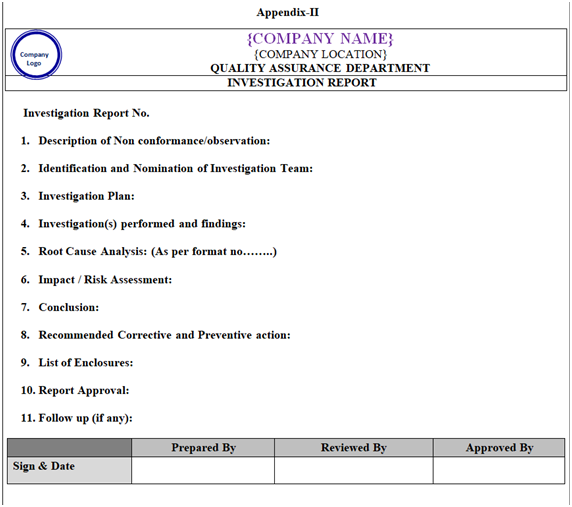
Investigation report shall be prepared by following the template mentioned in Appendix-II.
After completion of investigation of all possible / probable causes, the team / designee shall prepare a final Investigation report within 30 days from date of initiation of investigation.
CAPA shall be handled as a part of source documents, wherever applicable.
Investigation report should be completed within 30 working days.
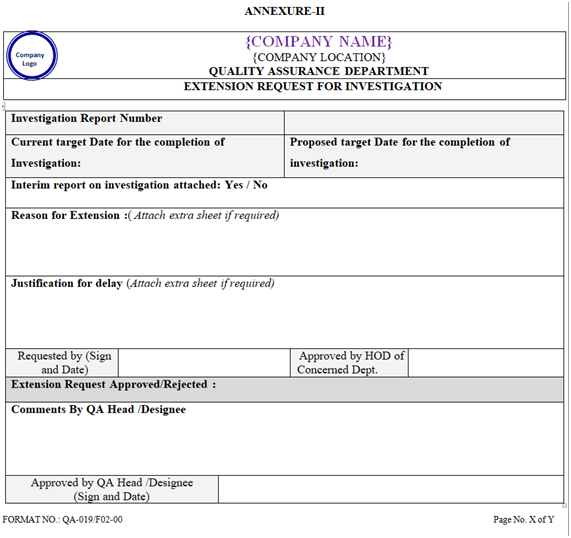
If the investigation followed by report preparation is not completed within 30 working days, then extension can be granted for maximum 30 days. Maximum 2 extensions can be taken as per Annexure-II.
The approved comprehensive Investigation report shall be enclosed to its reference source documents.
- REFERENCES:
Not Applicable.
- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE/APPENDIX | FORMAT No. |
| Annexure-I | Check List for Investigation | QA-019/F01-00 |
| Annexure-II | Extension Request for Investigation | QA-019/F02-00 |
| Appendix-I | Investigation Flow Chart | NA |
| Appendix-II | Template for Investigation Report | NA |
| Appendix-III | Investigation Tools | NA |
ENCLOSURES: SOP Training Record.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
DISTRIBUTION:
| Controlled Copy No. 01 | : | Head Quality Assurance |
| Controlled Copy No. 02 | : | Head Quality Control |
| Controlled Copy No. 03 | : | Head Production |
| Controlled Copy No. 04 | : | Head Engineering |
| Controlled Copy No. 05 | : | Head Warehouse |
| Controlled Copy No. 06 | : | Head Human Resources |
| Master Copy | : | Quality Assurance Department |
ABBREVIATIONS:
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| cGMP | : | Current Good Manufacturing Practices |
| OOS | : | Out of specification |
| CAPA | : | Corrective actions & preventive actions |
| OOT | : | Out of Trend |
| NA | : | Not Applicable |
REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be enter manual |
ANNEXURE-I
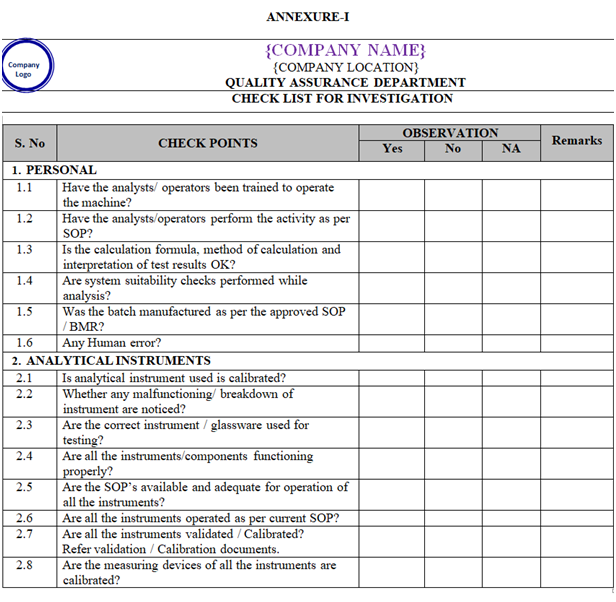
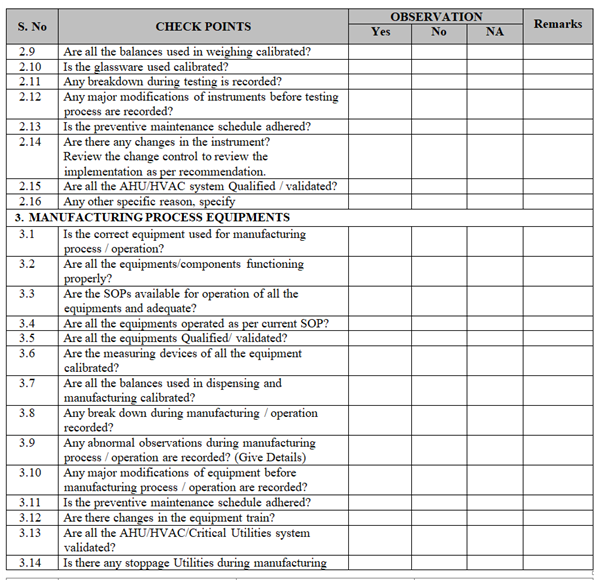
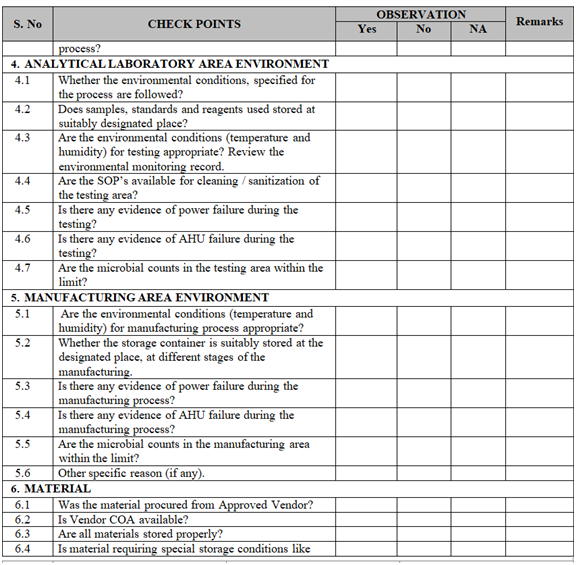
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
ANNEXURE II
APPENDIX – I
APPENDIX -II
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/
APPENDIX -III



Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/sop-for-investigation/





Thank you for wonderful website.