Objective:
To lay down standard Testing procedure for microbial contamination in nonsterile products by membrane Filtration method, Pour plate method & Surface-spread method.
Applicability / Scope:
This STP is applicable to the Microbiology Section of {Company Name} {Location}.
RESPONSIBILITY:
It is the responsibility of the Jr. Microbiologist / Microbiologist/ Senior Microbiologist to follow this STP and Technical Manager / Quality Manager shall ensure implementation.
It is the responsibility of the Jr. Microbiologist / Microbiologist/ Senior Microbiologist to follow this STP and Technical Manager / Quality Manager shall ensure implementation.
PROCEDURE:
Principle:
The microbial limit test (MLT) is performed to assess how many and which of certain viable microorganisms are present in non-sterile pharmaceutical, healthcare or cosmetics manufacturing products that range from raw materials to finished products.
Requirements:
Equipment:
- Weigh Balance
- pH Meter
- Autoclave
- Water bath
- Laminar Air Flow
- Biosafety Cabinet
- Micropipette
- Incubator
- BOD Incubator
- Colony Counter
- Microscope
Glassware/Accessories:
- Conical Flask / bottle
- Conical Flask / bottle
- Test Tube- 25ml
- Micropipette tips
- Loop
- Glass Beaker
- Petri Plate- 90mm
Media:
- Buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution pH 7.0
- Casein soyabean digest broth
- Casein soyabean digest agar
- Sabouraud dextrose agar
- Enterobacteria enrichment broth-Mossel
- Violet red bile glucose agar
- MacConkey broth
- MacConkey agar
- Rappaport Vassiliadis Salmonella Enrichment broth
- Wilson and Blair’s BBS Agar
- GN Broth
- Xylose-Lysine-Deoxycholate agar
- Cetrimide agar
- Mannitol Salt Agar Medium
- Reinforced medium for Clostridia
- Columbia agar
Procedure / Methodology:
Total Aerobic Microbial Count–
Pre-treatment of Sample: Use suitable alternative method if following methods are not applicable.-
Water-soluble products: Dissolve 10 g or dilute 10 ml of the preparation under examination, unless otherwise specified, in buffered sodium chloride peptone solution pH 7.0/SCDM or any other suitable medium shown to have no antimicrobial activity under the conditions of the test and adjust the volume to 100 ml with the same. If necessary, adjust the pH to about 7.0. If required, further dilutions are prepared with the same diluent.
Products insoluble in water (non-fatty): Suspend 10 g or 10 ml of the preparation under examination, unless otherwise specified, in buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution pH 7.0 or any other suitable medium shown to have no antimicrobial activity under the conditions of the test and adjust the volume to 100 ml with the same. If necessary, divide the preparation under examination and homogenize mechanically. A suitable surface active agent such as 0.1 per cent w/v solution of polysorbate 80may be added to assist the suspension of poorly wet table substances. If necessary, adjust the pH of the suspension to about 7. If required, further dilutions are prepared with the same diluent.
Fatty products: Homogenize 10 g or 10 ml of the preparation under examination in isopropyl myristateor unless otherwise specified, with 5 g of sterile polysorbate 20or polysorbate 80. If necessary, heat to not more than 40º. Mix carefully while maintaining the temperature in water bath. Add 85 ml of buffered sodium chloride peptone solution pH 7.0or any other suitable medium which does not have any antimicrobial activity under the conditions of the test, heated to not more than 40º, if necessary. Maintain this temperature for the shortest time necessary for formation of an emulsion and in any case for not more than 30 minutes. If necessary, adjust the pH to about 7.0. Further dilutions may be prepared using the same diluent containing a suitable concentration of sterile polysorbate 80.
Fluids or solids in aerosol form: In sterile conditions, transfer the product into a membrane filter apparatus or to a sterile container for further sampling. Use either the total contents or a defined number of metered doses from each of the containers tested.
Transdermal patches: Remove the protective cover sheets ‘release liners’ of transdermal patches using sterile forceps and place them adhesive side upwards, on sterile glass or plastic trays. Cover the adhesive surface with sterile gauze and transfer them to a suitable volume of buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution pH 7.0 containing in activator such as polysorbate 80or lecithin. Shake the preparation vigorously for at least 30 minutes.
Enumeration: Determine the total aerobic microbial count in the extract being examined by any of the following methods.-
Membrane filtration:
Prepare the sample using the method as described above.
Transfer appropriate amount to each of the two membrane filters and filter immediately.
Wash each filter following the procedure found to be suitable. For determination of total aerobic microbial count transfer one of the membrane filters to Casein soyabean digest agar (Medium 2). Incubate the plate at 30º to 35ºC for 3 to 5 days.
For total yeast and mould count transfer the other membrane to the surface of Sabouraud dextrose agar with antibiotic (Medium 3) and incubate at 20ºC to 25ºC for 5 to 7 days.
Calculate the number of CFU per g or per ml of the product.
Plate count method:
To a 90 mm diameter Petri dish add 1 ml of the sample prepared as described above
Pour 15 ml of Casein soyabean digest agar and Sabouraud dextrose agar.
Use at least two Petri dishes for each of the test organisms.
Incubate the plates of Casein soyabean digest agar at 30º to 35º for 3 to 5 days.
Similarly incubate the plates of Sabouraud dextrose agar with antibiotic at 20º to25º for 5 days.
Calculate the mean count on each medium and from that calculate the number of CFU.
Surface-spread method:
Using Petri dishes of 90 mm diameter add 15 ml of Casein soyabean digest agar for cultivation of aerobic microorganisms or Sabouraud dextrose agar with antibiotic for cultivation of fungi, at about 45º, to each Petri dish and allow to solidify.
Dry the plates, in an LAF bench or in an incubator.
Spread a measured volume of not less than 0.1 ml of the sample prepared as described earlier, over the surface of the medium. Use at least two Petri dishes for each medium and each strain of test organism.
For incubation and calculation of the number of colony forming units proceed as mentioned above.
Most probable number method:
Prepare a series of at least three subsequent tenfold dilutions of the product as described under 8.1.1.
From each level of dilution three aliquots of 1 g or 1 ml are used to inoculate three tubes with 9.0 ml of sterile Casein soyabean digest broth.
If necessary, polysorbate 80or an inactivator of antimicrobial agents may be added to the medium.
Thus, if three levels of dilution are prepared 9 tubes are inoculated.
Incubate all the tubes for three days at 30 ºC to 35 ºC.
Record for each level of dilution the number of tubes showing microbial growth.
If detection of growth is difficult or uncertain owing to the nature of the product under examination, sub-culture in the same broth, or on a suitable agar medium such as Casein soyabean digest agar for 18 to 24 hours at 30º to 35°C.
Determine the most probable number of bacteria per g or ml of the product from Annexure I.
Interpretation: The total aerobic viable count (TAC) is considered to be equal to the number of CFU found on Casein soyabean digest agar. If colonies of fungi are detected on this medium, they are counted as part of TAC. The total fungal count (TFC) is considered to be equal to the number of CFU found using Sabouraud dextrose agar with antibiotic. Acceptance criteria for microbiological quality should be interpreted as follows:-
101CFU : maximum acceptable count 20
102CFU : maximum acceptable count 200
103CFU : maximum acceptable count 2000, and so forth
Tests for Specified Microorganisms:
Bile-Tolerant Gram-Negative Bacteria:
Preparation of Sample and Incubation: Using Casein soyabean digest broth (Medium 1) as a diluent, make 1 in 10 dilution of more than 1 g of the product.
Mix well and keep at 20ºto 25º for about 2 to 5 hours to resuscitate the organisms.
Test for detection of organisms.
From above prepared sample, take a volume corresponding to 1 g of the product and inoculate in Enterobacteria Enrichment Broth –Mossel.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Subculture on plates of Violet red bile glucose agar.
Incubate at 30ºto 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
The product passes the test if there is no growth of colonies of gram negative bacteria.
Quantitative evaluation:
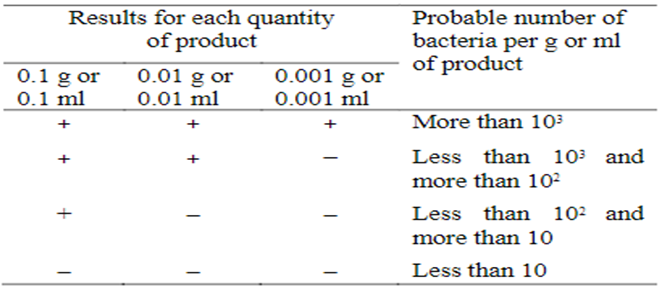
From the above mentioned prepared sample take a volume corresponding to 0.1 g, 0.01 g and 0.001 g (or 0.1 ml, 0.01 ml, and 0.001 ml) of the product in suitable quantity of Enterobacteria enrichment Broth–Mossel.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Subculture each of the cultures on a plate of Violet red bile glucose agar with dextrose.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours. Growth of well-developed reddish colonies of Gram negative bacteria is considered positive.
Note the smallest quantity of the product that gives the positive result and the largest quantity that gives the negative result. Determine from Table 4 the most probable number of bacteria.
Escherichia coli:
Using Casein soyabean digest broth as a diluent make 1 in 10 dilution of more than 1 g of the product as mentioned under Total aerobic viable count in Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use 10 ml or the quantity corresponding to 1 g or 1 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method) of Casein soyabean digest broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
After incubation shake the broth and transfer 1 ml to 100 ml of MacConkey broth.
Incubate at 42º to 44º for 24 to 48 hours.
Subculture on a plate of MacConkey agar and incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 72 hours.
Growth of pink, non-mucoid colonies indicates the possible presence of Escherichia coli.
This should be confirmed by identification test. If there is no growth of such type of colonies, or the identification tests are negative it indicates absence of E. coli and the product passes the test.
Salmonella:
Prepare a sample from the product as mentioned under Total aerobic viable count in Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use the quantity corresponding to 10 g or 10 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method.) of Casein soyabean digest broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
After incubation shake the broth and transfer 0.1 ml to 10 ml of Rappaport Vassiliadis Salmonella enrichment broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Subculture on a plate of Wilson and Blair’s BBS Agar or Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Wilson and Blair’s BBS Agar -Green colonies with black center develop and in 48 hours the colonies become uniformly black. Colonies surrounded by a dark zone and metallic sheen indicates possibility of presence of Salmonella. Xylose lysine deoxycholate agar- Well devolped, red colonies with or without black centers indicates possibility of Salmonella.
This should be confirmed by identification tests. If there is no growth of such type of colonies, or identification tests are negative it indicates absence of Salmonella and the product passes the test.
Shigella:
Prepare a sample from the product to be examined as mentioned under Total aerobic viable count in Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use the quantity corresponding to 10 g or 10 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method.) of Casein soyabean digest broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
After incubation shake the growth and transfer 1 ml to 100 ml of GN Broth
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Subculture on a plate of Xylose lysine deoxycholate medium.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
A red coloured translucent colony without black centre indicates possibility of presence of Shigella.
This should be confirmed by identification tests. If there is no growth of such colonies or if identification tests are negative, it indicates absence of Shigella and the product passes the test.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa:
Using Casein soyabean digest broth as a diluent make 1 in 10 dilution of more than 1 g of the product as mentioned in Total aerobic viable count under Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use 10 ml or the quantity corresponding to 1 g or 1 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method.) of Casein soyabean digest broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
Subculture on a plate of Cetrimide agar.
Incubate at 30ºC to 35ºC for 18 to 72 hours.
A greenish color colony indicates the possibility of presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
This should be confirmed by identification tests. If there is no growth of such type of colonies, or identification tests are negative it indicates absence of P. aeruginosa and the product passes the test
Staphylococcus aureus:
Using Casein soyabean digest broth as a diluent make 1 in 10 dilution of more than 1 g of the product as mentioned in Total aerobic viable count under Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use 10 ml or the quantity corresponding to 1 g or 1 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method.) of Casein soyabean digest broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 24 hours.
Sub-culture on a plate of Mannitol salt agar.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 18 to 72 hours.
Yellow or white colonies with yellow zones indicate the possibility of presence of S. aureus.
This should be confirmed by identification tests. If there is no growth of such type of colonies, or the identification tests are negative it indicates absence of S. aureus and the product passes the test.
Clostridia:
Prepare a sample from the product under examination as mentioned under Total aerobic viable count in Microbial contamination in nonsterile products Take two equal portions corresponding to 1 g or 1 ml of the product.
Heat one portion 80º for 10 minutes and cool rapidly.
Do not heat the other portion.
Transfer 10 ml of each of the homogenized portions to two containers containing 100 ml of Reinforced medium for Clostridia.
Incubate under anaerobic conditions at 30º to 35º for 48 hours.
After incubation, make sub-culture from each container on Columbia agar.
Incubate under anaerobic conditions at 30º to 35º for 48 hours. The occurrence of anaerobic growth of Gram positive bacilli with or without endospores.
Giving a negative catalase test indicates possibility of presence of Clostridia. If no anaerobic growth of microorganisms is detected on Columbia agar or identification test is negative, it indicates absence of Clostridia and the product passes the test.
Candida albicans:
Prepare a sample from the product to be examined as mentioned in Total aerobic viable count under Microbial contamination in nonsterile products and use the quantity corresponding to 1 g or 1 ml of the product to inoculate a suitable amount (determined as under Validity of the Test method) of Sabouraud dextrose broth.
Incubate at 30º to 35º for 3 to 5 days.
Subculture on a plate of Sabouraud dextrose agar and incubate at 30º to 35º for 24 to 48 hours.
Growth of cream coloured colonies may indicate the possibility of presence of C. albicans.
This is confirmed by identification tests. If such colonies are not present, or the identification tests are negative, C. albicans is absent and the product passes the test.
Result: Observe, note and submit result for all parameters as below mention unit-
Total Aerobic Microbial Count:
Total Aerobic Count (TAC) – CFU/g or ml
Total Fungal Count (TFC)- CFU/g or ml
Tests for Specified Microorganisms:
Bile-Tolerant Gram-Negative Bacteria:
Present / Absent per g
MPN per g or ml
Escherichia coli – Absent / Present per g
Salmonella – Absent / Present per 10g
Shigella – Absent / Present per 10g
Pseudomonas aeruginosa – Absent / Present per g
Staphylococcus aureus – Absent / Present per g
Clostridia – Absent / Present per g
Candida albicans – Absent / Present per g
Calibration / Validation:
Internal Calibration: NA
External Calibration: NA
Validation: NA
Precaution:
Perform all activities for testing under LAF and Biosafety Cabinet.
Do not over incubate Media during Incubation.
Distribution:
Master Copy : Quality Assurance
Controlled Copy : Microbiology Department
Reference:
IP 2022
Abbreviations:
| S. No. | Short Form | Full Form |
| 1 | STP | Standard Testing procedure |
| 2 | QA | Quality Assurance |
| 3 | S. | Serial |
| 4 | No. | Number |
| 5 | ECL | Enviro Calibration Lab |
| 6 | Jr. | Junior |
| 7 | NA | Not Applicable |
| 8 | Amend. | Amendment |
| 9 | No. | Number |
| 10 | AHU | Air Handling Unit |
| 11 | MLT | Microbial Limit Test |
Related Documents:
| S. No. | Document / Record No. | Document / Record Detail |
| NA | NA | NA |
Related Formats:
| S. No. | Document / Record No. | Document / Record Detail | Format |
| NA | NA | NA | NA |
Document Change History:
| S. No. | Issue No. / Revision No. & Date | Supersedes Issue No. / Revision No. & Date | Reason for Revision/Changes |
| NA | NA | NA | NA |


