- OBJECTIVE:
To lay down a procedure for Technology Transfer.
- SCOPE:
This SOP is applicable for Technology Transfer of the manufacturing process from F & D {Company Name} and from party (for which Loan license products to be manufactured at Company Name to manufacturing Facility at {Company Name} {Company Location}.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
QA, QC, F&D, Production Officer/Executive, – Follow the instruction as per procedure.
QA Sr.Executive -Review and technical correction of SOP.
QA Head –Training, approval & implementation of SOP.
- ACCOUNTABILITY:
Head Quality Assurance, F&D Head & Production Head
- PROCEDURE:
Technology Transfer: Process of Transferring the Technology (Chemistry, Manufacturing, Control, and documents related to Drug product) from one Location to another Location to manufacture the consistent quality is termed as technology Transfer.
- Technology Transfer of the manufacturing Process from F&D to manufacturing Facility at {Company Name} – The F&D Head/Designee shall plan for the transfer of the manufacturing process from F&D to manufacturing Facility. Such planning may be done due to:
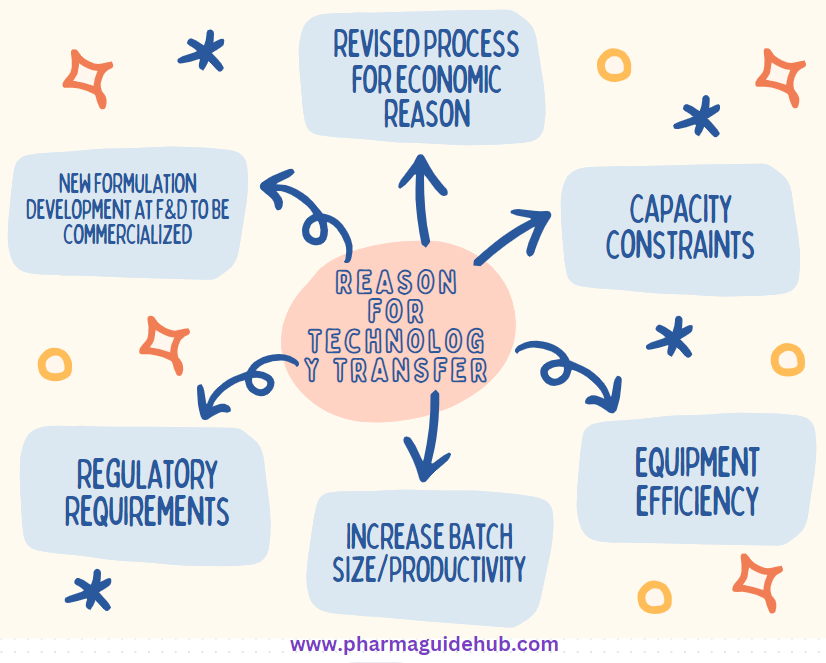
- New Formulation Development at F&D to be commercialized.
- Revised Process for economic /Cost effective Reason.
- Capacity constraints (Manufacturing/ Storage)
- Equipment efficiency.
- Increase Batch size/Productivity.
- Any Regulatory/Registration Requirements
- Proposal for Technology Transfer Shall be carried out by F&D Department.
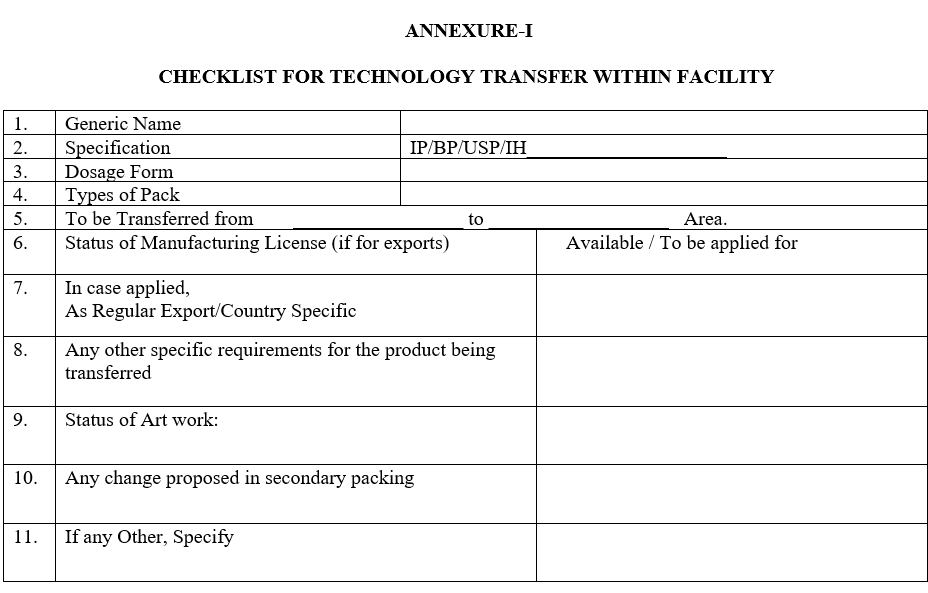
- The F&D Department shall coordinate for the collection of all relevant documents and prepare the checklist as per ANNEXURE-I shall hand over the documents to Quality Assurance Department.
- On receipt of information about new product, QA Shall fulfill the statutory requirement like test license, Manufacturing License, Pollution Control and ensure that statutory requirements shall be fulfilled prior to commencement of any manufacturing.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/technology-transfer-in-pharmaceutical/
- Key Elements of the Technology Transfer
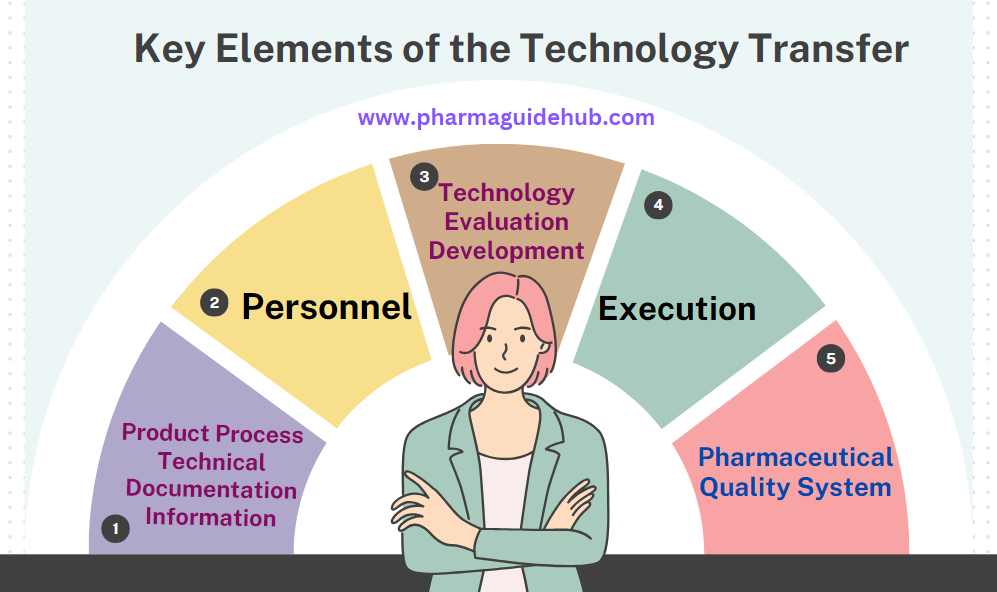
- Product Process Technical Documentation Information
- Personnel
- Technology Evaluation Development
- Execution
- Pharmaceutical Quality System
- Technology Transfer for the Loan license Products manufactured at {Company Name}
- Sending Unit: Technology Transfer team of the Company whose product is being manufactured at {Company Name}
- Receiving Unit: Manufacturing unit that is receiving the Technology.
- Technology Transfer Team of sending unit shall hand over the documents to Quality Assurance Department at receiving Unit.
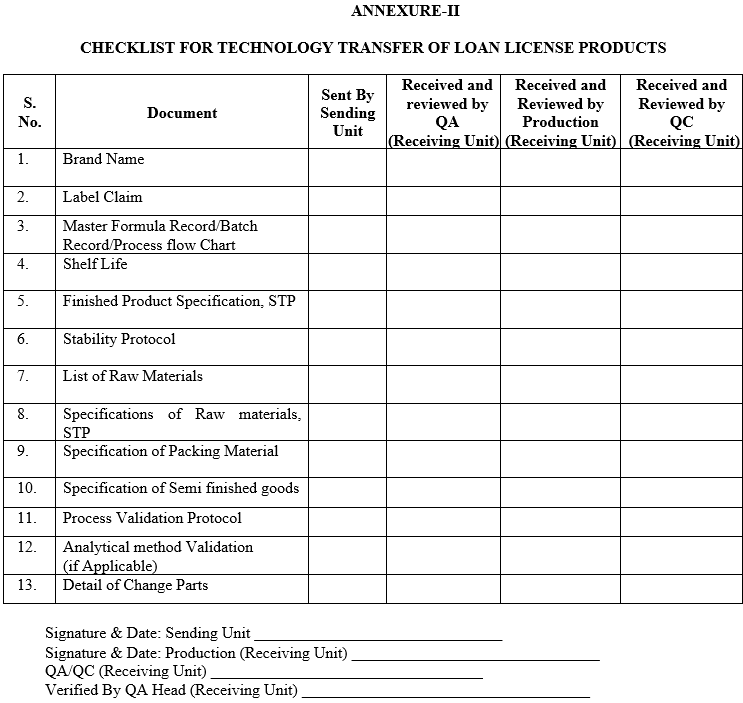
- Technology Transfer Team of Sending Unit shall prepare a technology transfer checklist as per ANNEXURE-II which shall include the following:
- Master Formula Record or Copy of the Master Batch record in use (if MFR is not available).
- Label claim.
- Justification of overages if required to be added.
- Critical process parameters at different stages of manufacturing (with justification).
- List of key equipments with material of construction.
- Any precaution during dispensing, transfer, and handling of raw material, in process materials and finished product.
- Requirements to maintain temperature and humidity during processing.
- Pack specification.
- List of packing components with item codes.
- Storage conditions for holding in process material.
- Recommended hold time at different stages of manufacturing as per data available.
- List of Qualified vendors (as applicable).
- QA Head designee shall review and send the documents to the QA Head designee, where product is to be transferred.
- The scanned copy of the above document may be sent through e-mail or the hard copy to be provided.
- The document sent from the Sending Unit to the Receiving Unit shall be reviewed by Production, QA & F&D (If applicable) for completeness and applicability.
- After reviewing of documents at Receiving Unit the comments (if any) shall be communicated to Head QA at Sending Unit for clarification and /or request for additional information /documents. Also to evaluate the requirement for any change part, accessory testing equipment, chemicals, column etc.
- QA Head, QC Head, F&D Head and production Head of Receiving unit shall initiate the preparation of documents such as batch record, specifications, and test procedures.
- If necessary, representative from F&D, manufacturing, QA and QC from Sending Unit shall visit at receiving unit to observe/demonstrate/analysis of initial batches.
- Production shall plan batches at receiving unit. The data generated after manufacturing and analysis of the first batch shall be reviewed against the laid down specification jointly by unit manufacturing and QA.
- If batches manufactured meet all the parameters as per specification and are successfully manufactured with respect to equipment operation, attaining process parameters transfer shall be considered as successful and complete. However, incase of any issue with respect to the above, suitable corrective actions shall be taken in consultation with QA.
- After addressing of problems identified batches shall be planned and document the same.
- The samples of process validation shall be charged on stability studies & Special recommendation of F&D/Regulatory shall be considered for stability Storage condition.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/technology-transfer-in-pharmaceutical/
- REFERENCES:
Not Applicable
- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURE No. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE |
| Annexure-I | Checklist for Technology Transfer within Facility |
| Annexure-II | Checklist for Technology Transfer of Loan License Products |
- DISTRIBUTION:
| Control copy No. 1 | : | Head Quality Assurance |
| Control copy No. 2 | : | Head Quality Control |
| Control copy No. 3 | : | Head Production |
| Control copy No. 4 | : | Head Warehouse |
| Control copy No. 5 | : | Head F&D |
| Master Copy | : | Quality Assurance Department |
- ABBREVIATIONS:
| QA | : | Quality Assurance |
| SOP | : | Standard Operating Procedure |
| No. | : | Number |
| F&D | : | Formulation and Development |
| QC | : | Quality Control |
| MFR | : | Master Formula Record |
- REVISION HISTORY:
CHANGE HISTORY LOG
| Revision No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date |
| 00 | New SOP | Not Applicable | To be written manual |
ANNEXURE-I
CHECKLIST FOR TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER WITHIN FACILITY
ANNEXURE-II
CHECKLIST FOR TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER OF LOAN LICENSE PRODUCTS
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/technology-transfer-in-pharmaceutical/
Frequently Asked Questions?
Q1: What is technology transfer in the context of the pharmaceutical industry?
A1: Technology transfer in the pharmaceutical industry refers to the process of transferring knowledge, skills, and technologies related to the development, manufacturing, and quality control of pharmaceutical products from one organization to another. It involves the transfer of scientific and technical know-how to ensure the efficient and effective production of drugs.
Q2: Why is technology transfer important in the pharmaceutical sector?
A2: Technology transfer is crucial in the pharmaceutical sector for several reasons. It allows for the replication of successful processes, facilitates the introduction of new products to the market, enhances manufacturing efficiency, ensures regulatory compliance, and promotes collaboration between different entities in the industry.
Q3: What are the key components involved in the technology transfer process in pharmaceuticals?
A3: The key components of the technology transfer process in pharmaceuticals include documentation of procedures, training of personnel, transfer of analytical methods, validation of manufacturing processes, establishment of quality control methods, and the transfer of regulatory and compliance knowledge.
Q4: How does technology transfer impact the speed of bringing new drugs to market?
A4: Technology transfer plays a critical role in expediting the introduction of new drugs to the market. By sharing expertise and processes, organizations can streamline the development and manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, reducing time-to-market and ensuring that patients have timely access to innovative therapies.
Q5: What challenges are commonly encountered during the technology transfer process in pharmaceuticals?
A5: Common challenges in pharmaceutical technology transfer include issues related to intellectual property, differences in equipment and facilities between the transferring and receiving organizations, regulatory variations, and ensuring consistent product quality during the transfer.
Q6: How does technology transfer impact global collaborations in the pharmaceutical industry?
A6: Technology transfer fosters global collaborations in the pharmaceutical industry by facilitating the exchange of knowledge and resources across borders. This collaboration can lead to more efficient drug development, improved manufacturing processes, and better access to pharmaceutical products worldwide.
Q7: What role does regulatory compliance play in the technology transfer process?
A7: Regulatory compliance is paramount in the technology transfer process to ensure that the transferred technology meets the standards and requirements set by regulatory authorities. Adherence to regulatory guidelines is crucial to obtaining approvals for new drugs and maintaining product quality and safety.
Q8: How can organizations mitigate the risks associated with technology transfer in the pharmaceutical sector?
A8: Organizations can mitigate risks through planning, establishing clear communication channels, conducting comprehensive risk assessments, ensuring proper documentation, providing robust training to personnel, and engaging in continuous monitoring and evaluation throughout the technology transfer process.
Q9: In what ways does technology transfer contribute to the improvement of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes?
A9: Technology transfer contributes to the improvement of pharmaceutical manufacturing processes by incorporating best practices, optimizing production efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring consistency in product quality. It enables the adoption of advanced technologies and methodologies for enhanced productivity.
Q10: Can you provide examples of successful technology transfer initiatives in the pharmaceutical industry?
A10: Examples of successful technology transfer initiatives include the transfer of bioprocessing technologies for the production of biologics, the replication of tablet manufacturing processes for generic drugs, and the sharing of vaccine production technologies to address global health challenges such as pandemics.
Click the link for download word file copy of this document: https://pharmaguidehub.com/product/technology-transfer-in-pharmaceutical/