Definition of limit test:
Limit test is defined as a quantitative or semi-quantitative test designed to identify and control small quantities of impurities which are likely to be present in the substance.
It is a limit test of the quantity of heavy metals contained as impurities in drugs. The heavy metals are the metallic inclusions that are darkened with sodium sulphide (TS) in acidic solution or hydrogen sulphide saturated solution, as their quantity is expressed in terms of the quantity of lead (Pb).
In each monograph, the permissible limit for heavy metals (as Pb) is described in terms of ppm in parentheses.
Apparatus Required
- Nessler cylinders
- Glass rod
- Stand
Chemicals Required
Dilute CH3COOH (10% v/v)
Dilute ammonia (10% v/v)
Hydrogen sulphide solution (saturated solution of H2S) (or sodium sulphide solution)
Standard lead solution (10 ml of the lead nitrate stock solution diluted to 100 ml with water). (20 ppm of lead).
Lead nitrate stock solution: Dissolve 0.1598 gm of lead nitrate in 100 ml of water, add 1 ml of cone. HNO3 and dilute to 1000 ml with water.
Reaction
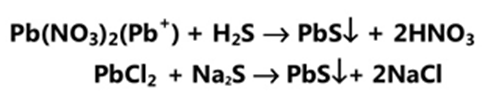
Principle
It is based on the reaction between the solution of heavy metals and a saturated solution of hydrogen sulphide. In acidic media, it produces reddish/black colour with hydrogen sulphide which is compared with the standard lead nitrate solution.
Procedure
Take two 50 ml Nessler cylinders. Label one as “Test” and the other as ‘Standard’.
| Standard | Test |
| 1. 2 ml of standard lead solution is taken in a Nessler cylinder and diluted to 25 ml with water. | 1. Dissolve the specified quantity of the substance in distilled water diluted to 25 ml with water and transfer to Nessler cylinder. |
| 2. Adjust the pH to 3-4 by dilute acetic acid or dilute ammonia solution. | 2. Adjust the pH to 3-4 by dilute acetic acid or dilute ammonia solution. |
| 3. Dilute further to 35 ml with water. | 3. Dilute further to 35 ml with water |
| 4. Add 10 ml of freshly prepared H2S solution. | 4. Add 10 ml of freshly prepared H2S solution. |
| 5. Dilute to 50 ml with water. | 5. Dilute to 50 ml with water. |
| 6. Mix and allow to stand for five minutes. | 6. Mix and allow to stand for five minutes. |
| 7. Observe the quantity of the black ppt of lead sulphide formed and compare with that of the standard. | 7. Observe the quantity of the black ppt of lead sulphide formed and compare with that of the standard. |
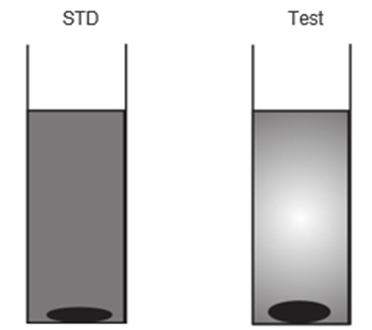
The quantity of the black ppt of lead sulphide in STD is seen less than that of the Test, thus the sample fails the limit test of heavy metals